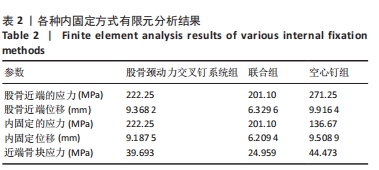
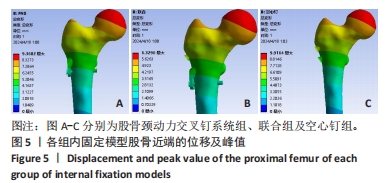
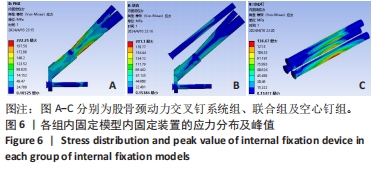
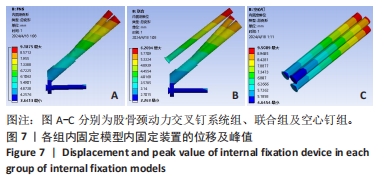
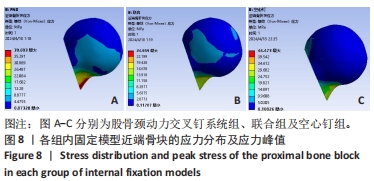
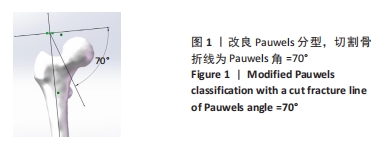
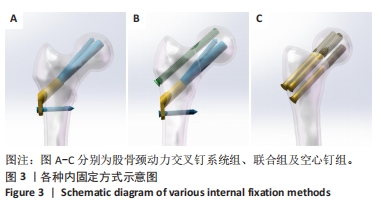
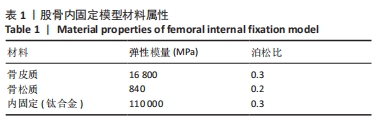
[1] 葛双雷, 王雪飞, 刘亮, 等. 股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合支撑空心钉对伴后内侧粉碎的中青年股骨颈骨折的疗效研究[J].中华医学杂志,2023,103(21):1631-1637.
[2] 张英泽. 临床创伤骨科流行病学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018:223-225.
[3] RAUDENBUSH B, WALTON I, SIMELA A, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease, high-dose steroids, osteoporosis, or an oncological etiology for a pathological femoral neck fracture in a young adult: a case report. Open Orthop J. 2014;8:27-33.
[4] FORTINA M, CARTA S, CRAINZ E, et al. Management of displaced intracapsulatfemoral neck fracture in young adult:why complications are still so high? Casereport of posttraumatic avascular necrosis in a 30-year-old man and a briefreview. J Trauma. 2009;67(5):E163-E166.
[5] LIU BC, SUN C, XING Y, et al. Analysis ofrisk factors for necrosis of femoral headafter internal fixation surgery in young and mid-aged patients with femoral neckfracture. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020;52(2):290-297.
[6] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1654-1659.
[7] MARSH JL, SLONGO TF, AGEL J, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium - 2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21:S1-133.
[8] KUNAPULI SC, SCHRAMSKI MJ, LEE AS, et al. Biomechanical analysis of augmented plate fixation for the treatment of vertical shear femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29:144-150.
[9] LI M, COLE PA. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures: how anatomy influences the treatment issues? Injury. 2015; 46(3):453-458.
[10] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659.
[11] JIAN-QIAO PENG M, CHEN HY, JU X, et al. CoMParative analysis for five fixations of Pauwels-I by the biomechanical finite-element method. J Invest Surg. 2020;33(5):428-437.
[12] FLORSCHUTZ AV, LANGFORD JR, HAIDUKEWYCH GJ, et al. Femoral neck fractures:current management. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):121 -129.
[13] WANG G, TANG Y, WU X, et al. Finite element analysis of a new plate for Pauwels type Ⅲ femoral neck fractures. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(2): 1220703221.
[14] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels III Femoral Neck Fractures: A CoMParison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[15] JUNG CH, CHA Y, YOON HS, et al. Mechanical effects of surgical variations in the femoral neck system on Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture : a finite element analysis. Bone Joint Res. 2022;11(2):102-111.
[16] 葛双雷, 王雪飞, 刘亮, 等. 股骨颈动力交叉钉系统联合支撑空心钉对伴后内侧粉碎的中青年股骨颈骨折的疗效研究[J].中华医学杂志,2023,103(21):1631-1637.
[17] ZHENG S, LIN D, CHEN P, et al. CoMParison of femoral neck shortening after femoral neck system and cannulated cancellous screw fixation for displaced femoral neck fractures in young adults. Injury. 2024;55(6):111564.
[18] WANG SH, YANG JJ, SHEN HC, et al. Using a modified Pauwels method to predict the outcome of femoral neck fracture in relatively young patients. Injury. 2015;46(10):1969-1974.
[19] LI J, WANG M, LI L, et al. Finite element analysis of different configurations of fully threaded cannulated screw in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):272.
[20] GARDNER MP, CHONG AC, POLLOCK AG, et al. Mechanical evaluation of large-size fourth-generation composite femur and tibia models. Ann Biomed Eng, 2010;38(3):613-620.
[21] HEINER AD. Structural properties of fourth-generation composite femurs and tibias. J Biomech. 2008;41(15):3282-3284.
[22] MA L, ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation with finite element analysis of the reconstruction of femoral tumor defects by using a double-barrel free vascularized fibular graft combined with a locking plate. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(9):2425-2434.
[23] ZHENG L, CHEN X, ZHENG Y, et al. Cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of two intertrochanteric fractures - a coMParative finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):1010.
[24] VAN HOUCKE J, SCHOUTEN A, STEENACKERS G, et al. Computer-basedestimation of the hip joint reaction force and hip flexion angle in three different sitting configurations. Appl Ergon. 2017;63:99-105.
[25] JACOB G, PAI S, HUGGI V, et al. Lag screw with DHS (LSD) for vertical angle femoral neck fractures in young adults. Injury. 2020;51(11): 2628-2633.
[26] WANG K, LIN D, CHEN P, et al. Incidence and factors influencing neck shortening after screw fixation of femoral neck fractures with the femoral neck system. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):317.
[27] 徐高伟,陈廷,张松,等.55-65 岁 Garden Ⅲ、W型股骨颈骨折患者手术方式选择及疗效的比较[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2020, 25(4):388-392.
[28] 张长青,张英泽,余斌,等.成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):921-928.
[29] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1654-1659.
[30] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46:484-491.
[31] DUCKWORTH AD, BENNET SJ, ADERINTO J, et al. Fixation of intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck in young patients: risk factors for failure. J Bone joint Surg Br. 2011;93:811-816.
[32] WANG Y, MA JX, BAI HH, et al. Mechanical analysis of the femoral neck dynamic intersection system with different nail angles and clinical applications. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(20):4814-4823.
[33] TENG Y, ZHANG Y, GUO C. Finite element analysis of femoral neck system in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Medicine. 2022;101(28):e29450.
[34] WANG K, LIN D, CHEN P, et al. Incidence and factors influencingneck shortening after screw fixation of femoral neck fractures with thefemoral neck system. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):317.
[35] LU Y, CANAVESE F, NAN G, et al. Is Femoral Neck System a Valid Alternative for the Treatment of Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures in Adolescents? A CoMParative Study of Femoral Neck System versus Cannulated Compression Screw. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(8):999.
[36] ZHANG YZ, LIN Y, LI C, et al. A CoMParative Analysis of Femoral Neck System and Three Cannulated Screws Fixation in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures: A Six-Month Follow-Up. Orthop Surg. 2022; 14(4):686-693.
[37] NIBE Y, MATSUMURA T, TAKAHASHI T, et al. A coMParison between the femoral neck system and other implants for elderly patients with femoral neck fracture: A preliminary report of a newly developed implant. J Orthop Sci. 2022;27(4):876-880.
[38] SAAD A, PATRALEKH MK, JAIN VK, et al. Femoral neck system reduces surgical time and complications in adults with femoral neck fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2022; 30:101917.
[39] 杨家赵,周雪锋,朱万博,等.FNS与空心钉固定治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的近期疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):761-768.
[40] 许翔宇,周方,田耘,等.FNS与DHS固定治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(9):754-760.
[41] FELTON J, SLOBOGEAN GP, JACKSON SS, et al. Femoral neck shorteningafter hip fracture fixation is associated with inferior hip function: results from the FAITH trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(10): 487-496.
[42] 李正刚,尚学红,吴张,等.不同载荷条件下三种内固定方式治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(3):455-463.
[43] 荆玉龙,张树栋,韩紫音,等.骨科机器人辅助股骨颈动力交叉钉系统治疗新鲜股骨颈骨折的近期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2022,36(8):946-950. |