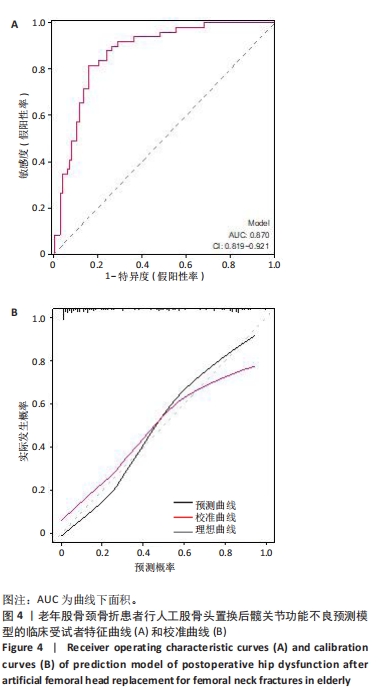
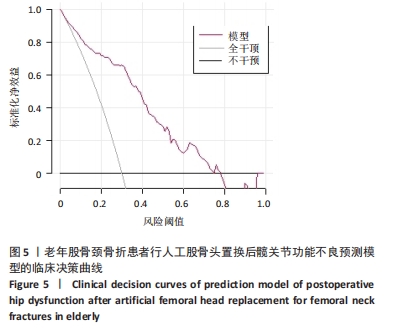
[1] SCHMITZ PP, SOMFORD MP, JAMESON SS, et al. Controversies around hip fracture treatment: clinical evidence versus trends from national registries. Hip Int. 2024;34(1):144-151.
[2] DYER SM, CROTTY M, FAIRHALL N, et al. A critical review of the long-term disability outcomes following hip fracture. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16(1):158.
[3] 王祚才, 陈建平, 王平. 半髋和全髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的疗效及安全性 [J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2024,23(3):176-180.
[4] RIDHA M, AL-JABRI T, STELZHAMMER T, et al. Osteosynthesis, hemiarthroplasty, total hip arthroplasty in hip fractures: All I need to know. Injury. 2024;55(3):111377.
[5] 吕辉, 黄邓华, 邹龙飞, 等. 全髋关节置换和人工股骨头置换修复移位型股骨颈骨折效果:基于14项随机对照试验的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(27):4421-4428.
[6] BURGERS PT, VAN GEENE AR, VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, et al. Total hip arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in the healthy elderly: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized trials. Int Orthop. 2012;36(8):1549-1560.
[7] WALTON TJ, BELLRINGER SF, EDMONDSON M, et al. Does a dedicated hip fracture unit improve clinical outcomes? A five-year case series. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2019;101(3):215-519.
[8] VAN DER SIJP MPL, VAN EIJK M, TONG WH, et al. Independent factors associated with long-term functional outcomes in patients with a proximal femoral fracture: A systematic review. Exp Gerontol. 2020; 139:111035.
[9] TAM TL, TSANG KK, LEE KB. Development of a prognostic model to predict post-operative mobility of patients with fragility hip fractures: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2020;38:100770.
[10] HAENTJENS P, AUTIER P, BARETTE M, et al. Survival and functional outcome according to hip fracture type: a one-year prospective cohort study in elderly women with an intertrochanteric or femoral neck fracture. Bone. 2007;41(6):958-964.
[11] SIU AL, PENROD JD, BOOCKVAR KS, et al. Early ambulation after hip fracture: effects on function and mortality. Arch Intern Med. 2006; 166(7):766-771.
[12] MORRI M, FORNI C, MARCHIONI M, et al. Which factors are independent predictors of early recovery of mobility in the older adults’ population after hip fracture? A cohort prognostic study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(1):35-41.
[13] MOERMAN S, MATHIJSSEN NM, TUINEBREIJER WE, et al. Less than one-third of hip fracture patients return to their prefracture level of instrumental activities of daily living in a prospective cohort study of 480 patients. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2018;18(8):1244-1248.
[14] 徐峰, 袁凯旋, 陈圣宝, 等. 髋关节功能评分研究进展 [J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(3):141-144.
[15] TAKAHASHI A, NARUSE H, KITADE I, et al. Functional outcomes after the treatment of hip fracture. PLoS One. 2020;15(7):e0236652.
[16] HAENTJENS P, AUTIER P, BARETTE M, et al. Predictors of functional outcome following intracapsular hip fracture in elderly women. A one-year prospective cohort study. Injury. 2005;36(7):842-850.
[17] WONG RMY, QIN J, CHAU WW, et al. Prognostic factors related to ambulation deterioration after 1-year of geriatric hip fracture in a Chinese population. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):14650.
[18] KANG MJ, KIM BR, LEE SY, et al. Factors predictive of functional outcomes and quality of life in patients with fragility hip fracture: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(7):e32909.
[19] UNNANUNTANA A, REBOLLEDO BJ, GLADNICK BP, et al. Does vitamin D status affect the attainment of in-hospital functional milestones after total hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3):482-489.
[20] LIU W, WAHAFU T, CHENG M, et al. The influence of obesity on primary total hip arthroplasty outcomes: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(3):289-296.
[21] OOSTING E, HOOGEBOOM TJ, APPELMAN-DE VRIES SA, et al. Preoperative prediction of inpatient recovery of function after total hip arthroplasty using performance-based tests: a prospective cohort study. Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(13):1243-1249.
[22] BELLELLI G, NOALE M, GUERINI F, et al. A prognostic model predicting recovery of walking independence of elderly patients after hip-fracture surgery. An experiment in a rehabilitation unit in Northern Italy. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(8):2189-2200.
[23] SONG J, ZHANG G, LIANG J, et al. Effects of delayed hip replacement on postoperative hip function and quality of life in elderly patients with femoral neck fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):487.
[24] AL-ANI AN, SAMUELSSON B, TIDERMARK J, et al. Early operation on patients with a hip fracture improved the ability to return to independent living. A prospective study of 850 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(7):1436-1442.
[25] CHA YH, HA YC, YOO JI, et al. Effect of causes of surgical delay on early and late mortality in patients with proximal hip fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(5):625-630.
[26] BUTLER A, HAHESSY S, CONDON F. The effect of time to surgery on functional ability at six weeks in a hip fracture population in Mid-West Ireland. Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2017;26:36-42.
[27] MENG D, BAI X, WU H, et al. Patient and Perioperative Factors Influencing the Functional Outcomes and Mortality in Elderly Hip Fractures. J Invest Surg. 2021;34(3):262-269.
[28] VISSER M, HARRIS TB, FOX KM, et al. Change in muscle mass and muscle strength after a hip fracture: relationship to mobility recovery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55(8):M434-M440.
[29] HOOGEBOOM TJ, DRONKERS JJ, HULZEBOS EH, et al. Merits of exercise therapy before and after major surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2014; 27(2):161-166.
[30] OOSTING E, HOOGEBOOM TJ, DRONKERS JJ, et al. The Influence of Muscle Weakness on the Association Between Obesity and Inpatient Recovery From Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(6): 1918-1922.
[31] SHIRAISHI R, SATO K, CHIJIIWA N, et al. Relationship between Trunk Muscle Mass Index at Admission and Walking Independence in Patients with Hip Fracture. Prog Rehabil Med. 2023;8:20230036.
[32] MADANAT R, MÄKINEN TJ, OVASKA MT, et al. Dislocation of hip hemiarthroplasty following posterolateral surgical approach: a nested case-control study. Int Orthop. 2012;36(5):935-940.
[33] SALEM KM, SHANNAK OA, SCAMMELL BE, et al. Predictors and outcomes of treatment in hip hemiarthroplasty dislocation. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2014;96(6):446-451.
[34] ORIVE M, ANTON-LADISLAO A, GARCÍA-GUTIÉRREZ S, et al. Prospective study of predictive factors of changes in pain and hip function after hip fracture among the elderly. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(2):527-536.
[35] APRISUNADI, NURSALAM N, MUSTIKASARI M, et al. Effect of Early Mobilization on Hip and Lower Extremity Postoperative: A Literature Review. SAGE Open Nurs. 2023;9:23779608231167825.
[36] STINNER DJ, RIVERA JC, SMITH CS, et al. Early Advanced Weight-Bearing After Periarticular Fractures: A Randomized Trial Comparing Antigravity Treadmill Therapy Versus Standard of Care. J Orthop Trauma. 2022; 36(Suppl 1):S8-S13.
[37] KURU T, OLÇAR HA. Effects of early mobilization and weight bearing on postoperative walking ability and pain in geriatric patients operated due to hip fracture: a retrospective analysis. Turk J Med Sci. 2020; 50(1):117-125.
[38] ZHANG J, ANG ML, KWEK EB. Who Will Walk Again? Effects of Rehabilitation on the Ambulatory Status in Elderly Patients Undergoing Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6(3):168-172.
[39] FRANDSEN CF, STILLING M, GLASSOU EN, et al. The majority of community-dwelling hip fracture patients return to independent living with minor increase in care needs: a prospective cohort study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(5):2475-2484.
[40] THÜRIG G, SCHMITT JW, SLANKAMENAC K, et al. Safety of total hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures using the direct anterior approach: a retrospective observational study in 86 elderly patients. Patient Saf Surg. 2016;10:12.
|