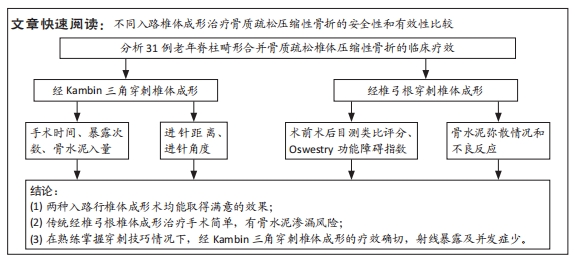
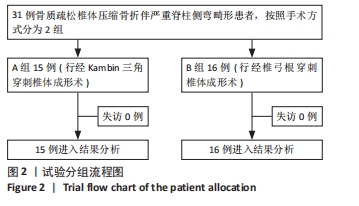
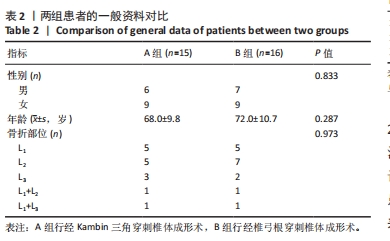
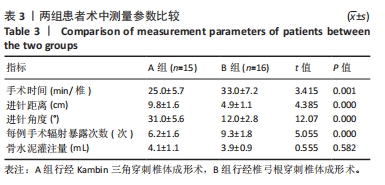
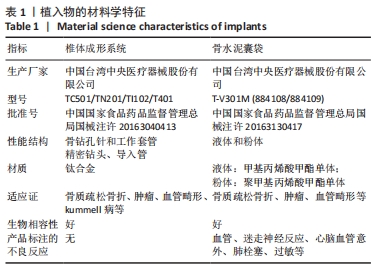
[1] GIANGREGORIO LM, PAPAIOANNOU A, MACINTYRE NJ, et al. Too Fit To Fracture: exercise recommendations for individuals with osteoporosis or osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(3):821-835.
[2] KENDLER DL, BAUER DC, DAVISON KS, et al. Vertebral Fractures: Clinical Importance and Management. Am J Med. 2016;129(2):221.e1-10.
[3] LEE JT, KO MJ, LEE BJ, et al. Pain Intervention for Osteoporotic Compression Fracture, From Physical Therapy to Surgery: A Literature Review. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2024;20(3):159-167.
[4] YANG EZ, XU JG, HUANG GZ, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Conservative Treatment in Aged Patients With Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(8):653-660.
[5] WANG B, GUO H, YUAN L, et al. A prospective randomized controlled study comparing the pain relief in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with the use of vertebroplasty or facet blocking. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3486-3494.
[6] PARRY SM, PUTHUCHEARY ZA. The impact of extended bed rest on the musculoskeletal system in the critical care environment. Extrem Physiol Med. 2015; 4:16.
[7] WANG Q, DONG JF, FANG X, et al. Application and modification of bone cement in vertebroplasty: A literature review. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2022;33(2):467-478.
[8] LIEBERMAN IH, TOGAWA D, KAYANJA MM. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: filler materials. Spine J. 2005;5(6 Suppl):305S-316S.
[9] BU BX, WANG MJ, LIU WF, et al. Short-segment posterior instrumentation combined with calcium sulfate cement vertebroplasty for thoracolumbar compression fractures: radiographic outcomes including nonunion and other complications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(2):227-233.
[10] ZHAO S, XU CY, ZHU AR, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of 3 treatments for patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(26):e7328.
[11] RYU KS, HUH HY, JUN SC, et al. Single-balloon kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: far-lateral extrapedicular approach. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;45(2):122-126.
[12] LIU L, CHENG S, LU R, et al. Extrapedicular Infiltration Anesthesia as an Improved Method of Local Anesthesia for Unipedicular Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Percutaneous Kyphoplasty. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:5086414.
[13] TAN G, LI F, ZHOU D, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures-A systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(33):e11968.
[14] CHENG X, LONG HQ, XU JH, et al. Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of patients with osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture (OVCF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11):3439-3449.
[15] HAIBIER A, YUSUFU A, LIN H, et al. Effect of different cement distribution in bilateral and unilateral Percutaneous vertebro plasty on the clinical efficacy of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):908.
[16] KIM T, PARK J, CHO J, et al. Quantitative Comparison of Vertebral Structural Changes After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Between Unilateral Extrapedicular Approach and Bilateral Transpedicular Approach Using Voxel-Based Morphometry. Neurospine. 2023;20(4): 1287-1302.
[17] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, CHEN H, et al. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of unilateral and bilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(51):e28453.
[18] RINGER AJ, BHAMIDIPATY SV. Percutaneous access to the vertebral bodies: a video and fluoroscopic overview of access techniques for trans-, extra-, and infrapedicular approaches. World Neurosurg. 2013; 80(3-4):428-435.
[19] HAIBIER A, YUSUFU A, LIN H, et al. Effect of different cement distribution in bilateral and unilateral Percutaneous vertebro plasty on the clinical efficacy of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):908.
[20] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(7):1929-1937.
[21] BEALL DP, PARSONS B, BURNER S. Technical Strategies and Anatomic Considerations for an Extrapedicular Modified Inferior Endplate Access to Thoracic and Lumbar Vertebral Bodies. Pain Physician. 2016; 19(8):593-601.
[22] LIU L, CHENG S, WANG Q, et al. An anatomical study on lumbar arteries related to the extrapedicular approach applied during lumbar PVP (PKP). PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0213164.
[23] HEO DH, CHO YJ. Segmental artery injury following percutaneous vertebroplasty using extrapedicular approach. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011;49(2):131-133.
[24] OZER AF, SUZER T, CAN H, et al. Anatomic Assessment of Variations in Kambin’s Triangle: A Surgical and Cadaver Study. World Neurosurg. 2017;100:498-503.
[25] WAGUIA R, GUPTA N, GAMEL KL, et al. Current and Future Applications of the Kambin’s Triangle in Lumbar Spine Surgery. Cureus. 2022;14(6): e25686.
[26] LIU Y, WANG B, LONG Y, et al. Extrapedicular unilateral percutaneous vertebroplasty via transverse process for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures of upper lumbar. Chin J Trauma. 2018;34(4): 312-318.
[27] MOLLOY S, MATHIS JM, BELKOFF SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1549-1554.
[28] MATTIE R, LAIMI K, YU S, et al. Comparing Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Conservative Therapy for Treating Osteoporotic Compression Fractures in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(12):1041-1051.
[29] KWON HM, LEE SP, BAEK JW, et al. Appropriate Cement Volume in Vertebroplasty: A Multivariate Analysis with Short-Term Follow-Up. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(2):128-134.
[30] MOLLOY S, MATHIS JM, BELKOFF SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(14):1549-1554.
[31] SUN HB, JING XS, LIU YZ, et al. The Optimal Volume Fraction in Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Evaluated by Pain Relief, Cement Dispersion, and Cement Leakage: A Prospective Cohort Study of 130 Patients with Painful Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture in the Thoracolumbar Vertebra. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e677-e688.
[32] CHENG X, LONG HQ, XU JH, et al. Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of patients with osteoporosis vertebral compression fracture (OVCF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(11): 3439-3449.
[33] WIDMER SOYKA RP, HELGASON B, HAZRATI MARANGALOU J, et al. The Effectiveness of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Is Determined by the Patient-Specific Bone Condition and the Treatment Strategy. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0151680.
[34] SUN Y, LI X, MA S, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of unilateral and bilateral approach kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: A meta-analysis. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2024;35(3):491-503.
[35] ZHAN Y, JIANG J, LIAO H, et al. Risk Factors for Cement Leakage After Vertebroplasty or Kyphoplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Published Evidence. World Neurosurg. 2017;101:633-642.
[36] HONG SJ, LEE S, YOON JS, et al. Analysis of intradiscal cement leakage during percutaneous vertebroplasty: multivariate study of risk factors emphasizing preoperative MR findings. J Neuroradiol. 2014;41(3): 195-201.
[37] COSAR M, SASANI M, OKTENOGLU T, et al. The major complications of transpedicular vertebroplasty. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009;11(5): 607-613.
[38] YALTIRIK K, ASHOUR AM, REIS CR, et al. Vertebral augmentation by kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: 8 years experience outcomes and complications. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2016;7(3):153-160.
[39] LIM JB, PARK JS, KIM E. Nonaneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: rare complication of vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 45(6):386-389.
[40] BAEK IH, PARK HY, KIM KW, et al. Paraplegia due to intradural cement leakage after vertebroplasty: a case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):741.
[41] TSAI YD, LILIANG PC, CHEN HJ, et al. Anterior spinal artery syndrome following vertebroplasty: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35(4):E134-E136.
[42] BIRKENMAIER C, SEITZ S, WEGENER B, et al. Acute paraplegia after vertebroplasty caused by epidural hemorrhage. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(8):1827-1831.
[43] XIE S, CUI L, WANG C, et al. Contact between leaked cement and adjacent vertebral endplate induces a greater risk of adjacent vertebral fracture with vertebral bone cement augmentation biomechanically. Spine J. 2024:S1529-9430(24)01034-9.
[44] ZHAO Z, WANG R, GAO L, et al. Pulmonary embolism and intracardiac foreign bodies caused by bone cement leakage: a case report and literature review. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024;19(1):544.
[45] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, VAN ERKEL AR, DIJKSTRA PD. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011;11(9):839-848.
[46] WU Y, XU LJ. Incidence of Cement Leakage and Potential Risk Factors in Surgery for Spinal Metastasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2024;184:e95-e110.
[47] ZHU D, HU JN, WANG L, et al. A Modified Unilateral Extrapedicular Approach Applied to Percutaneous Kyphoplasty to Treat Lumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture: A Retrospective Analysis. Pain Physician. 2023;26(3):E191-E201. |