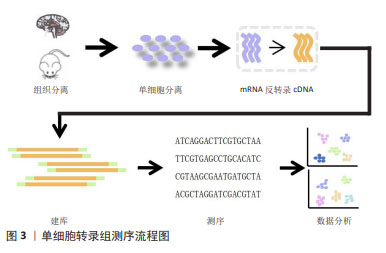
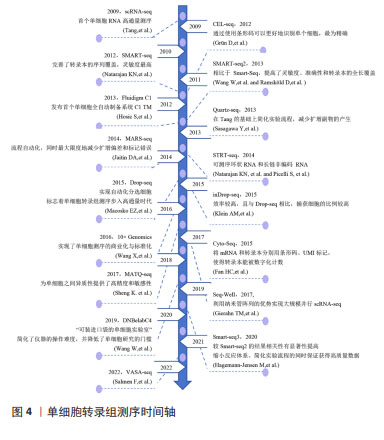
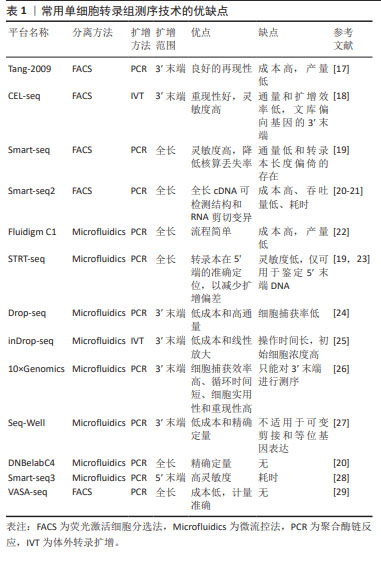
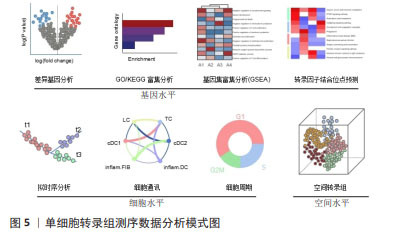
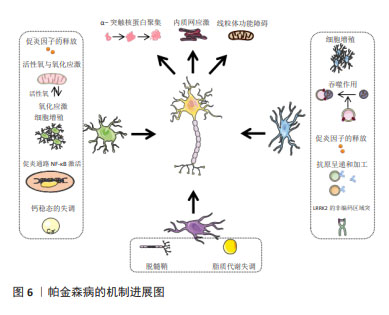
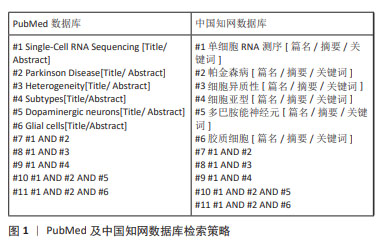
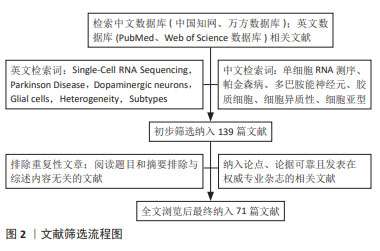
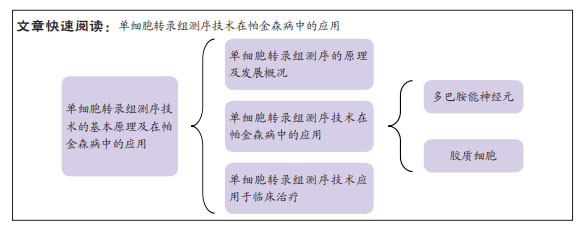
[1] YE H, ROBAK LA, YU M, et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Syndrome. Annu Rev Pathol. 2023;18:95-121.
[2] HAYES MT. Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonism. Am J Med. 2019;132(7): 802-807.
[3] BLOEM BR, OKUN MS, KLEIN C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021;397 (10291):2284-2303.
[4] PAJARES M, I ROJO A, MANDA G, et al. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells. 2020;9(7):1687.
[5] ZHANG S, LIU YQ, JIA C, et al. Mechanistic basis for receptor-mediated pathological α-synuclein fibril cell-to-cell transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(26):e2011196118.
[6] BAE YJ, KIM JM, SOHN CH, et al. Imaging the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson Disease and Other Parkinsonian Syndromes. Radiology. 2021;300(2): 260-278.
[7] VRIJSEN S, HOUDOU M, CASCALHO A, et al. Polyamines in Parkinson’s Disease: Balancing Between Neurotoxicity and Neuroprotection. Annu Rev Biochem. 2023;92:435-464.
[8] TANG F, BARBACIORU C, WANG Y, et al. mRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods. 2009;6(5):377-382.
[9] HEDLUND E, DENG Q. Single-cell RNA sequencing: Technical advancements and biological applications. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;59:36-46.
[10] PAPALEXI E, SATIJA R. Single-cell RNA sequencing to explore immune cell heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(1):35-45.
[11] LI X, WANG CY. From bulk, single-cell to spatial RNA sequencing. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):36.
[12] HWANG B, LEE JH, BANG D. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(8):1-14.
[13] GROSS A, SCHOENDUBE J, ZIMMERMANN S, et al. Technologies for Single-Cell Isolation. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(8):16897-16919.
[14] STUART T, SATIJA R. Integrative single-cell analysis. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; 20(5):257-272.
[15] PAN Y, CAO W, MU Y, et al. Microfluidics Facilitates the Development of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Biosensors (Basel). 2022;12(7):450.
[16] KISELEV VY, ANDREWS TS, HEMBERG M. Challenges in unsupervised clustering of single-cell RNA-seq data. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(5):273-282.
[17] WU X, LIU T, YE C, et al. scAPAtrap: identification and quantification of alternative polyadenylation sites from single-cell RNA-seq data. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(4):bbaa273.
[18] GRÜN D, KESTER L, VAN OUDENAARDEN A. Validation of noise models for single-cell transcriptomics. Nat Methods. 2014;11(6):637-640.
[19] NATARAJAN KN. Single-Cell Tagged Reverse Transcription (STRT-Seq). Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1979:133-153.
[20] WANG W, ZHONG Y, ZHUANG Z, et al. Multiregion single-cell sequencing reveals the transcriptional landscape of the immune microenvironment of colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e253.
[21] RAMSKÖLD D, LUO S, WANG YC, et al. Full-length mRNA-Seq from single-cell levels of RNA and individual circulating tumor cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(8):777-782.
[22] HOSIC S, MURTHY SK, KOPPES AN. Microfluidic Sample Preparation for Single Cell Analysis. Anal Chem. 2016;88(1):354-380.
[23] PICELLI S, FARIDANI OR, BJÖRKLUND AK, et al. Full-length RNA-seq from single cells using Smart-seq2. Nat Protoc. 2014;9(1):171-181.
[24] MACOSKO EZ, BASU A, SATIJA R, et al. Highly Parallel Genome-wide Expression Profiling of Individual Cells Using Nanoliter Droplets. Cell. 2015; 161(5):1202-1214.
[25] KLEIN AM, MAZUTIS L, AKARTUNA I, et al. Droplet barcoding for single-cell transcriptomics applied to embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2015;161(5):1187-1201.
[26] WANG X, HE Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Direct Comparative Analyses of 10X Genomics Chromium and Smart-seq2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021;19(2):253-266.
[27] GIERAHN TM, WADSWORTH MH 2ND, HUGHES TK, et al. Seq-Well: portable, low-cost RNA sequencing of single cells at high throughput. Nat Methods. 2017;14(4):395-398.
[28] HAGEMANN-JENSEN M, ZIEGENHAIN C, CHEN P, et al. Single-cell RNA counting at allele and isoform resolution using Smart-seq3. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(6):708-714.
[29] SALMEN F, DE JONGHE J, KAMINSKI TS, et al. High-throughput total RNA sequencing in single cells using VASA-seq. Nat Biotechnol. 2022;40(12): 1780-1793.
[30] JOVIC D, LIANG X, ZENG H, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: A brief overview. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(3):e694.
[31] HONG M, TAO S, ZHANG L, et al. RNA sequencing: new technologies and applications in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):166.
[32] WU Y, ZHANG K. Tools for the analysis of high-dimensional single-cell RNA sequencing data. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(7):408-421.
[33] ZHAO T, FU Y, ZHU J, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Reveals Dynamic Early Embryonic-like Programs during Chemical Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23(1):31-45.e7.
[34] BALZER MS, MA Z, ZHOU J, et al. How to Get Started with Single Cell RNA Sequencing Data Analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021;32(6):1279-1292.
[35] HUANG M, XU L, LIU J, et al. Cell-Cell Communication Alterations via Intercellular Signaling Pathways in Substantia Nigra of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:828457.
[36] YIP SH, SHAM PC, WANG J. Evaluation of tools for highly variable gene discovery from single-cell RNA-seq data. Brief Bioinform. 2019;20(4):1583-1589.
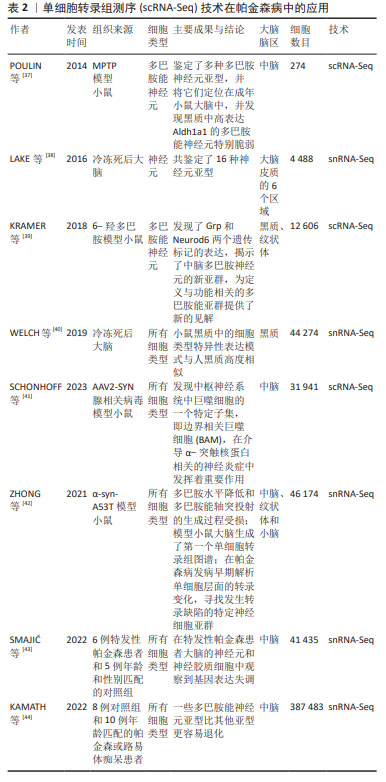
[37] POULIN JF, ZOU J, DROUIN-OUELLET J, et al. Defining midbrain dopaminergic neuron diversity by single-cell gene expression profiling. Cell Rep. 2014; 9(3):930-943.
[38] LAKE BB, AI R, KAESER GE, et al. Neuronal subtypes and diversity revealed by single-nucleus RNA sequencing of the human brain. Science. 2016;352(6293):1586-1590.
[39] KRAMER DJ, RISSO D, KOSILLO P, et al. Combinatorial Expression of Grp and Neurod6 Defines Dopamine Neuron Populations with Distinct Projection Patterns and Disease Vulnerability. eNeuro. 2018;5(3): ENEURO.0152-18.2018.
[40] WELCH JD, KOZAREVA V, FERREIRA A, et al. Single-Cell Multi-omic Integration Compares and Contrasts Features of Brain Cell Identity. Cell. 2019;177(7):1873-1887.e17.
[41] SCHONHOFF AM, FIGGE DA, WILLIAMS GP, et al. Border-associated macrophages mediate the neuroinflammatory response in an alpha-synuclein model of Parkinson disease. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3754.
[42] ZHONG J, TANG G, ZHU J, et al. Single-cell brain atlas of Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J Genet Genomics. 2021;48(4):277-288.
[43] SMAJIĆ S, PRADA-MEDINA CA, LANDOULSI Z, et al. Single-cell sequencing of human midbrain reveals glial activation and a Parkinson-specific neuronal state. Brain. 2022;145(3):964-978.
[44] KAMATH T, ABDULRAOUF A, BURRIS SJ, et al. Single-cell genomic profiling of human dopamine neurons identifies a population that selectively degenerates in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Neurosci. 2022; 25(5):588-595.
[45] TIKLOVÁ K, BJÖRKLUND ÅK, LAHTI L, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals midbrain dopamine neuron diversity emerging during mouse brain development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):581.
[46] HOOK PW, MCCLYMONT SA, CANNON GH, et al. Single-Cell RNA-Seq of Mouse Dopaminergic Neurons Informs Candidate Gene Selection for Sporadic Parkinson Disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(3):427-446.
[47] MASATO A, PLOTEGHER N, BOASSA D, et al. Impaired dopamine metabolism in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Mol Neurodegener. 2019;14(1):35.
[48] GUATTEO E, BERRETTA N, MONDA V, et al. Pathophysiological Features of Nigral Dopaminergic Neurons in Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4508.
[49] AGARWAL D, SANDOR C, VOLPATO V, et al. A single-cell atlas of the human substantia nigra reveals cell-specific pathways associated with neurological disorders. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4183.
[50] WANG ZL, YUAN L, LI W, et al. Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease: glia-neuron crosstalk. Trends Mol Med. 2022;28(4):258-269.
[51] COPE EC, GOULD E. Adult Neurogenesis, Glia, and the Extracellular Matrix. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24(5):690-705.
[52] GUO Y, MA J, HUANG H, et al. Defining Specific Cell States of MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease by Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(18):10774.
[53] BRYOIS J, SKENE NG, HANSEN TF, et al. Genetic identification of cell types underlying brain complex traits yields insights into the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Genet. 2020;52(5):482-493.
[54] LANGSTON RG, BEILINA A, REED X, et al. Association of a common genetic variant with Parkinson’s disease is mediated by microglia. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14(655):eabp8869.
[55] ARMSTRONG MJ, OKUN MS. Choosing a Parkinson Disease Treatment. JAMA. 2020;323(14):1420.
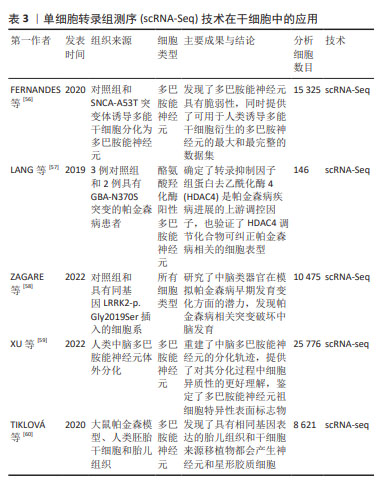
[56] FERNANDES HJR, PATIKAS N, FOSKOLOU S, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Parkinson’s Disease Human In Vitro Models Reveals Dopamine Neuron-Specific Stress Responses. Cell Rep. 2020;33(2):108263.
[57] LANG C, CAMPBELL KR, RYAN BJ, et al. Single-Cell Sequencing of iPSC-Dopamine Neurons Reconstructs Disease Progression and Identifies HDAC4 as a Regulator of Parkinson Cell Phenotypes. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24(1):93-106.e6.
[58] ZAGARE A, BARMPA K, SMAJIC S, et al. Midbrain organoids mimic early embryonic neurodevelopment and recapitulate LRRK2-p.Gly2019Ser-associated gene expression. Am J Hum Genet. 2022;109(2):311-327.
[59] XU P, HE H, GAO Q, et al. Human midbrain dopaminergic neuronal differentiation markers predict cell therapy outcomes in a Parkinson’s disease model. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(14):e156768.
[60] TIKLOVÁ K, NOLBRANT S, FIORENZANO A, et al. Single cell transcriptomics identifies stem cell-derived graft composition in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):2434.
[61] BARKER RA, GÖTZ M, PARMAR M. New approaches for brain repair-from rescue to reprogramming. Nature. 2018;557(7705):329-334.
[62] FIORENZANO A, SOZZI E, PARMAR M, et al. Dopamine Neuron Diversity: Recent Advances and Current Challenges in Human Stem Cell Models and Single Cell Sequencing. Cells. 2021;10(6):1366.
[63] NILSSON F, STORM P, SOZZI E, et al. Single-Cell Profiling of Coding and Noncoding Genes in Human Dopamine Neuron Differentiation. Cells. 2021;10(1):137.
[64] ÁSGRÍMSDÓTTIR ES, ARENAS E. Midbrain Dopaminergic Neuron Development at the Single Cell Level: In vivo and in Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:463.
[65] BARKER RA, TRANSEURO CONSORTIUM. Designing stem-cell-based dopamine cell replacement trials for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med. 2019; 25(7):1045-1053.
[66] SONNTAG KC, SONG B, LEE N, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-based therapy for Parkinson’s disease: Current status and future prospects. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;168:1-20.
[67] ZHANG X, LIU L. Applications of single cell RNA sequencing to research of stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(10):722-728.
[68] LA MANNO G, GYLLBORG D, CODELUPPI S, et al. Molecular Diversity of Midbrain Development in Mouse, Human, and Stem Cells. Cell. 2016; 167(2):566-580.e19.
[69] HILLER BM, MARMION DJ, THOMPSON CA, et al. Optimizing maturity and dose of iPSC-derived dopamine progenitor cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Regen Med. 2022;7(1):24.
[70] CRAIG DW, HUTCHINS E, VIOLICH I, et al. RNA sequencing of whole blood reveals early alterations in immune cells and gene expression in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Aging. 2021;1(8):734-747.
[71] AHMED S, KOMEILI M, PARK J. Predictive modelling of Parkinson’s disease progression based on RNA-Sequence with densely connected deep recurrent neural networks. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):21469. |