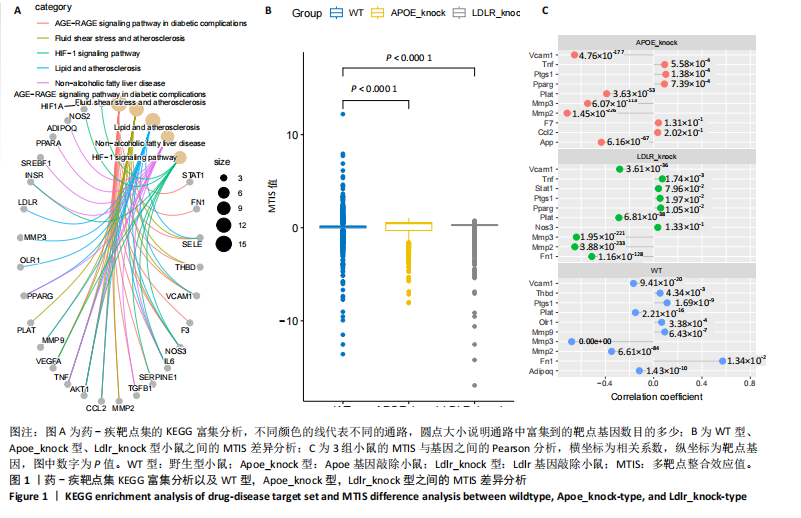
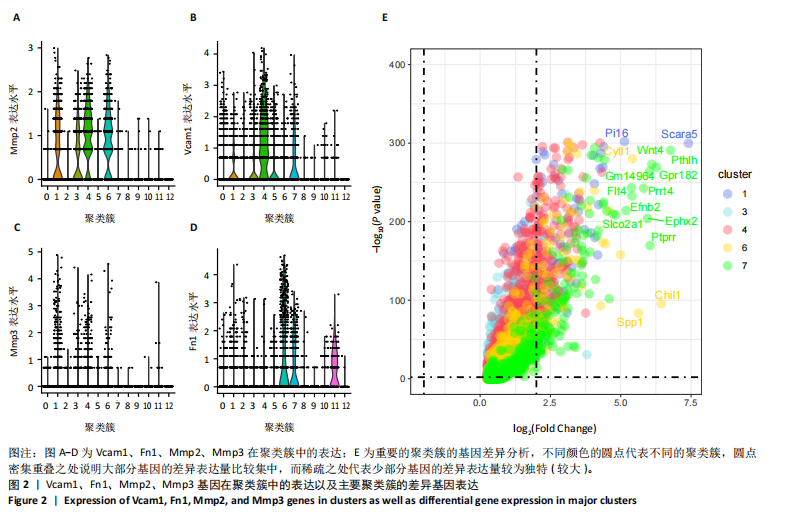
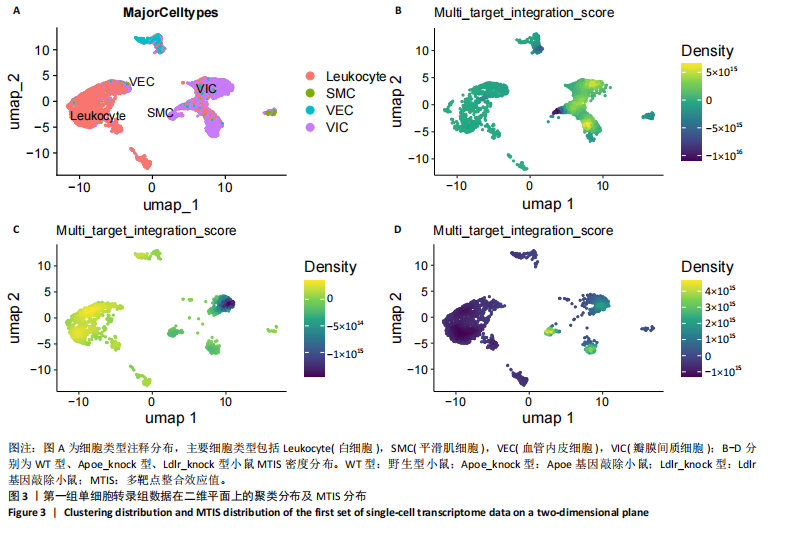
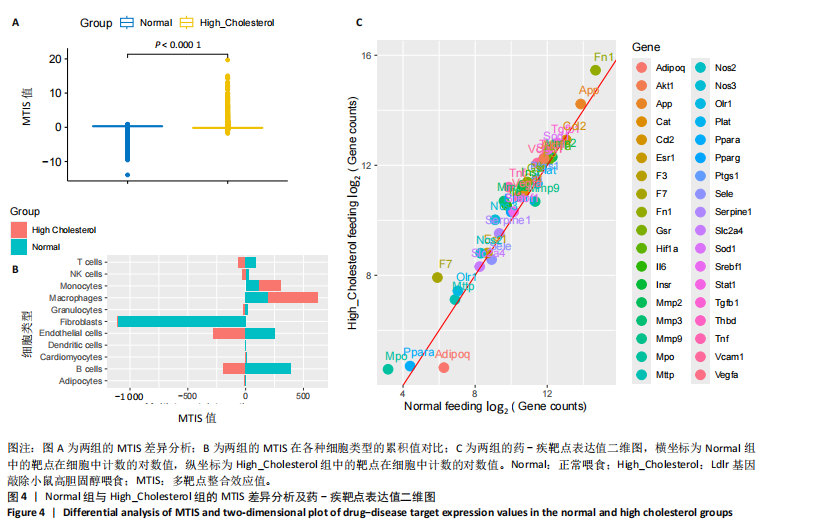
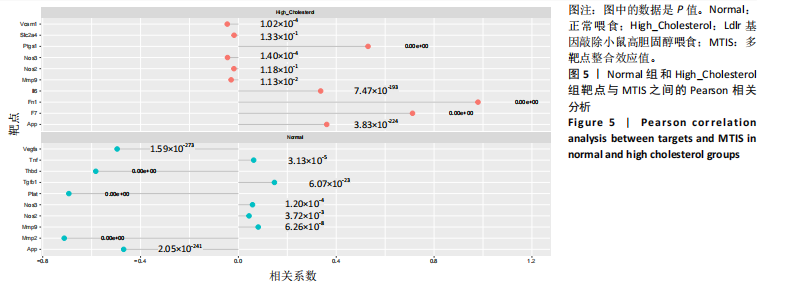
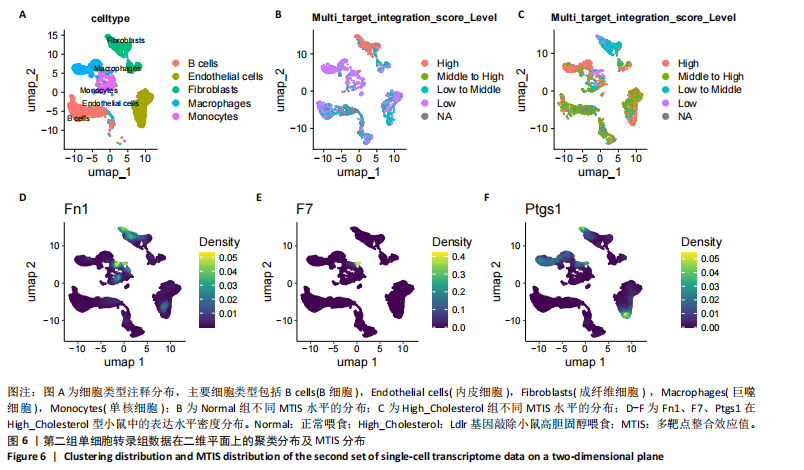
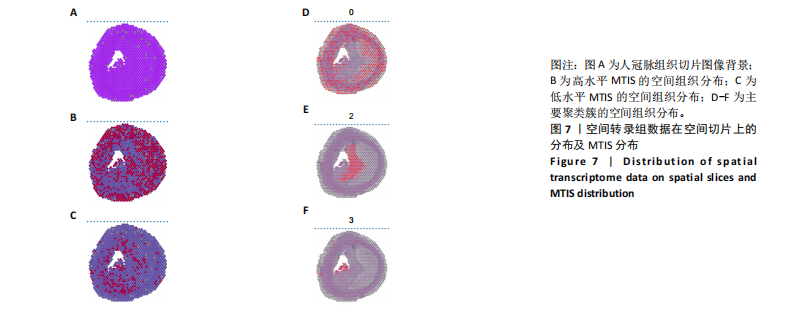
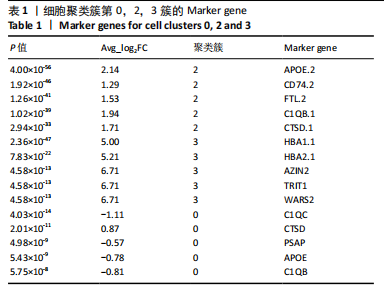
[1] 王志杰,樊薛津,王豫骞,等.机器学习方法在中医药研究中的应用进展[J].药物评价研究,2024,47(8):1906-1913.
[2] 邓乐,丁长松,黄辛迪,等.基于多层前馈神经网络的中药药性量化研究[J].中草药,2020,51(16):4277-4283.
[3] 姜皓,张冰,张晓朦,等.基于4种机器学习算法的妊娠期中药“禁忌慎”判别[J].中草药,2021,52(24):7596-7605.
[4] CHEN C, LI SX, WANG SM, et al. A support vector machine based pharmacodynamic prediction model for searching active fraction and ingredients of herbal medicine: Naodesheng prescription as an example. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;56(2):443-447.
[5] 王宁.基于异质网络的中药靶点预测及应用研究[D].北京:北京交通大学, 2022.
[6] ZHANG P, ZHANG D, ZHOU W, et al. Network pharmacology: towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine. Brief Bioinform. 2023; 25(1):bbad518.
[7] 杨鹏挥,金丽君,廖杰,等.基于单细胞组学的中药现代研究:技术及思路[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(15):3977-3985.
[8] 陈嘉鋆,郭秋岩,徐承超,等.中药现代化研究的崭新模式:单细胞药理学[J].药学学报,2021,56(12):3300-3312.
[9] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[10] STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016;54:1.30.1-1.30.33.
[11] GEER LY, MARCHLER-BAUER A, GEER RC, et al. The NCBI BioSystems database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(Database issue):D492-496.
[12] ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, ZHAO D, et al. TTD:Therapeutic Target Database describing target druggability information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(D1):D1465-D1477.
[13] 梁天坚,李黎明,李本杰,等.基于网络药理学分析大柴胡汤治疗高脂血症的作用机制[J].中成药,2021,43(6):1645-1652.
[14] LEE SH, KIM N, KIM M, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveal cellular diversity of aortic valve and the immunomodulation by PPARγ during hyperlipidemia.Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5461.
[15] VAN KUIJK K, MCCRACKEN IR, TILLIE RJHA, et al. Human and murine fibroblast single-cell transcriptomics reveals fibroblast clusters are differentially affected by ageing and serum cholesterol. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;119(7):1509-1523.
[16] KAWAI K, SAKAMOTO A, MOKRY M, et al. Clonal Proliferation Within Smooth Muscle Cells in Unstable Human Atherosclerotic Lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43(12):2333-2347.
[17] ERASLAN G, SIMON LM, MIRCEA M, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq denoising using a deep count autoencoder. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):390.
[18] BAHL E, CHATTERJEE S, MUKHERJEE U, et al. Using deep learning to quantify neuronal activation from single-cell and spatial transcriptomic data. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):779.
[19] 刘恺.大柴胡汤治疗高脂血症的临床研究[J].内蒙古中医药,2023,42(8):82-84.
[20] 宋伟.大柴胡汤治疗高脂血症50例[J].实用中医药杂志,2022,38(5):735-736.
[21] 杨荣来,王凤荣,史海蛟,等.以“痰瘀毒”立论探讨大柴胡汤防治动脉粥样硬化的炎症反应[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(8):94-96.
[22] 郑娴,王凤荣.大柴胡汤对动脉粥样硬化家兔血脂及炎性因子表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2013,54(19):1681-1685.
[23] 温尔刚,高杰,丁怡铭,等.巨噬细胞MED1缺失促进雌性ApoE和LDLR敲除小鼠动脉粥样硬化发展[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2023,44(1):89-94.
[24] 曹盼夏,彭紫凝,刘珊珊,等.腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶介导巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化:中药防治动脉粥样硬化的途径[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(18):3906-3914.
[25] 郭泽浩.家族性高甘油三酯血症外泌体lncRNA表达特点及调控通路探究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2020.
[26] 阚昊.高脂肪饮食对小鼠主动脉细胞组成和功能的影响及机制研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2023.
[27] 杨珺,殷鹏,郑中华.水苏碱激活自噬改善高脂喂养小鼠动脉粥样硬化的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(24):5140-5147.
[28] 杨牧祥,马全庆,田元祥,等.脂调康胶囊对高脂血症大鼠血清IL-6的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2003,9(9):12-13.
[29] 黄汝哨.血清MMP-2及基因多态性对颈动脉斑块易损性及动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死的影响[D].福州:福建医科大学,2021.
[30] 毛萍,吕方超,徐晨凯,等.冠心宁通过TNFAIP3-ASK1/JNK通路对动脉粥样硬化血管平滑肌细胞表型转换的调控作用[J].心脑血管病防治,2024, 24(10):5-9+18.
[31] 刘燕,高茸,汤小涵,等.基于网络药理学和细胞实验探讨柚皮苷抗动脉粥样硬化的作用机制[J].空军航空医学,2024,41(3):236-242.
[32] Azevedo Martins JM, Rabelo-Santos SH, do Amaral Westin MC, et al. Tumoral and stromal expression of MMP-2,MMP-9,MMP-14,TIMP-1,TIMP-2,and VEGF-A in cervical cancer patient survival:a competing risk analysis. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):660.
[33] 李洪涛.环氧合酶与动脉粥样硬化[J].心血管病学进展,2004,25(1):62-65.
[34] 姚明鹤,闫海峰,王静,等.基于网络药理学探讨荷丹片治疗高脂血症的作用机制[J].天津中医药大学学报,2021,40(6):783-789.
[35] 吴佩洋.Apoe~(-/-)和Ldlr~(-/-)小鼠动脉粥样硬化发生发展及造血系统变化的对比研究[D].上海:上海师范大学,2024.
[36] 曾静,花雷,阳勇,等.异功散通过调控脑水液代谢改善APP/PS1转基因小鼠的学习记忆能力[J].南方医科大学学报,2024,44(10):2015-2023. |