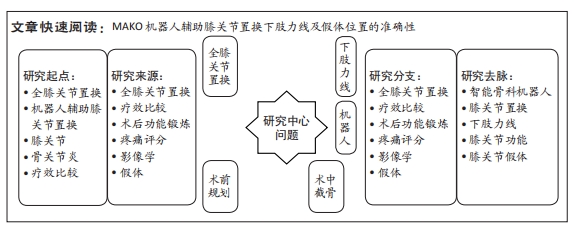
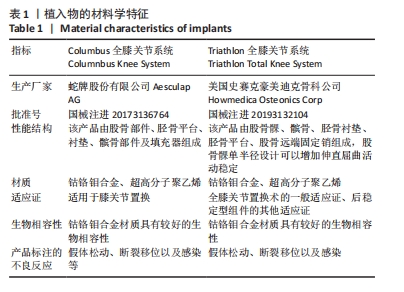
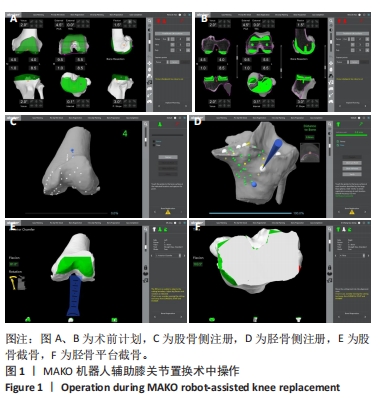
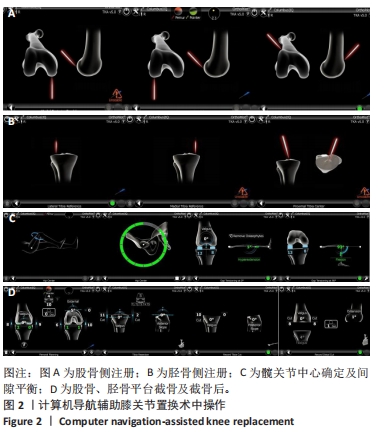
[1] 张先龙,王坤正. 关节外科的未来—数字骨科技术在关节外科的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(8):525-531.
[2] GANKO A, DONNELLY W, BRENNAN S, et al. Early Results & Accuracy of the MAKO Robtic Unicompartmental Knee Replacement. Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(5):PMC5455949.
[3] WEBB ML, HUTCHISON CE, SLOAN M, et al. Reduced postoperative morbidity in computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty: A retrospective comparison of 225,123 cases. Knee. 2021;30:148-156.
[4] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and kneearthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[5] BANERJEE S, CHERIAN JJ, ELMALLAH RK, et al. Robot-assisted total hip arthro-plasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13:47-56.
[6] BANERJEE S, CHERIAN JJ, ELMALLAH RK, et al. Robotic-assisted kneearthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2015;12:727-735.
[7] DE STEIGER RN, LIU YL, GRAVES SE. Computer naviga-tion for Total knee arthroplasty reduces revision ratefor patients less than sixty-five years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97: 635-642.
[8] 雷凯,刘力铭,熊然,等.全膝关节置换术中智能精准辅助技术的应用及研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2022,38(8):761-768.
[9] BUMPASS DB, NUNLEY RM. Assessing the value of atotal joint replacement. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2012;5(4):274-282.
[10] LEARMONTH ID, YOUNG C, RORABECK C. The opera-tion of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet. 2007;370(9597):1508-1519.
[11] LIOW MHL, XIA Z, WONG MK, et al. Robot-assisted total knee arthroplasty accuratelyrestores the joint line and mechanical axis. A prospec-tive randomised study. J Arthroplast. 2014;29:2373-2377.
[12] YILDIRIM G, FERNANDEZ-MADRID I, SCHWARZKOPF R, et al. Comparison of robot surgery mod-ular and Total knee arthroplasty kinematics. J Knee Surg. 2014;27:157-164.
[13] PLATE JF, MOFIDI A, MANNAVA S, et al. Achievingaccurate ligament balancing using robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Adv Orthop. 2013;2013:1-6.
[14] 钱春晓,储旭东,过锡民,等.全膝关节置换术治疗膝骨关节炎合并固定性髌骨脱位对HSS、VAS评分及股骨胫骨角的影响[J].重庆医学,2022,51(S02):240-242.
[15] 赵资坚,张荣臻,蔡史健,等.3D打印截骨导板辅助全膝关节置换术治疗膝关节外骨折后遗膝关节骨性关节炎[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(6):580-584.
[16] 牛鸣,王秋入,李军伟,等.全膝关节置换术中采用内侧髌旁软组织重叠缝合法处理重度膝关节骨关节炎合并骨性髌骨脱位的早中期临床结果[J].南方医科大学学报,2022,42(2):244-249.
[17] ELSAYED A, ALLAN D, DAVIES PSE, et al. Total knee replacement in a transtibial amputee. BMJ Case Rep. 2022;15(12):e252080.
[18] KONNYU KJ, THOMA LM, CAO W, et al. Rehabilitation for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023; 102(1):19-33.
[19] CHENG GHM, TAN GKY, KAMARUDIN MFB, et al. Steroids Significantly Decrease Postoperative Postural Hypotension in Total Knee Replacement. J Knee Surg. 2023;36(2):208-215.
[20] VAKHARIA RM, SODHI N, COHEN-LEVY WB, et al. Comparison of Patient Demographics and Utilization Trends of Robotic-Assisted and Non-Robotic-Assisted Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(6):621-627.
[21] ROSS J. Smart Robotics Tool. Mater Eval. 2021;79(7):612-612.
[22] SUN Y, LIU W, HOU J, et al. Does robotic-assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty have lower complication and revision rates than the conventional procedure? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(8):e044778.
[23] MULLAJI A. Can isolated removal of osteophytes achieve correction of varus deformity and gap-balance in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty? An analysis of navigation data. Bone Joint J. 2020;102(6): 49-58.
[24] DANIEL HV, ALFONSO NF, SERGIO RG, et al. Can the need for soft tissue release in total knee replacement be predicted pre-operatively? A study based on surgical navigation. Int Orthop. 2022;46(4):815-821.
[25] 汝跃方,何荣新.Mako机器人辅助全膝关节置换术在膝骨性关节炎的早期应用[J].中国骨伤,2023,36(2):133-139.
[26] SIRES JD, CRAIK JD, WILSON CJ,等.Mako机器人辅助下全膝关节置换术截骨精度[J].临床骨科杂志,2022,25(1):71.
[27] 张鹏远,马明阳,孔祥朋,等.MAKO机器人辅助与传统手工全膝关节置换术后下肢力线的对比研究[J].骨科,2023,14(2):155-160.
[28] 汪洋,纪保超,陈永杰,等.MAKO机器人在复杂性人工全髋关节置换术中应用的近期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(5): 555-560.
[29] 刘杠,李国庆,汪洋,等.MAKO机器人辅助全膝关节置换术的早期临床疗效[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(3):232-238.
[30] 戴慧勇,朱科朝,王俏杰,等.机器人辅助直接前侧入路全髋关节置换术学习曲线及早期临床疗效[J].中华医学杂志,2022,102(1): 49-55.
[31] 穆文博,胥伯勇,郭文涛,等.MAKO机器人辅助下全膝关节置换术治疗伴有严重内翻畸形膝骨关节炎的早期疗效研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(8):612-618.
[32] 智信,汪澜,倪明,等.MAKO机器人辅助全膝关节置换术的学习曲线[J].中华骨科杂志,2023,43(1):48-54.
[33] 赵晶,余沐洋,彭慧明,等.机器人辅助全膝关节置换术流程优化及学习曲线研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(4):333-339.
[34] SOUSA PL, SCULCO PK, MAYMAN DJ, et al. Robots in the operating room during hip and knee arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3):309-317.
[35] MISSO D, ZHEN E, KELLY J, et al. A progressive scholarly acceptance analysis of robot-assisted arthroplasty: a review of the literature and prediction of future research trends. J Robot Surg. 2021;15(5):813-819.
[36] CHILDERS CP, MAGGARD-GIBBONS M. Understanding costs of care in the operating room. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(4):e176233.
[37] PUGELY AJ, MARTIN CT, GAO Y, et al. The incidence of and risk factors for 30-day surgical site infections following primary and revision total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(9 Suppl): 47-50.
[38] SODHI N, KHLOPAS A, PIUZZI NS, et al. The learning curve associated with robotic total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(1):17-21.
[39] COOL CL, JACOFSKY DJ, SEEGER KA, et al. A 90-day episodeof- care cost analysis of robotic- arm assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Comp Eff Res. 2019;8(5):327-336.
[40] SOUSA PL, SCULCO PK, MAYMAN DJ, et al. Robots in the operating room during hip and knee arthroplasty. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2020;13(3):309-317.
[41] KAYANI B, KONAN S, PIETRZAK JRT, et al. The learning curve associated with robotic- arm assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. Bone Joint J. 2018; 100-b(8):1033-1042.
[42] SHERMAN WF, WU VJ. Robotic surgery in total joint arthroplasty: a survey of the AAHKS membership to understand the utilization, motivations, and perceptions of total joint surgeons. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(12):3474-3481, e2.
|