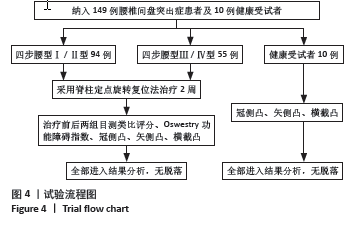
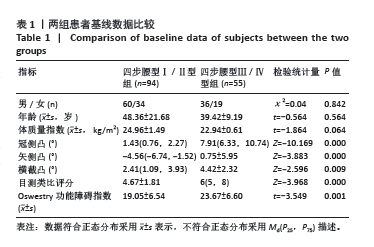
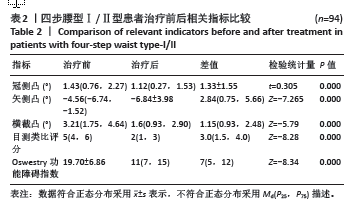
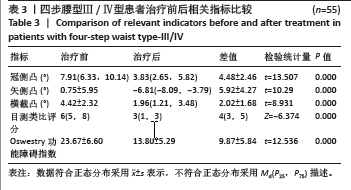
[1] 冯天有.中西医结合治疗软组织损伤[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社,2002.
[2] 冯天有.中西医结合治疗软组织损伤的临床研究[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社,2002.
[3] NAVARRO IJRL, ROSA BND, CANDOTTI CT. Anatomical reference marks, evaluation parameters and reproducibility of surface topography for evaluating the adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Gait Posture. 2019;69:112-120.
[4] HANNINK E, DAWES H, SHANNON TML, et al. Validity of sagittal thoracolumbar curvature measurement using a non-radiographic surface topography method. Spine Deform. 2022;10(6):1299-1306.
[5] NAVARRO IJRL, GODINHO RAT, CANDOTTI CT. Validating Surface Topography for the Measurement of the Thoracic Kyphosis Angle in Patients With Scoliosis: A Prospective Study of Accuracy. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2021;44(6):497-503.
[6] BOLZINGER M, BERNARDINI I, THEVENIN LEMOINE C, et al. Monitoring adolescent idiopathic scoliosis by measuring ribs prominence using surface topography device. Spine Deformity. 2021;9(5):1349-1354.
[7] 胡希鉴, 赵斌, 柴火, 等. 体表形态度量在脊柱弯曲异常中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1462-1468.
[8] 龚成,谢瑛,郭伟,等.脊柱定点旋转复位手法治疗对613例腰椎间盘突出症患者腰椎活动度及活动度对称性的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(1):599-601.
[9] 郭伟,赵颀,龚成,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者手法治疗前后腰椎关节活动度的力学评估研究[J].空军航空医学,2020,36(3):231-233.
[10] 冯伟, 冯天有, 许奎, 等. 新医正骨疗法治疗Ⅲ、Ⅳ型腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中医正骨,2015,27(5):62-64.
[11] 冯子鹤, 冯伟, 王飞, 等. 单(多)个椎体位移致足下垂型腰椎间盘突出的临床研究[J]. 空军航空医学,2023,40(1):44-48.
[12] 范宇, 张军, 郭伟, 等. 脊柱手法纠正“骨错缝”治疗腰椎间盘突出症的随机对照临床研究[J]. 北京中医药,2015,34(8):603-607.
[13] 许尘鏖. 腰椎间盘突出症非手术治疗与MRI影像表现的相关性研究[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2017,26(10):1091-1093.
[14] 冯宇, 毕永民, 杨文东. 应用320排螺旋CT三维重建腰椎棘突顶线的临床研究[J]. 颈腰痛杂志,2019,40(4):461-463.
[15] ZHANG Y, LI W, XU L, et al. Sciatic Scoliosis Evolution after Lumbar Discectomy: A Comparison Between Adolescents and Young Adults. Pain Physician. 2019;22(5):E457-E465.
[16] KIM R, KIM RH, KIM CH, et al. The Incidence and Risk Factors for Lumbar or Sciatic Scoliosis in Lumbar Disc Herniation and the Outcomes after Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy. Pain Physician. 2015;18(6): 555-564.
[17] 张兴祥, 廖运生, 张成明. 针刀、拨松针配合整脊手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症伴脊柱侧弯60例临床疗效观察[J]. 按摩与康复医学, 2020,11(5):8-11.
[18] 陈伟凯, 戴寿旺, 葛成孟. 经皮内镜下椎板间入路治疗合并脊柱侧弯的青少年腰椎间盘突出症的早期疗效观察[J]. 浙江医学,2018, 40(9):987-989.
[19] 吴巍, 杨川, 谢波, 等. 经皮内镜椎间孔入路治疗青少年腰椎间盘突出症合并脊柱侧弯28例[J]. 中国微创外科杂志,2024,24(3):208-212.
[20] 李丽, 于少泓, 周霞, 等. 中医康复临床实践指南·儿童青少年特发性脊柱侧弯[J]. 康复学报,2023,33(4):295-302.
[21] 中国康复医学会脊柱脊髓专业委员会基础研究与转化学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊治与康复管理指南[J]. 中华外科杂志,2022,60(5): 401-408.
[22] 中华医学会骨科学分会脊柱外科学组, 中华医学会骨科学分会骨科康复学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊疗指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(8):477-487.
[23] 马超, 王飞, 刘晓民, 等. 应用体表地形图量化腰椎间盘突出症腰型客观化指标:下腰曲线弹性固定转折点的三维成角[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(6):924-928.
[24] MATSUI H, OHMORI K, KANAMORI M, et al. Significance of sciatic scoliotic list in operated patients with lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 1998;23(3):338-342.
[25] 董津含, 于忠行. 针刺阿是穴治疗腰椎间盘突出症发生侧弯腰痛患者的临床疗效[J]. 中国药物经济学,2020,15(11):67-70.
[26] TU Z, WANG B, LI L, et al. Early Experience of Full-Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy for Adolescent Lumbar Disc Herniation with Sciatic Scoliosis. Pain Physician. 2018;21(1):E63-E70.
[27] YANG J, LUAN H, REN J, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for single and double segment lumbar disc herniation with sciatic scoliosis in adults: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2024;24(1): 41.
[28] YANG J, ZHANG K, FAN H, et al. Development and validation of deep learning algorithms for scoliosis screening using back images. Commun Biol. 2019;2:390.
[29] MADIRAJU A, MULCAHEY PJ, KNOTT PT, et al. Assessing clinical trunk change with surface topography: anterior scoliosis correction as a model to evaluate curve progression. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(12): 3533-3539.
[30] MINOTTI M, NEGRINI S, CINA A, et al. Deep learning prediction of curve severity from rasterstereographic back images in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2023. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-08052-1.
[31] ZHAO Y, QI L, DING C, et al. Characteristics of Sciatic Scoliotic List in Lumbar Disc Herniation. Global Spine J. 2024;14(3):894-901.
[32] WU W, CHEN Y, YU L, et al. Coronal and sagittal spinal alignment in lumbar disc herniation with scoliosis and trunk shift. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1): 264.
[33] 冯宇. 冯天有教授脊柱定点旋转复位法治疗腰椎间盘突出症学术思想研究[D]. 北京: 中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2012.
[34] 冯伟. 新医正骨疗法治疗难治型旋盆翘臀型腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J]. 空军航空医学,2020,36(4):307-309.
[35] 陈龙, 刘伟东, 张维顺, 等. 微创与开放TLIF治疗腰椎间盘突出伴功能性侧弯[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(18):1708-1711.
[36] 吕立江, 李景虎, 杨超, 等. 杠杆定位手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效及对Cobb角影响[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(1):86-90.
[37] ENDO K, SUZUKI H, TANAKA H, et al. Sagittal spinal alignment in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(3):435-438. |