| [1] 崔红新,程方荣,王键智. 有限元法及其在生物力学中的应用[J].中医正骨,2005,17(1):53-55.[2] Kemper A, Stitzel J, Duma S, et al. Biofidelity of the SID-IIs and a Modified SID-IIs Upper Extremity: Biomechanical Properties of the Human Humerus. Proceedings of the 19th Enhanced Safety of Vehicles Conference,Washington, DC; 05-0123.[3] Masami I, Kazuo M,Yang King H. Development of a Finite Element Model of the Human Shoulder to Investigate the Mechanical Responses and injuries in Side Impact.JSME Inter J. 2001;44(4):1072-1081.[4] 苏佳灿,张春才,王家林,等. 肱骨三维有限元分析及其生物力学意义[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(23):3200-3201.[5] 杨志勇,程黎明,涂熙,等.锁骨三维有限元模型的建立及其生物力学分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2008,29(11):1316-1318.[6] 丁峻宏,丁海.人体生物力学研究中的有限元仿真计算[J].高性能计算发展与应用.2010,31:31-35.[7] 张美超,钟世镇. 国内生物力学中有限元的应用研究进展[J].解剖科学进展,2003,9(1):53.[8] 关振群,石俊,李爱群,等. Mimics辅助快速建立颅上颌复合体的三维有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(43): 7998-8012.[9] 陈以慈.儿童解剖学研究简况[J].广东解剖学通报,1994, 16(1): 69-71.[10] 李莉,杨济匡.汽车与行人碰撞的动力学响应仿真分析[J].计算机仿真,2003,20(7):49-51.[11] 阮国模,苏佳灿,张春才,等.锁骨三维有限元模型的全程数字化构建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(26): 5121-5124.[12] 何叶松,杨华哲.逆向工程在重构髋关节骨CAD模型中的应用[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2011,28(1):2378-2381.[13] 刘飞,楼跃,唐凯,等.儿童肱骨远端有限元模型的建立及力学分析[J].热带医学杂志,2011,11(5):527-528.[14] 徐自胜,任伯绪.基于有限元的人体四肢骨折的生物力学研究进展[J].实用医学杂志, 2011,27(4):699-701.[15] 颜冰珊,尹望平,聂文忠,等.正常下尺桡关节三维有限元模型的建立及验证[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(17): 3135- 3137.[16] 李颖,费王华,樊黎霞,等.新鲜长管状骨的三维有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(11):991-993.[17] 李文杰,丁玉兰,简小刚. 汽车碰撞事故中乘员人体动力学分析[J].中国工程机械学报,2007,5(3):277-281.[18] 魏高峰. 人体骨肌系统的整体生物力学建模与仿真分析研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2010.[19] 杨杏梅. 汽车前碰撞中6岁儿童乘员约束系统的仿真研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学,2006.[20] 高敬党. 身材矮小乘员在正面碰撞过程中伤害的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2007.[21] 李飞跃. 儿童股骨上段有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[D].湖南衡阳:南华大学,2007.[22] Ruan J. Finite element modeling of the human head and the biomechanical basis of head injury criterion (HIC).J Human University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2002; 29(6):24-43.[23] 张建国,王芳,薛强.后碰撞中人体颈部动力学响应的有限元分析[J].工程力学,2010,27(4):208-211.[24] 裴永生,阮世捷,李海岩,等.头部撞击损伤的有限元模型建立[J].燕山大学学报,2009,33(5):405-410.[25] 孙乃祥,王岩. 创伤的AIS评分与损伤程度评定的对比分析[J].中国法医学杂志,2002,17(3):139-140.[26] 陈秉智.计算骨力学若干问题研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学, 2002.[27] 成思源. 有限元的方法论[J].重庆大学学报,2001,7(4):61.[28] 张建国,王芳,薛强.后碰撞中人体颈部动力学响应的有限元分析[J].工程力学,2010,27(4):208-211.[29] 朱振安等.骨的结构、成份和力学特性[J].医用生物力学,1999,9 (3):177-183.[30] 汤斌,王晓旭. 应用Mimics软件重建儿童股骨颈骨折内固定三维有限元模型的研究[J]. 现代医药卫生,2009,25(23):3621-3622. |
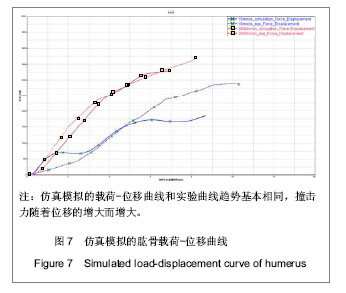
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)