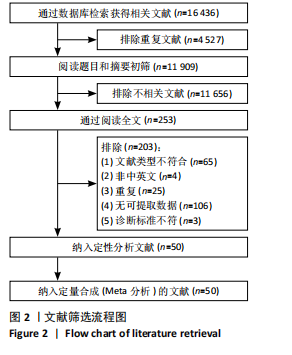
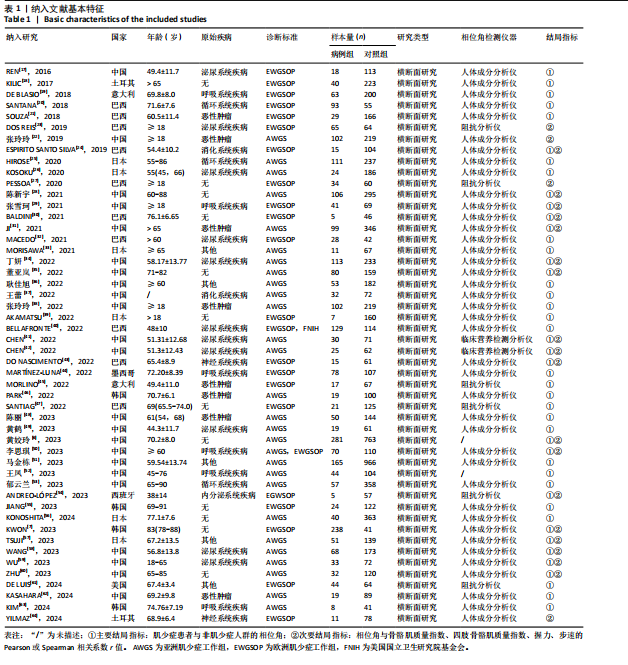
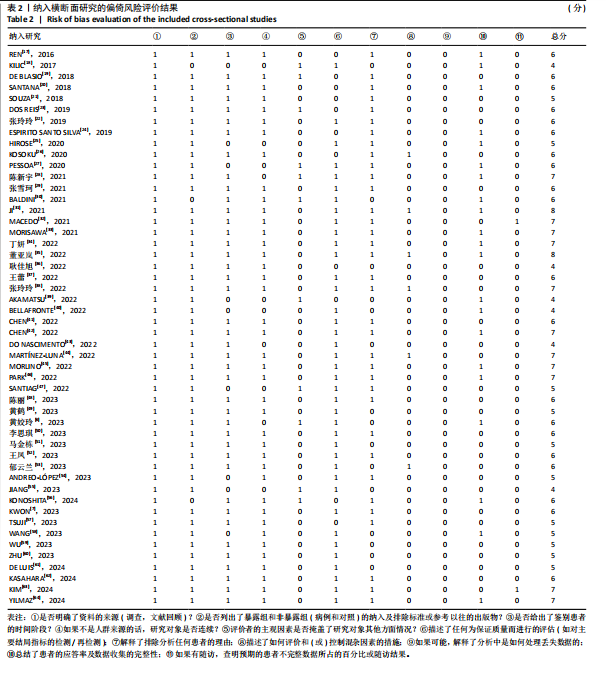
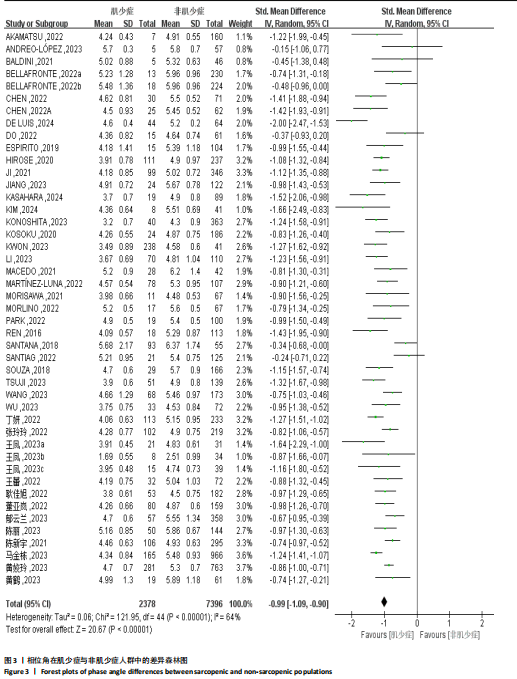
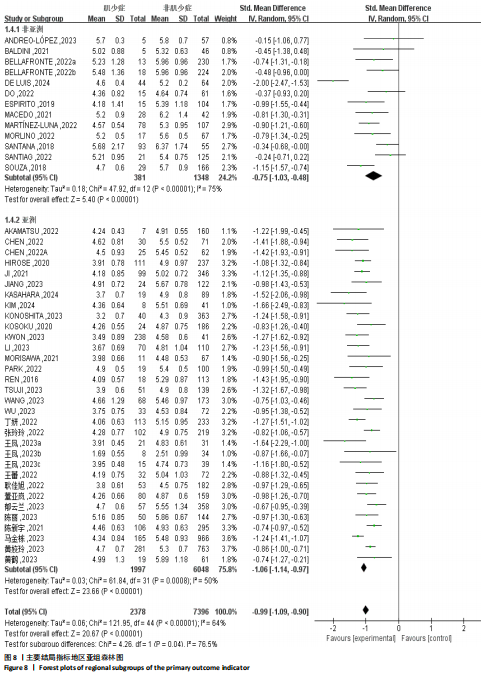
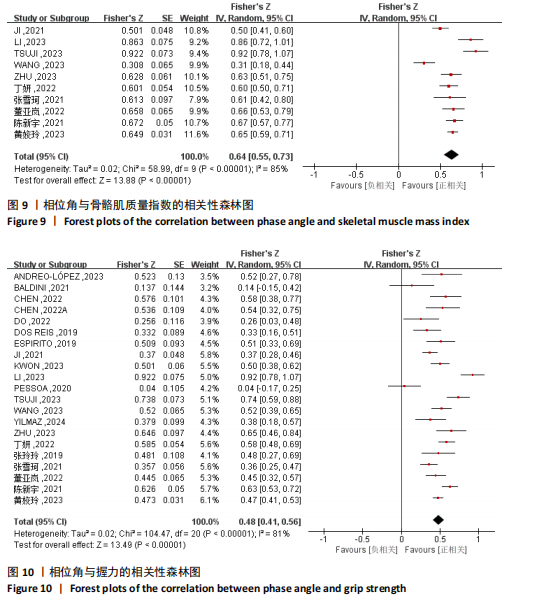
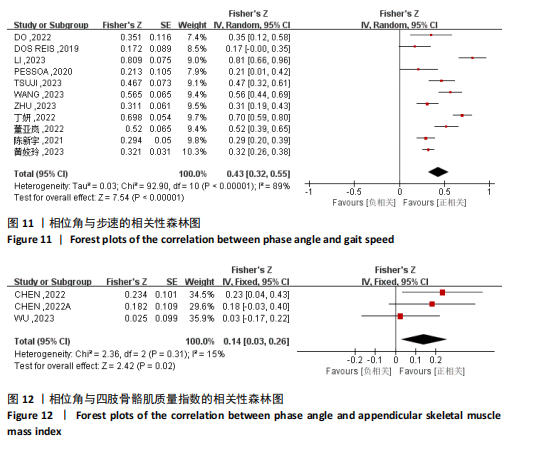
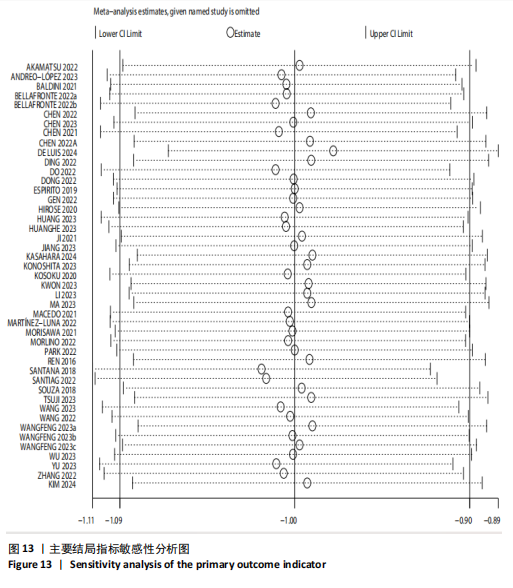
[1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646.
[2] YUAN S, LARSSON SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: Prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. 2023;144:155533.
[3] BASILE C, DELLA-MORTE D, CACCIATORE F, et al. Phase angle as bioelectrical marker to identify elderly patients at risk of sarcopenia. Exp Gerontol. 2014;58:43-46.
[4] GARLINI LM, ALVES FD, CERETTA LB, et al. Phase angle and mortality: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(4):495-508.
[5] ROSAS-CARRASCO O, RUIZ-VALENZUELA RE, LÓPEZ-TEROS MT. Phase Angle Cut-Off Points and Their Association With Sarcopenia and Frailty in Adults of 50-64 Years Old and Older Adults in Mexico City. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:617126.
[6] 黄姣玲,华楠,李玉华,等.相位角在社区老年人肌少症筛查中的应用[J].护理研究,2023, 37(10):1724-1728.
[7] KWON YE, LEE JS, KIM JY, et al. Impact of sarcopenia and phase angle on mortality of the very elderly. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(1):279-287.
[8] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1): 16-31.
[9] 杨光.248例原发性肝癌患者生物电阻抗相位角数值与预后的相关性分析[D].长春:吉林大学,2020.
[10] CHEN LK, LIU LK, WOO J, et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(2):95-101.
[11] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(3):300-307.e2.
[12] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAEYENS JP, BAUER JM, et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412-423.
[13] STUDENSKI SA, PETERS KW, ALLEY DE, et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014;69(5):547-558.
[14] FIELDING RA, VELLAS B, EVANS WJ, et al. Sarcopenia: an undiagnosed condition in older adults. Current consensus definition: prevalence, etiology, and consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2011; 12(4):249-256.
[15] 曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等.Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(4):297-299.
[16] TSILIGIANNI I, KOCKS J, TZANAKIS N, et al. Factors that influence disease-specific quality of life or health status in patients with COPD: a review and meta-analysis of Pearson correlations. Prim Care Respir J. 2011;20(3):257-268.
[17] REN H, GONG D, JIA F, et al. Sarcopenia in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: incidence rate, risk factors and its effect on survival risk. Ren Fail. 2016;38(3):364-371.
[18] KILIC MK, KIZILARSLANOGLU MC, ARIK G, et al. Association of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis-Derived Phase Angle and Sarcopenia in Older Adults. Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(1):103-109.
[19] DE BLASIO F, DI GREGORIO A, DE BLASIO F, et al. Malnutrition and sarcopenia assessment in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease according to international diagnostic criteria, and evaluation of raw BIA variables. Respir Med. 2018;134:1-5.
[20] SANTANA NM, PINHO CPS, DA SILVA CP, et al. Phase Angle as a Sarcopenia Marker in Hospitalized Elderly Patients. Nutr Clin Pract. 2018;33(2):232-237.
[21] SOUZA BU, SOUZA NCS, MARTUCCI RB, et al. Factors Associated with Sarcopenia in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Nutr Cancer. 2018;70(2):176-183.
[22] 张玲玲.恶性肿瘤患者人体成分和肌肉减少症的现况研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学, 2019.
[23] DOS REIS AS, SANTOS HO, LIMIRIO LS, et al. Phase Angle Is Associated With Handgrip Strength but Not With Sarcopenia in Kidney Transplantation Patients. J Ren Nutr. 2019;29(3):196-204.
[24] ESPIRITO SANTO SILVA DD, WAITZBERG DL, PASSOS DE JESUS R, et al. Phase angle as a marker for sarcopenia in cirrhosis. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019; 32:56-60.
[25] HIROSE S, NAKAJIMA T, NOZAWA N, et al. Phase Angle as an Indicator of Sarcopenia, Malnutrition, and Cachexia in Inpatients with Cardiovascular Diseases. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):2554.
[26] KOSOKU A, UCHIDA J, NISHIDE S, et al. Association of sarcopenia with phase angle and body mass index in kidney transplant recipients. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):266.
[27] PESSOA DF, DE BRANCO FMS, DOS REIS AS, et al. Association of phase angle with sarcopenia and its components in physically active older women. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(8):1469-1475.
[28] 陈新宇,周军良,李婷婷,等.相位角与老年肌少症的关系研究[J].肠外与肠内营养,2021, 28(5):275-280.
[29] 张雪珂.相位角与AECOPD合并营养不良和肌肉减少症的现况研究及影响因素分析[D].郑州:河南大学,2021.
[30] BALDINI JMF, MUÑOZ FERNÁNDEZ SS, RIBEIRO SML. Association between raw bioelectrical impedance parameters and muscle mass and strength measured by DXA and dynamometry in older adults: a pilot study. Nutrire.2021;46(5). doi: 10.1186/s41110-021-00134-8.
[31] JI W, LIU X, ZHENG K, et al. Correlation of phase angle with sarcopenia and its diagnostic value in elderly men with cancer. Nutrition. 2021;84: 111110.
[32] MACEDO C, AMARAL TF, RODRIGUES J, et al. Malnutrition and Sarcopenia Combined Increases the Risk for Mortality in Older Adults on Hemodialysis. Front Nutr. 2021;8:721941.
[33] MORISAWA T, KUNIEDA Y, KOYAMA S, et al. The Relationship between Sarcopenia and Respiratory Muscle Weakness in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13257.
[34] 丁妍,常立阳,张红梅.相角与维持性血液透析患者肌少症的关系及其预测价值分析[J].中国血液净化,2022,21(3):172-176.
[35] 董亚岚.相位角测定在老年肌少症诊断中的价值研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2022.
[36] 耿佳旭,魏雅楠,王晶桐.相位角与住院老年慢病患者肌少症的相关性分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):499-504.
[37] 王蕾,蔡婷婷,胡凤爱,等.梗阻性黄疸合并肌肉减少症的相关影响因素[J].滨州医学院学报,2022,45(2):130-133.
[38] 张玲玲,郑峥,何丽,等.恶性肿瘤住院患者肌肉减少症的调查及影响因素分析[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志,2022,9(5):645-651.
[39] AKAMATSU Y, KUSAKABE T, ARAI H, et al. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis is a useful indicator of muscle quality. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):180-189.
[40] BELLAFRONTE NT, GOVÊIA TR, CHIARELLO PG. Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease: prevalence by different definitions and relationship with adiposity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2022;47(9): 915-925.
[41] CHEN Y, WU J, RAN L, et al. The combination of phase angle and age has a good diagnostic value for sarcopenia in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Front Nutr. 2022;9: 1036796.
[42] CHEN Y, WU J, RAN L, et al. The phase angle is associated with upper arm muscle circumference but not with sarcopenia in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. medRxiv. 2022:2022. 07.10.22277470.
[43] DO NASCIMENTO TG, PAES-SILVA RP, DA LUZ MCL, et al. Phase angle, muscle mass, and functionality in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci. 2022;43(7):4203-4209.
[44] MARTÍNEZ-LUNA N, OREA-TEJEDA A, GONZÁLEZ-ISLAS D, et al. Association between body composition, sarcopenia and pulmonary function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Pulm Med. 2022;22(1):106.
[45] MORLINO D, MARRA M, CIOFFI I, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia in Women with Breast Cancer. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1839.
[46] PARK HY, PARK YH, LEE JY, et al. Bioimpedance phase angle and sarcopenia in older patients with prostate cancer. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2022; 22(8):623-627.
[47] SANTIAGO LB, RORIZ AKC, DE OLIVEIRA CC, et al. Phase angle as a screening method for sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. Revista de Nutrição. 2022;35:1-8.
[48] 陈丽.结直肠癌合并肌肉减少症患者的营养状况评估及危险因素研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学,2023.
[49] 黄鹤,邹志卓,李琴,等.肾移植受者小腿围与肌肉减少症的关系研究[J].中国全科医学,2023, 26(27):3403-3410.
[50] 李思琪.相位角与慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者合并肌肉减少症及衰弱的相关性研究[D].郑州:河南大学,2023.
[51] 马金栋,王蕾,蔡婷婷,等.腹部外科住院患者肌肉减少症状况及其影响因素分析[J].中华普通外科学文献(电子版),2023,17(1):69-74.
[52] 王凤.肌少症对COPD、哮喘及ACO患者肺功能、血气分析指标的影响[D].长春:吉林大学,2023.
[53] 郁云兰,吕万勇,易海维.老年高血压住院患者肌肉减少症调查及影响因素分析[J].肿瘤代谢与营养电子杂志,2023,10(3):389-394.
[54] ANDREO-LÓPEZ MC, ZARCO-MARTÍN MT, CONTRERAS-BOLÍVAR V, et al. Prevalence of Sarcopenia and Dynapenia and Related Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2023;15(23):4914.
[55] JIANG FL, TANG S, EOM SH, et al. Distribution of Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis and Phase Angle in Korean Elderly and Sarcopenia. Sensors (Basel). 2023;23(16):7090.
[56] KONOSHITA N, ONISHI H, MIZUKAMI Y, et al. Can bone mass measured via bioelectrical impedance analysis be used to diagnose sarcopenia? J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2024;74(2):154-161.
[57] TSUJI H, TETSUNAGA T, MISAWA H, et al. Association of phase angle with sarcopenia in chronic musculoskeletal pain patients: a retrospective study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):87.
[58] WANG Y, HU Y, ZHANG M, et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle predicts sarcopenia in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Nutr Clin Pract. 2023;38(4):881-888.
[59] WU J, GUAN J, LIN S, et al. Prediction of sarcopenia among peritoneal dialysis patients using a combination of irisin and phase angle. Nephrol Ther. 2023;19(1):66-75.
[60] ZHU X, DONG X, WANG L, et al. Screening efficacy of PhA and MNA-SF in different stages of sarcopenia in the older adults in community. BMC Geriatr. 2023;23(1):13.
[61] DE LUIS D, PRIMO D, IZAOLA O, et al. Role of irisin and myostatin on sarcopenia in malnourished patients diagnosed with GLIM criteria. Nutrition. 2024;120:112348.
[62] KASAHARA R, FUJITA T, JINBO R, et al. Is Phase Angle Useful in Screening for Sarcopenia in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies? Nutr Cancer. 2024;76(1):121-127.
[63] KIM SH, HONG CH, SHIN MJ, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of Sarcopenia in older adult patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional and follow-up study. BMC Pulm Med. 2024;24(1):219.
[64] YILMAZ M, ATIK-ALTINOK Y, SEYIDOGLU YÜKSEL D, et al. Evaluation of sarcopenia and phase angle in elderly patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Neurosci. 2024:1-8. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2024.2310180.
[65] DI VINCENZO O, MARRA M, SCALFI L. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle in sport: a systematic review. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2019;16(1):49.
[66] SERGI G, DE RUI M, STUBBS B, et al. Measurement of lean body mass using bioelectrical impedance analysis: a consideration of the pros and cons. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017;29(4):591-597.
[67] PATRIZIO E, CALVANI R, MARZETTI E, et al. Physical Functional Assessment in Older Adults. J Frailty Aging. 2021;10(2):141-149.
[68] NORMAN K, STOBÄUS N, PIRLICH M, et al. Bioelectrical phase angle and impedance vector analysis--clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin Nutr. 2012;31(6): 854-861.
[69] SEPÚLVEDA-LOYOLA W, OSADNIK C, PHU S, et al. Diagnosis, prevalence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia in COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(5):1164-1176.
[70] 刘莹,谭寅凤,于苗,等.老年恶性肿瘤肌少症发生率及影响因素[J].中国老年学杂志, 2024,44(2):281-284.
[71] 王晓琳,宋世明.恶性肿瘤患者相位角与肌肉质量的相关性研究[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2023,15(6):27-33.
[72] VOULGARIDOU G, TYROVOLAS S, DETOPOULOU P, et al. Diagnostic Criteria and Measurement Techniques of Sarcopenia: A Critical Evaluation of the Up-to-Date Evidence. Nutrients. 2024; 16(3):436.
[73] CHAE M, PARK H, PARK K. Estimation of Dietary Amino Acid Intake and Independent Correlates of Skeletal Muscle Mass Index among Korean Adults. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1043.
[74] CESARI M, KRITCHEVSKY SB, NEWMAN AB, et al. Added value of physical performance measures in predicting adverse health-related events: results from the Health, Aging And Body Composition Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009;57(2):251-259. |