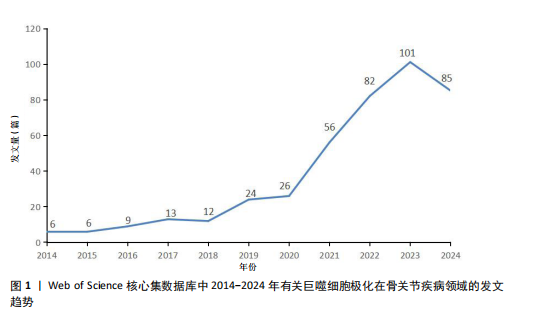
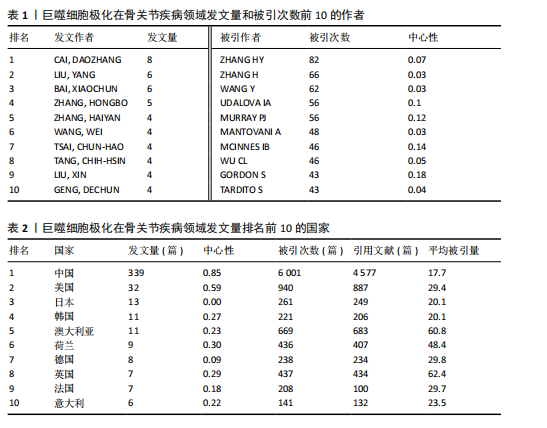
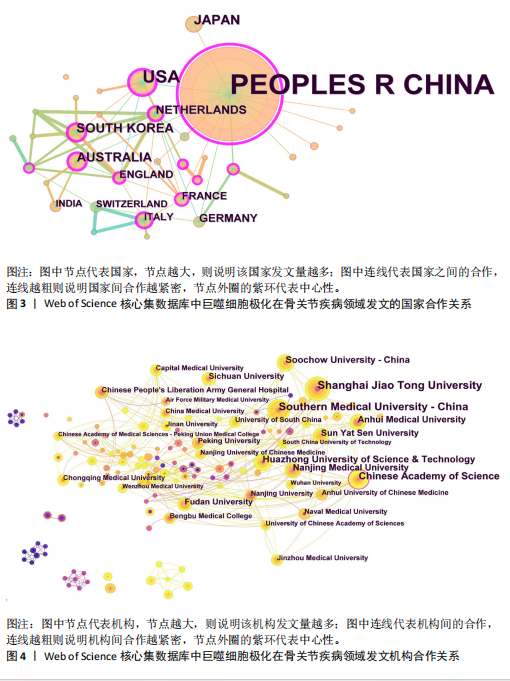
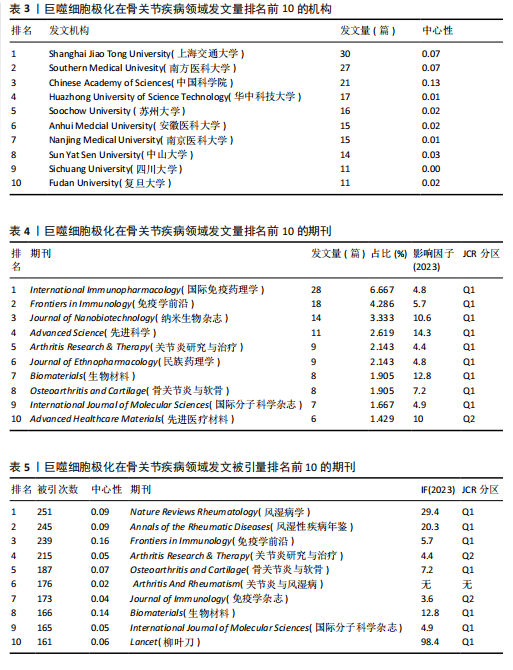
[1] CAI L, LV Y, YAN Q, et al. Cytokines: The links between bone and the immune system. Injury. 2024;55(2):111203.
[2] LUO M, ZHAO F, CHENG H, et al. Macrophage polarization: an important role in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1352946.
[3] MUÑOZ J, AKHAVAN NS, MULLINS AP, et al. Macrophage Polarization and Osteoporosis: A Review. Nutrients. 2020;12(10):2999.
[4] HU K, SHANG Z, YANG X, et al. Macrophage Polarization and the Regulation of Bone Immunity in Bone Homeostasis. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:3563-3580.
[5] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310.
[6] NINKOV A, FRANK JR, MAGGIO LA. Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. 2022;11(3):173-176.
[7] 沈爱宗,邵义伟,张圣雨,等.基于CiteSpace可视化分析我国医院智慧药学现状[J].中国药业,2023,32(7):1-8.
[8] 魏锦强,曾宪中,曹学伟,等.基于CiteSpace的中医外治法治疗膝骨关节炎可视化分析[J].中医药导报,2021,27(8): 154-159,184.
[9] MONDAL H, DEEPAK KK, GUPTA M, et al. The h-Index: Understanding its predictors, significance, and criticism. J Family Med Prim Care. 2023;12(11):2531-2537.
[10] 刘祎如,葛莉,杨献军,等.基于CiteSpace的妊娠糖尿病饮食干预研究的文献计量学分析[J].广西医学,2021, 43(6):777-782.
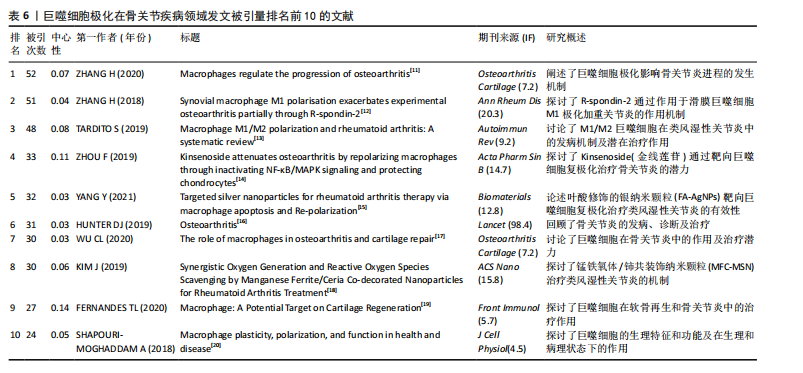
[11] ZHANG H, CAI D, BAI X. Macrophages regulate the progression of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):555-561.
[12] ZHANG H, LIN C, ZENG C, et al. Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018; 77(10):1524-1534.
[13] TARDITO S, MARTINELLI G, SOLDANO S, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. 2019;18(11):102397.
[14] ZHOU F, MEI J, HAN X, et al. Kinsenoside attenuates osteoarthritis by repolarizing macrophages through inactivating NF-κB/MAPK signaling and protecting chondrocytes. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019;9(5): 973-985.
[15] YANG Y, GUO L, WANG Z, et al. Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization. Biomaterials. 2021; 264:120390.
[16] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[17] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):544-554.
[18] KIM J, KIM HY, SONG SY, et al. Synergistic Oxygen Generation and Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging by Manganese Ferrite/Ceria Co-decorated Nanoparticles for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2019;13(3):3206-3217.
[19] FERNANDES TL, GOMOLL AH, LATTERMANN C, et al. Macrophage: A Potential Target on Cartilage Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2020;11:111.
[20] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440.
[21] TIAN H, QI H, XU X, et al. Research hotspots and trends in postlaparoscopic shoulder pain from 2003 to 2023: A bibliometric analysis. Heliyon. 2024;10(4):e25846.
[22] LU Y, LIU L, PAN J, et al. MFG-E8 regulated by miR-99b-5p protects against osteoarthritis by targeting chondrocyte senescence and macrophage reprogramming via the NF-κB pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(6):533.
[23] LIN R, YIN J, HUANG J, et al. Macrophage-derived ectosomal miR-350-3p promotes osteoarthritis progression through downregulating chondrocyte H3K36 methyltransferase NSD1. Cell Death Discov. 2024;10(1):223.
[24] ZHANG J, RONG Y, LUO C, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(24):25138-25152.
[25] LI Z, WANG Y, LI S, et al. Exosomes Derived From M2 Macrophages Facilitate Osteogenesis and Reduce Adipogenesis of BMSCs. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:680328.
[26] RENDRA E, RIABOV V, MOSSEL DM, et al. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology. 2019;224(2): 242-253.
[27] FAN C, WANG W, YU Z, et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes promote intervertebral disc degeneration by enhancing nucleus pulposus cell senescence through LCN2/NF-κB signaling axis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):301.
[28] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8920-8930.
[29] YANG X, CHANG Y, WEI W. Emerging role of targeting macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on polarization, metabolism and apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(7): e12854.
[30] CUTOLO M, CAMPITIELLO R, GOTELLI E, et al. The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:867260.
[31] WANG L, HE C. Nrf2-mediated anti-inflammatory polarization of macrophages as therapeutic targets for osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:967193.
[32] CHENG H, CHAWLA A, YANG Y, et al. Development of nanomaterials for bone-targeted drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2017;22(9):1336-1350.
[33] SUN J, DU J, LIU X, et al. Chondroitin sulfate-modified tragacanth gum-gelatin composite nanocapsules loaded with curcumin nanocrystals for the treatment of arthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):270. |