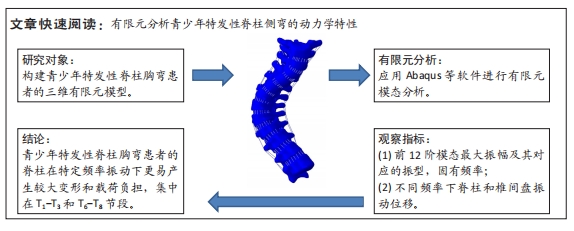
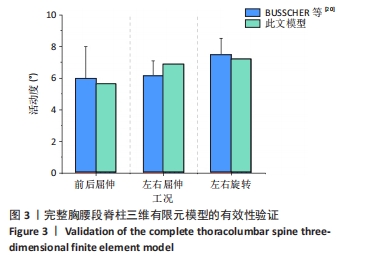
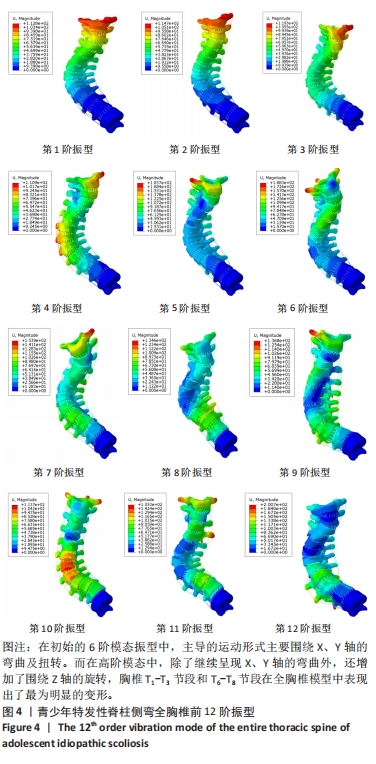
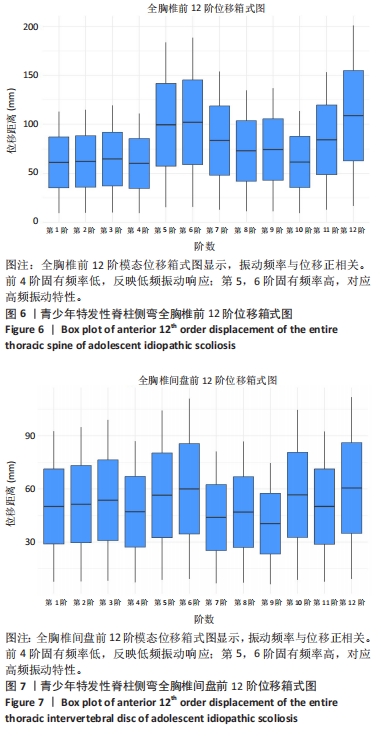
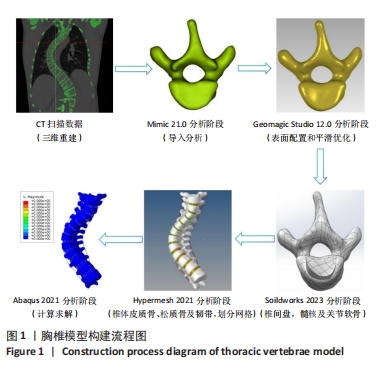
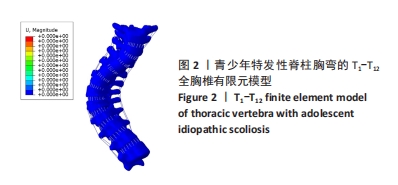
[1] KUZNIA AL, HERNANDEZ AK, LEE LU. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(1):19-23.
[2] CHUNG CL, KELLY DM, SAWYER JR, et al. Mechanical Testing of a Novel Fastening Device to Improve Scoliosis Bracing Biomechanics for Treating Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2018;2018:7813960.
[3] ENGELBERT RH, UITERWAAL CS, VAN DER HULST A, et al. Scoliosis in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: influence of severity of disease and age of reaching motor milestones. Eur Spine J. 2003;12:130-134.
[4] LENKE LG, SIDES BA, KOESTER LA, et al. Vertebral column resection for the treatment of severe spinal deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(3):687-699.
[5] 蔡振宁,朱泽章,邱勇.Lenke 1型和2型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸选择性胸弯融合术后腰弯自发性纠正的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2023,33(3):270-273.
[6] FAN W, ZHAO D, GUO LX. A finite element model of the human lower thorax to pelvis spinal segment: Validation and modal analysis. Biomed Mater Eng. 2021;32(5):267-279.
[7] GOEL VK, PARK H, KONG W. Investigation of vibration characteristics of the ligamentous lumbar spine using the finite element approach. J Biomech Eng. 1994;116(4):377-383.
[8] JIA S, LI Y, XIE J, et al. Differential response to vibration of three forms of scoliosis during axial cyclic loading: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):370.
[9] BRINCKMANN P, FROBIN W, BIGGEMANN M, et al. Quantification of overload injuries to thoracolumbar vertebrae and discs in persons exposed to heavy physical exertions or vibration at the work-place The shape of vertebrae and intervertebral discs - study of a young, healthy population and a middle-aged control group. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1994;9 Suppl 1:S3-S83.
[10] LI S, PATWARDHAN AG, AMIROUCHE FM, et al. Limitations of the standard linear solid model of intervertebral discs subject to prolonged loading and low-frequency vibration in axial compression. J Biomech. 1995;28(7):779-790.
[11] XU M, YANG J, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite element method-based study for effect of adult degenerative scoliosis on the spinal vibration characteristics. Comput Biol Med. 2017;84:53-58.
[12] GOULD SL, CRISTOFOLINI L, DAVICO G, et al. Computational modelling of the scoliotic spine: A literature review. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021;37(10):e3503.
[13] LERCHL T, NISPEL K, BAUM T, et al. Multibody Models of the Thoracolumbar Spine: A Review on Applications, Limitations, and Challenges. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(2):202.
[14] LIAO JC, CHEN WP, WANG H. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by short-segment pedicle screw fixation using a combination of two additional pedicle screws and vertebroplasty at the level of the fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):262.
[15] ZHANG W, ZHAO J, LI L, et al. Modelling tri-cortical pedicle screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae under osteoporotic condition: A finite element analysis based on computed tomography. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;187:105035.
[16] WANG TN, WU BL, DUAN RM, et al. Treatment of Thoracolumbar Fractures Through Different Short Segment Pedicle Screw Fixation Techniques: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(2):601-608.
[17] 富荣昌,杨骁峥,李现政.最佳Halo重力牵引治疗Lenke3型脊柱侧凸的生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(18):2901-2905.
[18] DONG R, ZHU S, CHENG X, et al. Study on the biodynamic characteristics and internal vibration behaviors of a seated human body under biomechanical characteristics. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2024;23(5):1449-1468.
[19] XIN DQ, HU XM, HANDY, et al. Parameter modification and validation of the finite element model of Lenke type 3 adult idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Tissue Eng Res. 2017;21(31):4975-4982.
[20] BUSSCHER I, VAN DIEËN JH, KINGMA I, et al. Biomechanical characteristics of different regions of the human spine: an in vitro study on multilevel spinal segments. Srine. 2009;34(26):2858-2864.
[21] PENG Y, WANG SR, QIU GX, et al. Research progress on the etiology and pathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(4):483-493.
[22] LI P, FU R, YANG X, et al. Finite element method-based study for spinal vibration characteristics of the scoliosis and kyphosis lumbar spine to whole-body vibration under a compressive follower preload. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2024:1-10. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2024.2333925.
[23] GUO LX, ZHANG YM, ZHANG M. Finite element modeling and modal analysis of the human spine vibration configuration. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2011;58(10):2987-2990.
[24] TANG SJ, DONG RC, CHENG X, et al. Effect of anteroposterior vibration frequency on the risk of lumbar injury in seated individuals. Ergonomics. 2024:1-13. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2024.2391591.
[25] CARREAU JH, BASTROM T, PETCHARAPORN M, et al. Computer-Generated, Three-Dimensional Spine Model From Biplanar Radiographs: A Validity Study in Idiopathic Scoliosis Curves Greater Than 50 Degrees. Spine Deform. 2014;2(2):81-88.
[26] SELEVICIENE V, CESNAVICIUTE A, STRUKCINSKIENE B, et al. Physiotherapeutic Scoliosis-Specific Exercise Methodologies Used for Conservative Treatment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis, and Their Effectiveness: An Extended Literature Review of Current Research and Practice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(15):9240.
[27] KAWCHUK GN, HARTVIGSEN J, EDGECOMBE T, et al. Structural health monitoring (vibration) as a tool for identifying structural alterations of the lumbar spine: a twin control study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22974.
[28] SHU D, DAI S, WANG J, et al. Impact of Running Exercise on Intervertebral Disc: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2024;16(6):958-970.
[29] LI N, CAVAGNARO MJ, XIONG K, et al. The Multi-Modal Risk Analysis and Medical Prevention of Lumbar Degeneration, Fatigue, and Injury Based on FEM/BMD for Elderly Chinese Women Who Act as Stay-Home Grandchildren Sitters. Front Public Health. 2021;9:700148.
[30] MACEDO LG, NOGUCHI KS, DE OLIVEIRA LA, et al. The association between whole body vibration exposure and spine degeneration on imaging: A systematic review. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2022; 35(4):691-700.
[31] GUO LX, TEO EC. Influence prediction of injury and vibration on adjacent components of spine using finite element methods. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(2):118-124.
[32] BOVENZI M, SCHUST M. A prospective cohort study of low-back outcomes and alternative measures of cumulative external and internal vibration load on the lumbar spine of professional drivers. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2021;47(4):277-286.
[33] COMTE N, PUJADES S, COURVOISIER A, et al. Multi-Modal Data Correspondence for the 4D Analysis of the Spine with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023;10(7):874.
[34] OVERBERGH T, SEVERIJNS P, BEAUCAGE-GAUVREAU E, et al. Development and validation of a modeling workflow for the generation of image-based, subject-specific thoracolumbar models of spinal deformity. J Biomech. 2020;110:109946.
[35] WEI W, ZHANG T, HUANG Z, et al. Finite element analysis in brace treatment on adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2022;60(4):907-920.
[36] IDE K, NARITA K, YAMATO Y, et al. Effect of corrective stresses on rods in adult spinal deformity surgery-finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2024;29(3):711-717.
[37] JIA S, LIN L, YANG H, et al. The influence of the rib cage on the static and dynamic stability responses of the scoliotic spine. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):16916.
[38] PIERCE KE, HORN SR, JAIN D, et al. The Impact of Adult Thoracolumbar Spinal Deformities on Standing to Sitting Regional and Segmental Reciprocal Alignment. Int J Spine Surg. 2019;13(4):308-316.
[39] JIA S, LIN L, YANG H, et al. Biodynamic responses of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis exposed to vibration. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2023; 61(1):271-284.
[40] YANG Y, LIU Y, YUAN X, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution on short implants with different bone conditions and osseointegration rates. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):220. |