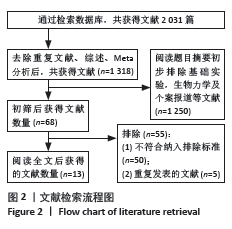
2.1 文献检索结果 通过上述检索方案,共获得2 031篇文献,中国知网数据库369篇,万方数据库284篇,维普数据库188篇,PubMed数据库297篇,Cochrane Library数据库46篇,Web of Science数据库317篇,Embase数据库530篇,排除重复文献、综述和Meta分析 713篇,通过阅读题目和摘要初筛得到68篇,最后全文阅读剔除不符合标准的文献,最终获得13篇符合纳入排除标准的文献[7,10-21],其中11篇回顾性队列研究[7,10-17,19,21],2篇随机对照试验[18,20],共1 136例患者,其中ROI-C组569例,融合器联合钉板组567例,见图2。
 2.2 纳入研究临床特征
2.2 纳入研究临床特征 纳入研究的基线特征见表1。
2.3 文献质量评价结果 采用Cochrane偏倚风险工具对随机对照试验进行质量评价,2篇文献均未见高风险[18,20],
见图3;用纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表对纳入的11篇回顾性队列研究进行质量评价,8篇文献为8分[7,10-11,13-17],
3篇文献为7分[12,19-20],评分结果见表2。
 2.4 Meta分析结果
2.4 Meta分析结果
2.4.1 各组手术时间差异 共12篇文献对比了手术时间[7,10-17,19-21],有5篇文献按节段分亚组比较了手术时间[13-15,17,19],其中4篇文献涉及2个手术时间组[13-15,19],1篇文献涉及3个手术时间组[17]。亚组分析的数据在http://statstodo.com/CombineMeansSDs.php网站上将每个亚组的均值和标准差进行合并,使用合并后的均值和标准差进行数据分析[22]。
HOFSTETTER等[12]的数据采用的是mean±SEM,在RevMan软件中将数据转换为mean±SD后,进行数据分析。采用固定效应模型(P=0.15,I2=30%)。结果显示:两组手术时间差异有显著性意义(MD=-15.52,95%CI:-18.62至-12.42,P < 0.000 01),见图4。
2.4.2 各组术中出血量差异 共12篇文献对比了术中出血量[7,10-17,19-21],有5篇文献按节段分亚组比较了手术出血量[13-15,17,19],其中4篇文献涉及2个术中出血量组[13-15,19],1篇文献涉及3个术中出血量组[17]。同样在http://statstodo.com/CombineMeansSDs.php网站上将亚组分析的均值和标准差进行合并,在RevMan软件中将HOFSTETTER等[12]的数据转换为Mean±SD后,再进行数据合并。各研究之间存在异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=76%),采用随机效应模型。结果显示:两组术中出血量差异有显著性意义(MD=-24.53,95%CI:-32.46至-16.61,P < 0.000 01),见图5。
2.4.3 各组术前与术后JOA评分差异 共8篇文献对比了术前JOA评分[7,10-11,13,15,17,19-20],采用固定效应模型进行分析(P=0.40,I2=4%),结果显示:两组术前JOA评分无显著性差异(MD=-0.01,95%CI:-0.22-0.21,P=0.96)。7篇文献对比两者术后1个月JOA评分[7,10-11,13,15,19-20],10篇文献对比两者末次随访JOA评分[7,10-11,13-17,19,20],各统计组之间具有统计学异质性(P=0.003,I2=63%),采用随机效应模型。结果显示,两组术后1个月JOA评分(MD=-0.05,95%CI:-0.35-0.24,P=0.72)与末次JOA评分(MD=0.17,95%CI:-0.11-0.45,P=0.23)均无显著性差异,见图6。
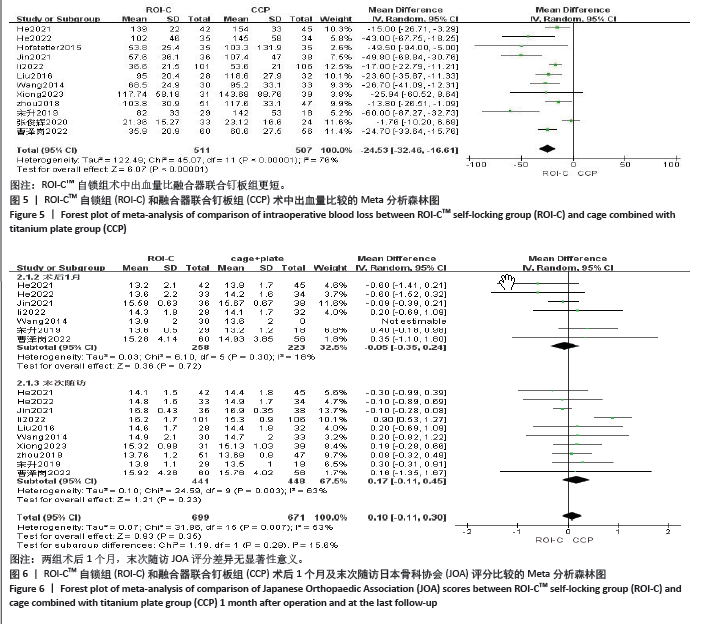
2.4.4 各组术前与术后颈椎功能障碍指数差异 共8篇文献对比两组术前颈椎功能障碍指数[7,10,11,13-15,17,19],
各研究之间存在异质性(P=0.14,I2=36%),采用固定效应模型,合并结果显示:两组术前颈椎功能障碍指数无显著性差异(MD=0.27,95%CI:-0.44-0.98,P=0.46)。共有5篇文献对比了两组术后1个月颈椎功能障碍指数[7,10-11,13,15],8篇文献对比了两组末次随访颈椎功能障碍指数[7,10-11,13-15,17,19],采用随机效应模型(P=0.06,I2=41%),结果显示:两组术后1个月颈椎功能障碍指数评分 (MD=0.23,95%CI:-0.72-1.17,P=0.64)与末次随访颈椎功能障碍指数评分指数评分 (MD=0.16,95%CI:-0.57-0.89,P=0.66,均无显著性差异,见图7。
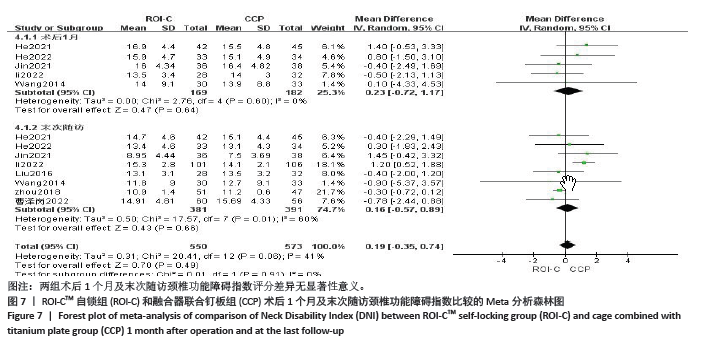
2.4.5 各组术前与术后C2-C7 Cobb角差异 术前有7篇文献对比了C2-C7 Cobb角[10,11,13-16,19],采用固定效应模型(P=1.00,I2=0%),合并结果显示两组术前C2-C7 Cobb角无显著性差异 (MD=0.60,95%CI:-0.19-1.39,P=0.13)。5篇文献对比了两组术后1个月C2-C7 Cobb角[10-11,13-15],7篇文献对比了两组末次随访C2-C7 Cobb角[10-11,13-16,19],采用固定效应模型(P=0.99,I2=0%)。结果显示:两组术后C2-C7 Cobb 角(MD =-0.00,95%CI:
-0.76-0.76,P=1.00)末次随访C2-C7 Cobb角(MD =-0.25,95%CI:-0.85-0.35,P=0.42)均无显著性差异,见图8。
2.4.6 各组末次随访融合率差异 共12篇文献比较了两组末次随访融合率[10-21],采用固定效应模型(P=0.99,I2=0%)。结果显示:两组末次随访融合率无显著性差异(RR=1.01,95%CI:0.99-1.03,P=0.34),见图9。
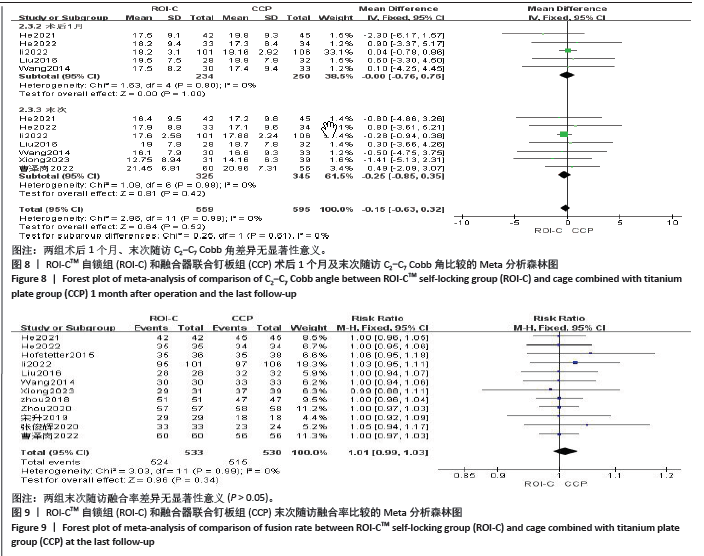
2.4.7 各组邻近节段退变发生率差异 共9篇文献对比了两组邻近节段退变情况[7,12-19],采用固定效应模型(P=0.49,I2=0%)。结果显示:两组邻近节段退变发生率差异有显著性意义(RR=0.40,95%CI:0.27-0.60,P < 0.000 01),见图10。
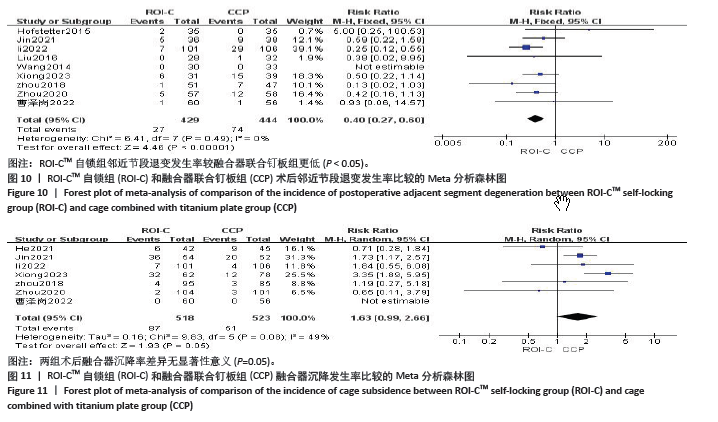
2.4.8 各组术后融合器沉降率差异 共7篇文献对比了两组术后融合器沉降情况[7,10,13,16-19],异质性较高(P=0.08,I2=49%),采用随机效应模型分析。结果显示:两组术后融合器沉降率无显著性差异(RR=1.63,95%CI:0.99-2.66,P=0.05),见图11。
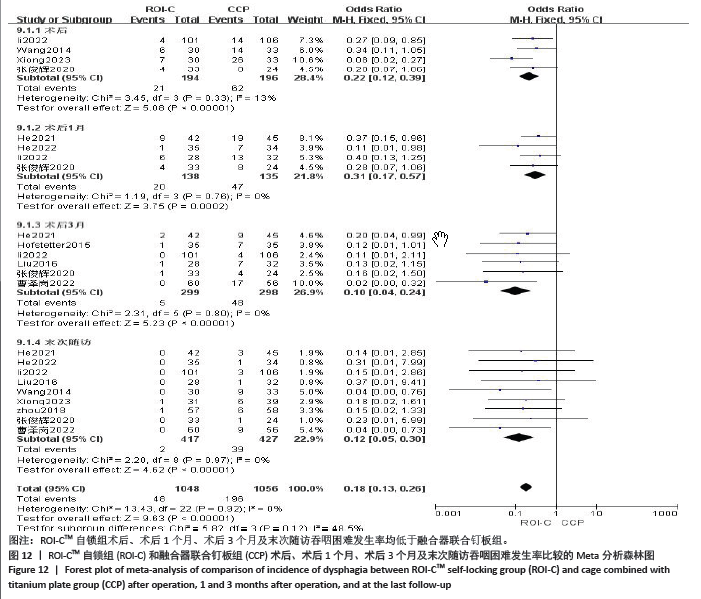
2.4.9 各组术后吞咽困难发生情况 共4篇文献对比了两组术后吞咽困难发生情况[13,15-16,21],4篇文献对比了两组术后1个月吞咽困难发生情况[10-11,13,21],6篇文献对比了两组术后3个月吞咽困难发生情况[10,12-14,19,21],9篇文献对比了两组术后末次随访吞咽困难发生情况[10,11,13-17,19,21],采用固定效应模型进行分析(P=0.92,I2=0%)。结果显示:两组术后(RR=0.22,95%CI:0.12-0.39,P < 0.000 01)、术后1个月(RR=0.31,95%CI:0.17-0.57,P =0.000 2)、3个月(RR =0.10,95%CI:0.04-0.24,P < 0.000 01)、末次随访(RR=0.12,95%CI:0.05-0.30,P < 0.000 01)吞咽困难发生率差异均有显著性意义,总的吞咽困难发生率也有显著性意义(OR=0.18,95%CI:0.13-0.26,P < 0.000 01),见图12。
2.5 亚组分析结果
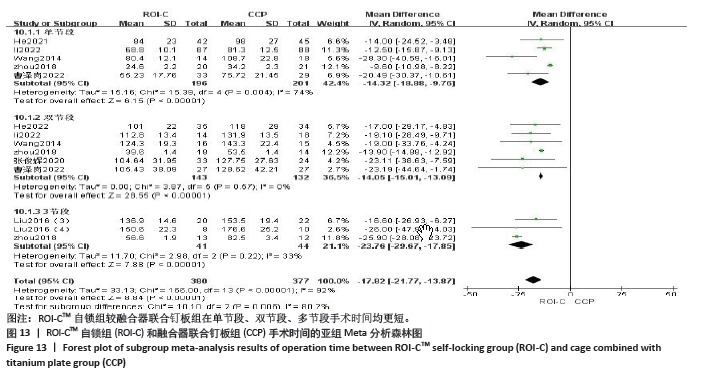
2.5.1 手术时间 按手术节段将手术时间分为单节段、双节段和多节段3个亚组进行分析。共有5篇文献记录了单节段的手术时间[10,13,15,17,19],有6篇文献记录了双节段的手术时间[10,13,15,17,19,21],2篇文献记录了多节段的手术时间[14,17],其中LIU等[14]分别记录了3节段和4节段的手术时间,一并纳入多节段组。异质性较高(P < 0.000 01,I2=92%),采用随机效应模型。结果显示:两组在单节段(MD=-14.32,95%CI:-18.88至-9.76,P < 0.000 01)、双节段(MD=-14.05,95%CI:-15.01至-13.09,P < 0.000 01)、多节段(MD=-23.76,95%CI:-29.67至-17.85,P < 0.000 01) 手术时间差异均有显著性意义,所有数据合并后两组手术时间差异也具有显著性意义(MD=-17.82,95%CI:-21.77至-13.86,P < 0.000 01)。3个亚组之间差异有显著性意义(P=0.006,I2=80.2%),见图13。
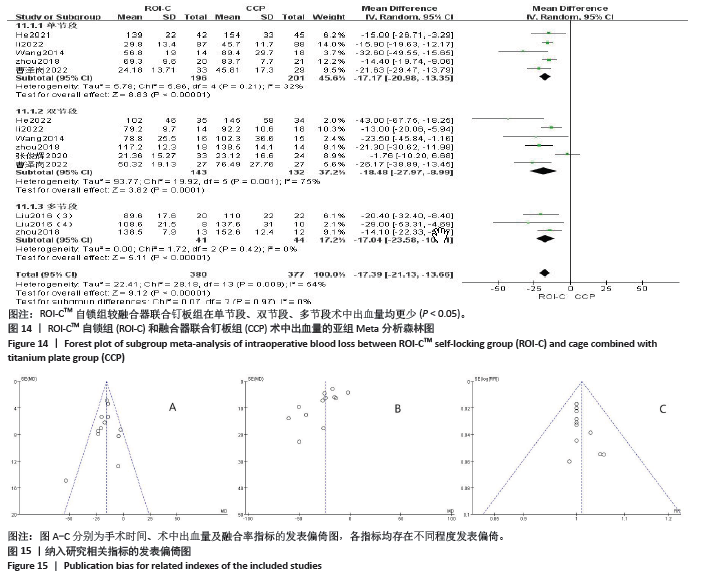
2.5.2 术中出血量 按手术节段将其分为单节段、双节段和多节段进行亚组分析。共有5篇文献记录了单节段的术中出血量[10,13,15,17,19],有6篇文献记录了双节段的术中出血量[10,13,15,17,19,21],2篇文献记录了多节段的术中出血量[14,17],同样将LIU等[14]的数据一并纳入多节段组,采用随机效应模型(P=0.09,I2=54%)。结果显示:两组术中出血量在单节段(MD=-17.17,95%CI:-20.98至-13.35,P < 0.000 01)、双节段(MD=-18.48,95%CI:-27.97至-8.99,P=0.000 1)、多节段(MD=-17.04,95%CI:-23.58至-10.51,P < 0.000 01)均有显著性意义,所有数据合并后两组术中出血量差异也具有显著性意义(MD=-17.39,95%CI:-21.13至-13.66,P < 0.000 01)。3个亚组之间不存在统计学上的差异(P=0.97,I2=0%),见图14。
2.6 敏感性分析结果 将ZHOU等[18]和宋升等[20]的随机对照研究剔除后重新合并分析,发现在手术时间、术中出血量、融合率和术后邻近椎体退变异质性较前无明显改变,同时两组比较结果与之前一致,提示Meta分析结果可靠。
对术后JOA评分和颈椎功能障碍指数进行敏感性分析,发现LI等[13]的研究可能为异质性来源,剔除该项研究后重新进行合并分析发现异质性明显减少(I2=0%),采用固定效应模型分析,结果表明两组患者术后JOA评分和颈椎功能障碍指数仍无显著性差异(P > 0.05),提示Meta分析结果相对可靠。
对术中出血量和手术时间进行逐一剔除研究后重新合并分析,发现异质性较前无明显变化,未找到明显异质性来源。考虑到术中出血量和手术时间与术者经验、习惯和熟练程度及手术节段等高度相关,从而导致研究间异质性较大。
对于术后融合器沉降进行逐一剔除研究后重新合并分析,发现Meta分析结果随之发生改变,提示Meta分析结果稳定性较差。考虑术后融合器沉降与术者的操作及骨密度等多种因素相关,可能是导致结果稳定性较差的原因,因该研究纳入的文献较少,关于两者术后融合器沉降率的高低,未来仍需进一步的研究。
 2.7 发表偏倚分析
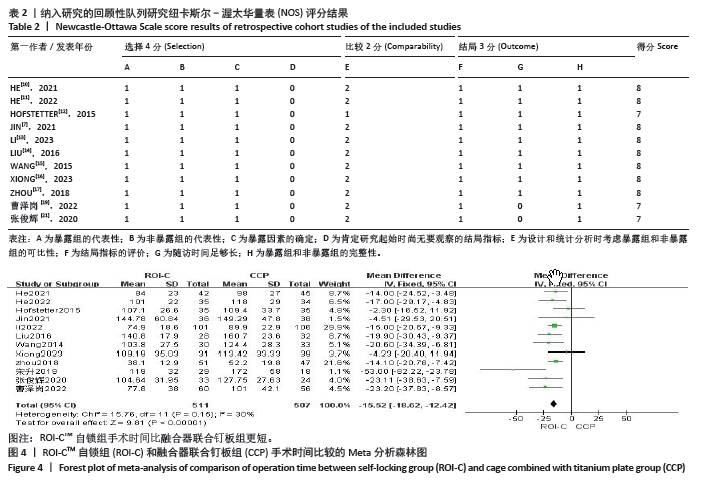
2.7 发表偏倚分析 研究中纳入的手术时间、术中出血量及融合率的文献均大于10篇,一般认为10篇文献以上可做漏斗图分析,故对以上指标进行发表偏倚分析,结果显示,各指标均存在不同程度发表偏倚,见图15。