中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 599-607.doi: 10.12307/2025.118
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
下肢关节置换前糖皮质激素静脉注射对疗效及安全性影响的Meta分析
王建磊1 ,何培亮2 ,孙永建1,3
- 1广东医科大学,广东省湛江市 524000;2暨南大学附属广州红十字会医院创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510000;3南方医科大学第三附属医院儿童骨科,广东省广州市 510000
A meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of intravenous glucocorticoids before lower limb joint arthroplasty
Wang Jianlei1, He Peiliang2, Sun Yongjian1, 3
- 1Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital Affiliated to Jinan University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Pediatric Orthopedics, Third Affiliated Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
糖皮质激素:能有效减轻术后急性疼痛,在术后第1天行走时疼痛评分明显降低,总住院时间缩短。糖皮质激素能抑制炎症反应,降低炎症标志物白细胞介素6和C-反应蛋白的水平,改善术后早期恢复。糖皮质激素可减少阿片类药物的使用量,降低与阿片类药物相关的不良反应如恶心和呕吐的发生。糖皮质激素使用并不增加术后感染风险,而且可以降低C-反应蛋白水平。该研究结果显示术前静脉注射糖皮质激素在髋膝关节置换术中具有一定的临床效果,且安全可行。
髋膝关节置换:是一种创伤较大的手术,主要用于治疗严重的髋膝关节疾病。术后常伴有手术应激反应,其中炎症因子起到重要作用,可能会影响术后恢复。炎症因子的增加可能导致疼痛、疲劳、头晕、恶心和呕吐等不适感,增加住院治疗的需要。为了解决这些问题,糖皮质激素被用作多模式镇痛方案的辅助手段。研究发现,术前静脉注射类固醇激素作为髋膝关节置换的辅助疗法有助于减少术后并发症并提高患者的术后恢复水平。
摘要
目的:术前静脉用糖皮质激素对下肢关节置换患者的临床疗效及安全性仍存在争议。因此进行了一项基于随机对照试验的荟萃分析,以评估术前静脉注射糖皮质激素对临床下肢关节置换治疗的有效性和安全性。
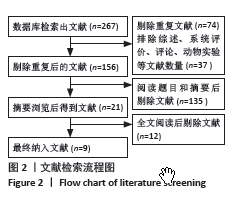
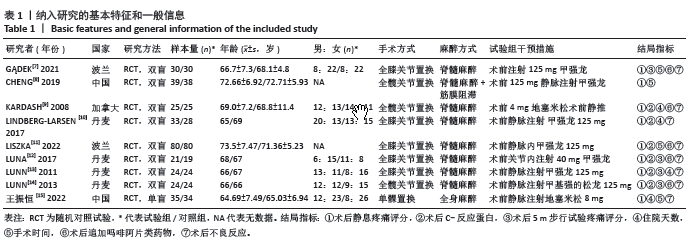
方法:系统检索了中外数据库截至2023年6月关于术前静脉注射糖皮质激素对下肢关节置换疗效及安全性影响的随机对照试验,包括PubMed、Embase、Web of Science、Cochrane图书馆、中国万方数据库和中国知网。试验组术前静脉注射糖皮质激素以控制疼痛;对照组使用安慰剂或静脉生理盐水;观察指标包括术后静息疼痛评分、术后C-反应蛋白、术后5 m步行试验疼痛评分、住院天数、手术时间、术后追加吗啡阿片类药物量、术后发生恶心呕吐反应及术后假体周围感染并发症。
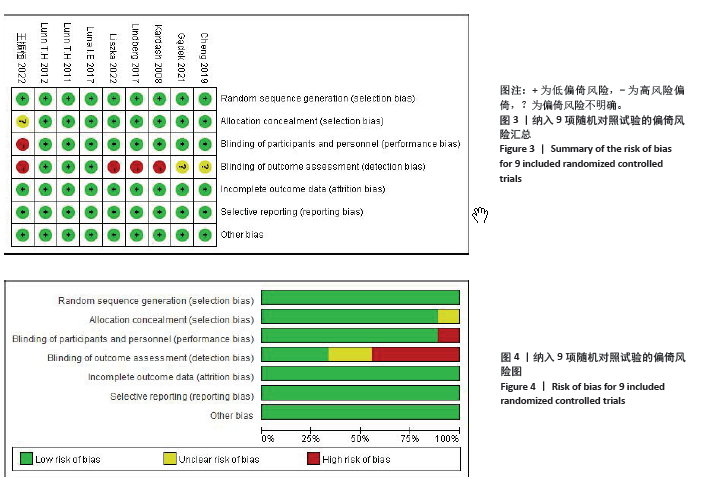
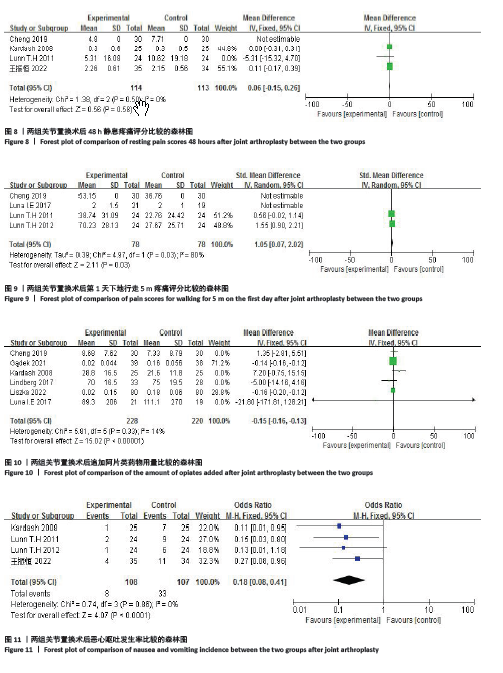
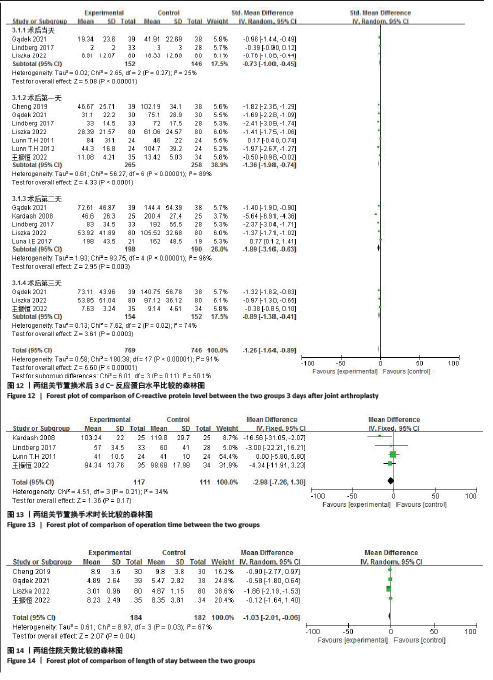
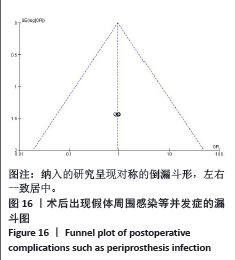
结果:①共纳入9项随机对照试验,包括613例患者(糖皮质激素311例,对照组302例);②与对照组相比,术前静脉注射糖皮质激素可显著降低下肢关节置换患者术后6,12 h的静息疼痛评分及术后第1天下地活动5 m的疼痛评分;此外,糖皮质激素组在术后追加吗啡阿片类药物需要量减少、术后恶心呕吐发生率降低,术后3 d内炎症C-反应蛋白水平较对照组降低,住院天数缩短,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③但是两组患者关节置换术后感染发生率、手术时长及24,48 h的疼痛评分则无明显差异。
结论:作为一种有效的围术期多模式镇痛方案,术前静脉注射糖皮质激素是改善下肢关节置换患者术后超急性疼痛和关节活动有效和安全的方法;但需要更多的研究来确定糖皮质激素的最佳剂量和类型,以最大限度地控制疼痛。
中图分类号: