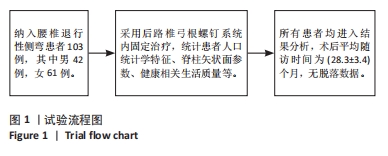
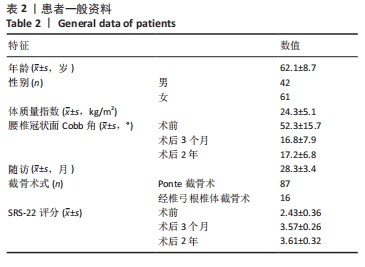
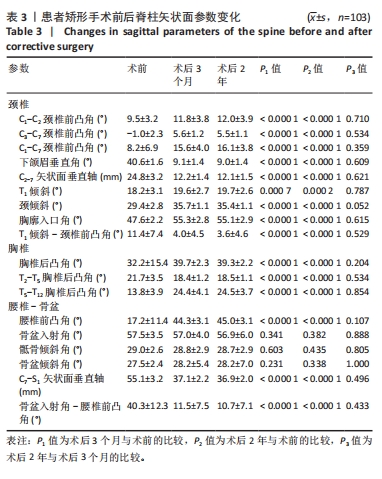
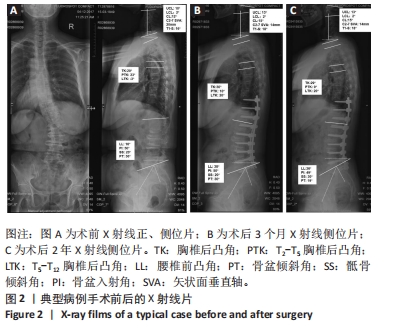
[1] WONG E, ALTAF F, OH LJ, et al. Adult Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. Orthopedics. 2017;40(6):e930-e939.
[2] LOWE T, BERVEN SH, SCHWAB FJ, et al. The SRS classification for adult spinal deformity: Building on the King/Moe and Lenke classification systems. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19 Suppl):S119-125.
[3] YORK PJ, KIM HJ. Degenerative Scoliosis. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017;10(4):547-558.
[4] SIMON J, LONGIS PM, PASSUTI N. Correlation between radiographic parameters and functional scores in degenerative lumbar and thoracolumbar scoliosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;103(2): 285-290.
[5] 陆明,马华松,王晓平,等.腰椎退变性侧弯植入物置入的内固定治疗[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44):8324-8331.
[6] HAN F, WEISHI L, ZHUORAN S, et al. Sagittal plane analysis of the spine and pelvis in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):2309499016684746.
[7] ZHANG H, DU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Outcomes of Ponte osteotomy combined with posterior lumbar interbody fusion for reconstruction of coronal and sagittal balance in degenerative scoliosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1): 904.
[8] TANG X, ZHAO J, ZHANG Y. Radiographic, clinical, and patients’ assessment of segmental direct vertebral body derotation versus simple rod derotation in main thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective, comparative cohort study. Eur Spine J. 2014;24(2):298-305.
[9] BERGEY DL, VILLAVICENCIO AT, GOLDSTEIN T, et al. Endoscopic lateral transpsoas approach to the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(15):1681-1688.
[10] WANG T, WANG H, MA L, et al. Correction of sagittal imbalance in treatment for adult degenerative scoliosis with thoracic lordosis and lumbar kyphosis: A case report. Medicine. 2017;96(16):e6416.
[11] KYRÖLÄ K, KAUTIAINEN H, PEKKANEN L, et al. Long-term clinical and radiographic outcomes and patient satisfaction after adult spinal deformity correction. Scand J Surg. 2018;108(4):343-351.
[12] GLASSMAN SD, BERVEN S, BRIDWELL K, et al. Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. SPINE. 2005;30 (6):682-688.
[13] PROTOPSALTIS TS, SCHEER JK, TERRAN JS, et al. How the neck affects the back: changes in regional cervical sagittal alignment correlate to HRQOL improvement in adult thoracolumbar deformity patients at 2-year follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(2):153-158.
[14] HA Y, SCHWAB F, LAFAGE V, et al. Reciprocal changes in cervical spine alignment after corrective thoracolumbar deformity surgery. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(3):552-559.
[15] NÚÑEZ-PEREIRA S, HITZL W, BULLMANN V, et al. Sagittal balance of the cervical spine: an analysis of occipitocervical and spinopelvic interdependence, with C7 slope as a marker of cervical and spinopelvic alignment. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23(1):16-23.
[16] BOISSIÈRE L, BERNARD J, VITAL JM, et al. Cervical spine balance: postoperative radiologic changes in adult scoliosis surgery. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(7):1356-1361.
[17] SMITH JS, SHAFFREY CI, LAFAGE V, et al. Spontaneous improvement of cervical alignment after correction of global sagittal balance following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(4):300-307.
[18] YANG C, YANG M, CHEN Y, et al. Radiographic parameters in adult degenerative scoliosis and different parameters between sagittal balanced and imbalanced ads patients. Med (United States). 2015; 94(29):1-5.
[19] WEISZ G, HOUANG M. Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. SPINE. 2005;30(13):1558-1559; author reply 1559.
[20] BERJANO P. Reviewer’s comment concerning “Classification of normal sagittal spine alignment: refounding the Roussouly classification” by F. Laouissat et al. (2017). doi:10.1007/s00586-017-5111-x (Epub ahead of print). Eur Spine J. 2018;27(8):2012-2013.
[21] SEBAALY A, GROBOST P, MALLAM L, et al. Description of the sagittal alignment of the degenerative human spine. Eur Spine J. 2017;27(2): 489-496.
[22] SHEN Y, SARDAR ZM, LE HUEC JC, et al. Variation in Lumbar Shape and Lordosis in a Large Asymptomatic Population: A MEANS Study. SPINE. 2023;48(11):758-765.
[23] THOMPSON W, COGNIET A, CHALLALI M, et al. Analysis of cervical sagittal alignment variations after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy for severe imbalance: study of 59 cases. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(s1):16-24.
[24] CHARLES YP, SFEIR G, MATTER-PARRAT V, et al. Cervical Sagittal Alignment in Idiopathic Scoliosis Treated by Posterior Instrumentation and in Situ Bending. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(7):E419-E427.
[25] GHOBRIAL GM, LEBWOHL NH, GREEN BA, et al. Changes in Cervical Alignment after Multilevel Schwab Grade II Thoracolumbar Osteotomies for Adult Spinal Deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(2):E82-E91.
[26] BARREY C, ROUSSOULY P, PERRIN G, et al. Sagittal balance disorders in severe degenerative spine. Can we identify the compensatory mechanisms? Eur Spine J. 2011;20 Suppl 5:626-633.
[27] TANG JA, SCHEER JK, SMITH JS, et al. The impact of standing regional cervical sagittal alignment on outcomes in posterior cervical fusion surgery. Clin Neurosurg. 2015;76(3):S14-S21.
[28] FALDINI C, DI MARTINO A, BORGHI R, et al. Long vs. short fusions for adult lumbar degenerative scoliosis: does balance matters? Eur Spine J. 2015;24:887-892.
[29] YANG C, YANG M, WEI X, et al. Lumbar Lordosis Minus Thoracic Kyphosis: A Novel Regional Predictor for Sagittal Balance in Elderly Populations. Spine. 2016;41(5):399-403.
[30] ZHOU S, LI W, SU T, et al. Does lumbar lordosis minus thoracic kyphosis predict the clinical outcome of patients with adult degenerative scoliosis? J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):290.
[31] QIU W, ZHOU S, HAN G, et al. The Role of Thoracic Tilt in Identifying Thoracic Compensation and Predicting Proximal Junctional Kyphosis in Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis. Spine. 2023;48(20):1446-1454.
[32] PROTOPSALTIS TS, LAFAGE R, VIRA S, et al. Novel Angular Measures of Cervical Deformity Account for Upper Cervical Compensation and Sagittal Alignment. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(7):E959-E967.
[33] CECCHINATO R, LANGELLA F, BASSANI R, et al. Variations of cervical lordosis and head alignment after pedicle subtraction osteotomy surgery for sagittal imbalance. Eur Spine J. 2014;23:S644-S649.
[34] QIAN J, QIU Y, QIAN BP, et al. Compensatory modulation for severe global sagittal imbalance: significance of cervical compensation on quality of life in thoracolumbar kyphosis secondary to ankylosing spondylitis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3715-3722.
[35] SCHEER JK, TANG JA, SMITH JS, et al. Cervical spine alignment, sagittal deformity, and clinical implications. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(2): 141-159.
[36] LEE SH, KIM KT, SEO EM, et al. The influence of thoracic inlet alignment on the craniocervical sagittal balance in asymptomatic adults. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(2):E41-E47.
[37] KNOTT PT, MARDJETKO SM, TECHY F. The use of the T1 sagittal angle in predicting overall sagittal balance of the spine. Spine J. 2010; 10(11):994-998.
[38] DAY LM, RAMCHANDRAN S, JALAI CM, et al. Thoracolumbar Realignment Surgery Results in Simultaneous Reciprocal Changes in Lower Extremities and Cervical Spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(11):799-807.
[39] LAFAGE V, AMES C, SCHWAB F, et al. Changes in thoracic kyphosis negatively impact sagittal alignment after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: A comprehensive radiographic analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(3):E180-E187.
[40] LAFAGE V, SCHWAB F, VIRA S, et al. Spino-pelvic parameters after surgery can be predicted: A preliminary formula and validation of standing alignment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(13):1037-1045.
[41] LAFAGE V, SCHWAB F, SKALLI W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(14):1572-1578. |