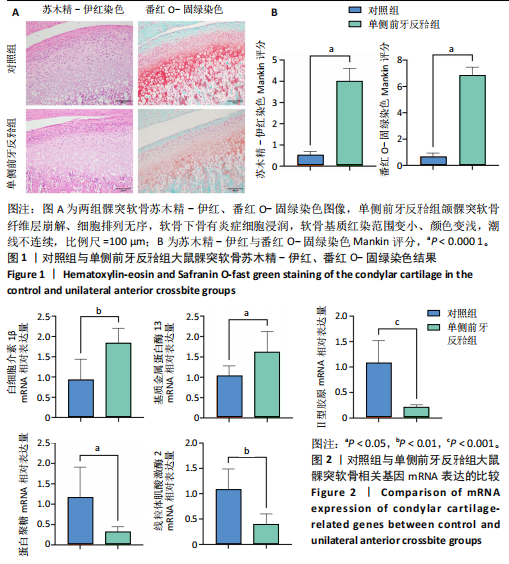
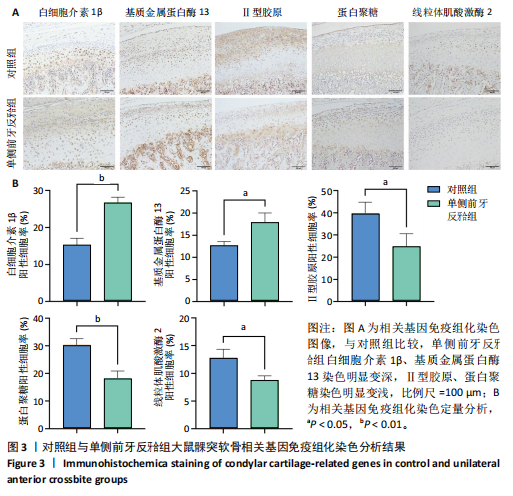
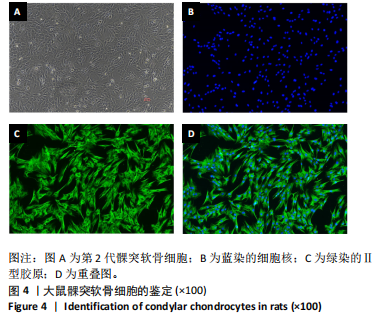
[1] TRINDADE D, CORDEIRO R, JOSÉ HC, et al. Biological Treatments for Temporomandibular Joint Disc Disorders: Strategies in Tissue Engineering. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):933.
[2] CARDONEANU A, MACOVEI LA, BURLUI AM, et al. Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis: Pathogenic Mechanisms Involving the Cartilage and Subchondral Bone, and Potential Therapeutic Strategies for Joint Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):171.
[3] MÉLOU C, PELLEN-MUSSI P, JEANNE S, et al. Osteoarthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint: A Narrative Overview. Medicina. 2022; 59(1):8.
[4] WANG GW, WANG MQ, WANG XJ, et al. Changes in the expression of MMP-3, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and aggrecan in the condylar cartilage of rats induced by experimentally created disordered occlusion. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(11):887-895.
[5] CHU M, CHEN G, CHEN K, et al. Heme oxygenase 1 linked to inactivation of subchondral osteoclasts in osteoarthritis. Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024;25(6):513-528.
[6] BRAZ MA, FREITAS PORTELLA F, SEEHABER KA, et al. Association between oxidative stress and temporomandibular joint dysfunction: A narrative review. J Oral Rehabil. 2020;47(4):536-546.
[7] MA T, WU CB, SHEN QX, et al. TRIM52 knockdown inhibits proliferation, inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in IL-1β-induced synovial fibroblasts to alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(8):e18244.
[8] CHEN BY, PATHAK JL, LIN HY, et al. Inflammation Triggers Chondrocyte Ferroptosis in TMJOA via HIF-1α/TFRC. J Dent Res. 2024;103(7):712-722.
[9] GE XP, GAN YH , ZHANG CG, et al. Requirement of the NF-κB pathway for induction of Wnt-5A by interleukin-1β in condylar chondrocytes of the temporomandibular joint: functional crosstalk between the Wnt-5A and NF-κB signaling pathways. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011; 19(1):111-117.
[10] CHEN X, HE F, ZHANG H, et al. Syndecan-4 inhibition attenuates cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Oral Rehabil. 2024;51(11):2324-2335.
[11] Tabeian H, Betti BF, Dos C, et al. IL-1β Damages Fibrocartilage and Upregulates MMP-13 Expression in Fibrochondrocytes in the Condyle of the Temporomandibular Joint. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2260.
[12] YI H, ZHANG W, CUI ZM, et al. Resveratrol alleviates the interleukin-1β-induced chondrocytes injury through the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):424.
[13] JUAN Z, XING-TONG M, XU Z, et al. Potential pathological and molecular mechanisms of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Dent Sci. 2023;18(3):959-971.
[14] ZHOU Y, LIN S, HUANG Z, et al. Receptor-interacting protein 1 inhibition prevents mechanical stress-induced temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by regulating apoptosis and later-stage necroptosis of chondrocytes. Arch Oral Biol. 2023;147:105612
[15] HE Y, ZHOU M, JIAN Z, et al. C-Reactive Protein Knockout Attenuates Temporomandibular Joint Inflammation in Rats. J Immunol Res. 2022; 2022(1):8613986.
[16] 胡敏.颞下颌关节骨关节炎:认识与挑战[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2022,57(7):665-673.
[17] LIANG Y, CHEN Y, TIAN T, et al. Molecular mechanism of the ESRRG-PERM1-CKMT2 signal axis in ovariectomized female rats with OSAHS. Transpl Immunol. 2022;74:101631.
[18] RICHARD I, DEVAUD C, CHERIF D, et al.The gene for creatine kinase, mitochondrial 2 (sarcomeric;CKMT2), maps to chromosome 5q13.3. Genomics. 1993;18(1):134-136.
[19] ZHUANG B, NI X, MIN Z, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA CKMT2-AS1 Reduces the Viability of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Iran J Public Health. 2022;51(2):327-335.
[20] RIZO-ROCA D, GUIMARÃES DSPSF, PENDERGRAST LA, et al. Decreased mitochondrial creatine kinase 2 impairs skeletal muscle mitochondrial function independently of insulin in type 2 diabetes. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(768):eado3022.
[21] LIN W, ZHOU J, MA Y, et al. Prognostic value of mitochondrial CKMT2 in Pan-cancer and its tumor immune correlation analysis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):342.
[22] 孙诗雨,李金岚,邢佳妮,等.简州大耳羊CKMT2基因克隆、生物信息学分析及时空表达研究[J].中国畜牧兽医,2024,51(6):2342-2353.
[23] 刘金华,于晟曼,薛菲,等.CKMT2在结直肠癌中的表达及意义[J].中国实验诊断学,2022,26(12):1811-1813.
[24] STAAL J, BLANCO LP, PERL A. Editorial: Mitochondrial dysfunction in inflammation and autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1304315.
[25] DOLDER M, WALZEL B, SPEER O, et al. Inhibition of the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition by Creatine Kinase Substrates: REQUIREMENT FOR MICROCOMPARTMENTATION. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(20): 17760-17766.
[26] GRZYB K, SKORKOWSKI EF. Izoenzymy kinazy kreatynowej-charakterystyka i funkcje w komórce. Postepy Biochem. 2008;54(3): 274-283.
[27] LIU S, WU C, ZHANG Y. Transcriptomics analyses of IL-1β-stimulated rat chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint condyles and effect of platelet-rich plasma. Heliyon. 2024;10(4):e26739.
[28] FUNATO S, YASUHARA R, YOSHIMURA K, et al. Extracellular matrix loss in chondrocytes after exposure to interleukin-1β in NADPH oxidase-dependent manner. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;368(1):135-144.
[29] ZHANG M, YANG H, LU L, et al. Matrix replenishing by BMSCs is beneficial for osteoarthritic temporomandibular joint cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(9):1551-1562.
[30] ZHANG HY, LIU YD, YANG HX, et al. Installing and thereafter removing an aberrant prosthesis elicited opposite remodelling responses in growing mouse temporomandibular joints. J Oral Rehabil. 2015;42(9):685-692.
[31] MA S, ZHANG A, LI X, et al. MiR-21-5p regulates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in TMJOA by targeting Spry1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):99-116.
[32] WANG YL, ZHANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Cartilage degradation in temporomandibular joint induced by unilateral anterior crossbite prosthesis. Oral Dis. 2014;20(3):301-306.
[33] 基于网络药理学和分子对接研究高山金莲花素对颞下颌关节骨关节炎细胞模型的作用机制[J].口腔疾病防治,2024,32(8):578-588.
[34] ZHANG C, WANG P, JIANG P, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR contributes to IL-1β-induced MMP overexpression and chondrocytes apoptosis in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Gene. 2016; 586(2):248-253.
[35] TUERXUN P, NG T, SUN J, et al. Lipoxin A4 modulates the PKA/CREB and NF-κB signaling pathway to mitigate chondrocyte catabolism and apoptosis in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Exp Cell Res. 2024;442(2):114249.
[36] CHEUNG C, TU S, FENG Y, et al. Mitochondrial quality control dysfunction in osteoarthritis: Mechanisms, therapeutic strategies & future prospects. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2024;125:105522.
[37] LI Q, GAO Z, CHEN Y, et al. The role of mitochondria in osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Protein Cell. 2017;8(6):439-445.
[38] ZHENG CX, SUI BD, QIU XY, et al. Mitochondrial Regulation of Stem Cells in Bone Homeostasis. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(1):89-104.
[39] CHEN Q, WU L, DAWA C, et al. [Research progress on the role of chondrocyte mitochondrial homeostasis imbalance in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023; 37(6):748-757.
[40] CAO H, ZHOU X, BOWEN XU, et al. Advances in the study of mitophagy in osteoarthritis. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2024;25(3):197-211.
[41] PRIESNITZ C, BECKER T. Pathways to balance mitochondrial translation and protein import. Genes Dev. 2018;32(19-20):1285-1296.
[42] RUIZ-ROMERO C, CALAMIA V, MATEOS J, et al. Mitochondrial dysregulation of osteoarthritic human articular chondrocytes analyzed by proteomics: a decrease in mitochondrial superoxide dismutase points to a redox imbalance. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8(1):172-189.
[43] BLANCO FJ, LÓPEZ-ARMADA MJ, MANEIRO E. Mitochondrial dysfunction in osteoarthritis. Mitochondrion. 2024;4(5-6):715-728.
|