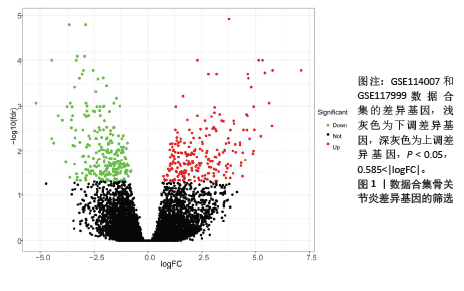
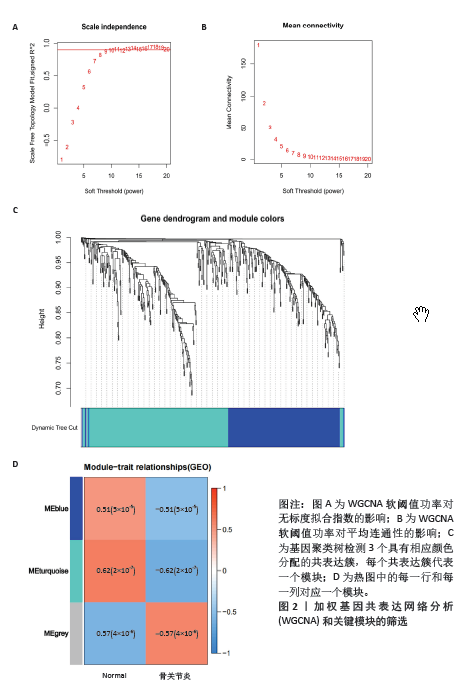
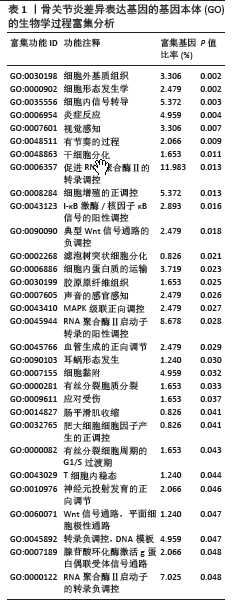
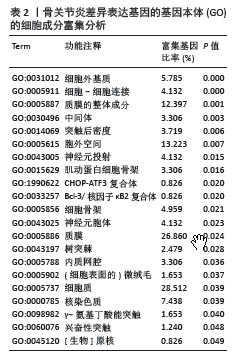
[1] XIONG Y, MI BB, LIU MF, et al. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2246-2256.
[2] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072.
[3] MCKENZIE S, TORKINGTON A. Osteoarthritis - management options in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2010;39(9):622-625.
[4] VINCENT TL. Targeting mechanotransduction pathways in osteoarthritis: a focus on the pericellular matrix. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(3): 449-454.
[5] SHEN S, WU Y, CHEN J, et al. CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):826-836.
[6] SCHULZE-TANZIL G. Intraarticular Ligament Degeneration Is Interrelated with Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019;8(9):990.
[7] MEDVEDEVA EV, GREBENIK EA, GORNOSTAEVA SN, et al. Repair of Damaged Articular Cartilage: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(8):2366.
[8] BHOSALE AM, RICHARDSON JB. Articular cartilage: structure, injuries and review of management. Br Med Bull. 2008;87: 77-95.
[9] MOBASHERI A, RAYMAN MP, GUALILLO O, et al. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(5): 302-311.
[10] JEON OH, KIM C, LABERGE RM, et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775-781.
[11] GAO X, JIANG S, DU Z, et al. KLF2 Protects against Osteoarthritis by Repressing Oxidative Response through Activation of Nrf2/ARE Signaling In Vitro and In Vivo. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019: 8564681.
[12] LU J, BI Y, ZHU Y, et al. CD3D, GZMK, and KLRB1 Are Potential Markers for Early Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Especially in Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody-Negative Patients. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:726529.
[13] WANG Z, CAO L, ZHOU S, et al. Construction and Validation of a Novel Pyroptosis-Related Four-lncRNA Prognostic Signature Related to Gastric Cancer and Immune Infiltration. Front Immunol. 2022;13:854785.
[14] LI N, LI Y, HU J, et al. A Link Between Mitochondrial Dysfunction and the Immune Microenvironment of Salivary Glands in Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:845209.
[15] ZHAO Z, HE S, YU X, et al. Analysis and Experimental Validation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Innate Immunity Gene CYFIP2 and Pan-Cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 954848.
[16] TAN Y, LU L, LIANG X, et al. Identification of a pyroptosis-related lncRNA risk model for predicting prognosis and immune response in colon adenocarcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20(1):118.
[17] CHEN M, ZHANG J, LIN X, et al. A pyroptosis-related prognosis model to predict survival in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2022;15(4):168-182.
[18] LAFEBER FP, VAN SPIL WE. Osteoarthritis year 2013 in review: biomarkers; reflecting before moving forward, one step at a time. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(10): 1452-1464.
[19] FISCH KM, GAMINI R, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, et al. Identification of transcription factors responsible for dysregulated networks in human osteoarthritis cartilage by global gene expression analysis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018; 26(11):1531-1538.
[20] AŞIK MD, GÜRSOY S, AKKAYA M, et al. Microarray analysis of cartilage: comparison between damaged and non-weight-bearing healthy cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(5):456-464.
[21] WANG J, FAN Q, YU T, et al. Identifying the Hub Genes and Immune Cell Infiltration in Synovial Tissue between Osteoarthritic and Rheumatoid Arthritic Patients by Bioinformatic Approach. Curr Pharm Des. 2022; 28(6):497-509.
[22] CHEN Y, LIAO R, YAO Y, et al. Machine learning to identify immune-related biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis based on WGCNA network. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41(4):1057-1068.
[23] LANGFELDER P, HORVATH S. WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9:559.
[24] EMERY CA, WHITTAKER JL, MAHMOUDIAN A, et al. Establishing outcome measures in early knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(7):438-448.
[25] GEYER M, SCHÖNFELD C. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):98-107.
[26] JIANG C, LI Z, WU Z, et al. Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis of Hub Genes and Pathways Associated with a Compression Model of Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e927107.
[27] STAHL D, GENTLES AJ, THIELE R, et al. Prognostic profiling of the immune cell microenvironment in Ewing´s Sarcoma Family of Tumors. Oncoimmunology. 2019;8(12):e1674113.
[28] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84.
[29] ZHANG Y, ZHU T, HE F, et al. Identification of Key Genes and Pathways in Osteoarthritis via Bioinformatic Tools: An Updated Analysis. Cartilage. 2021;13(1_suppl):1457S-1464S.
[30] JIANG F, ZHOU H, SHEN H. Identification of Critical Biomarkers and Immune Infiltration in Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on WGCNA and LASSO Algorithm. Front Immunol. 2022;13:925695.
[31] ZHANG C, HUANG R, XI X. Comprehensive Analysis of Pyroptosis-Related Genes and Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration Characterization in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9: 871602.
[32] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36(3):413-425.
[33] DUNCAN-LEWIS C, HARTENIAN E, KING V, et al. Cytoplasmic mRNA decay represses RNA polymerase II transcription during early apoptosis. Elife. 2021:10:e58342.
[34] WANG H, LIU H, ZHAO X, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-actin complex derived from extracellular vesicles facilitates proliferation and migration of human coronary artery endothelial cells by promoting RNA polymerase II transcription. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):11469-11486.
[35] LEPETSOS P, PAPAVASSILIOU KA, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. Redox and NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:90-100.
[36] LU J, ZHANG H, PAN J, et al. Fargesin ameliorates osteoarthritis via macrophage reprogramming by downregulating MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):142.
[37] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53.
[38] CAO Y, TANG S, NIE X, et al. Decreased miR-214-3p activates NF-κB pathway and aggravates osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. 2021;65:103283.
[39] QI Y, TANG R, SHI Z, et al. Wnt5a/Platelet-rich plasma synergistically inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory activity through NF-κB signaling pathway and prevents cartilage damage and promotes meniscus regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(7):612-624.
[40] ZHANG K, LI Z, LU Y, et al. Silencing of Vangl2 attenuates the inflammation promoted by Wnt5a via MAPK and NF-κB pathway in chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021; 16(1):136.
[41] DENG Z, HU X, ALAHDAL M, et al. High expression of MAPK-14 promoting the death of chondrocytes is an important signal of osteoarthritis process. PeerJ. 2021;9:e10656.
[42] SUTHON S, PERKINS RS, BRYJA V, et al. WNT5B in Physiology and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:667581.
[43] 郑莉芳, 陈佩杰, 肖卫华. 骨骼肌质量控制信号通路[J]. 生理学报, 2019,71(4): 671-679.
[44] LU HC, FORNILI A, FRATERNALI F. Protein-protein interaction networks studies and importance of 3D structure knowledge. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2013;10(6):511-520.
[45] JONSSON PF, BATES PA. Global topological features of cancer proteins in the human interactome. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(18): 2291-2297.
[46] RAMBALDI D, GIORGI FM, CAPUANI F, et al. Low duplicability and network fragility of cancer genes. Trends Genet. 2008;24(9): 427-430.
[47] FRANCESCHINI A, SZKLARCZYK D, FRANKILD S, et al. STRING v9.1: protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D808-D815.
[48] ZHANG Z, PAN J, CHENG D, et al. Expression of lactate-related signatures correlates with immunosuppressive microenvironment and prognostic prediction in ewing sarcoma. Front Genet. 2022;13:965126.
[49] TIBSHIRANI R. The lasso method for variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med. 1997;16(4):385-395.
[50] FENG Y, ZHANG C, WU Z, et al. Incorporation of liver chemistry score in predicting survival of liver-involved advanced gastric cancer patients who received palliative chemotherapy. Cancer Med. 2023;12(3):2831-2841.
[51] OBUCHOWSKI NA, BULLEN JA. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves: review of methods with applications in diagnostic medicine. Phys Med Biol. 2018;63(7):07TR01.
[52] WANG F, CHANG Y, LI J, et al. Strong correlation between ASPM gene expression and HCV cirrhosis progression identified by co-expression analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49(1):70-76.
[53] SAFIEDDINE A, COLENO E, SALLOUM S, et al. A choreography of centrosomal mRNAs reveals a conserved localization mechanism involving active polysome transport. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1): 1352.
[54] NASEER MI, ABDULKAREEM AA, MUTHAFFAR OY, et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies Three Novel Mutations in the ASPM Gene From Saudi Families Leading to Primary Microcephaly. Front Pediatr. 2020;8:627122.
[55] TU Z, HE X, ZENG L, et al. Exploration of Prognostic Biomarkers for Lung Adenocarcinoma Through Bioinformatics Analysis. Front Genet. 2021;12:647521. |