中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 202-210.doi: 10.12307/2025.001
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
类器官技术在医疗领域的应用和监管挑战
程玮璐1,王泽华1,张译丹2,刘英慧1
- 1国家药品监督管理局医疗器械技术审评中心,临床与生物统计一部,北京市 100081;2国家药品监督管理局医疗器械技术审评检查大湾区分中心,广东省深圳市 518045
-
收稿日期:2023-10-30接受日期:2023-12-18出版日期:2025-01-08发布日期:2024-05-20 -
作者简介:程玮璐,女,1987 年生,吉林省吉林市人,汉族,工学博士,医用材料器械高级工程师,主要从事医疗器械临床评价技术审评工作。
Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field
Cheng Weilu1, Wang Zehua1, Zhang Yidan2, Liu Yinghui1
- 1Department of Clinical and Biostatistics, Center for Medical Device Evaluation, NMPA, Beijing 100081, China; 2GBA Center for Medical Device Evaluation and Inspection, NMPA, Shenzhen 518045, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-30Accepted:2023-12-18Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-20 -
About author:Cheng Weilu, PhD, Senior engineer, Department of Clinical and Biostatistics, Center for Medical Device Evaluation, NMPA, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:

文题释义:
类器官:是由干细胞经体外3D培养产生的“类似”器官样、具有自我更新和组装能力以及结构和功能与来源组织或器官高度相似的微型器官,类似于组织器官。
疾病模型:是通过对疾病的生理、病理机制进行系统性建模,模拟疾病的发生发展和治疗效果变化的模型。
背景:3D类器官具有类似于生理组织并在一定程度上模仿器官功能的特点,使其成为从基础发育/干细胞研究到个性化医疗等应用的出色模型。
目的:综述并讨论类器官可应用的疾病类型和肿瘤建模等应用领域,以及其监管现状和挑战。
方法:以“类器官,干细胞,疾病模型,3D打印技术,医疗领域”为中文检索词,以“organoid,stem cell,disease model,3D printing technology,medical field”为英文检索词,检索PubMed、Elsevier、万方、中国知网等数据库,对国内外类器官产品进行汇总分析,总结出类器官技术在医疗领域中的应用情况,并对类器官产品在医疗领域的未来发展进行展望。
结果与结论:类器官组织可以打破传统细胞和动物模型的局限性,规避临床研究中存在的伦理问题,与源器官具有高度相似性,与人类系统的生理和病理具有更加相似的表现且遗传稳定,在当前研究中具有极大的优势。类器官在以下领域已得到应用:药效评价研究(临床前模型),包括肠道类器官、肾脏类器官、肝脏类器官、胆囊类器官、肺类器官、脑类器官、心脏类器官、皮肤类器官、生殖系统类器官等;传染病研究;肿瘤研究及精准治疗;再生医学;免疫类器官。美国、欧盟和中国虽暂无完善的监管规定,但均在努力推进类器官监管法律法规的制定。在国内,类器官医疗器械产品虽暂无已上市产品,但与其相关的再生医学产品已有突破性进展。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-0386-5167 (程玮璐)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
程玮璐, 王泽华, 张译丹, 刘英慧. 类器官技术在医疗领域的应用和监管挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(1): 202-210.
Cheng Weilu, Wang Zehua, Zhang Yidan, Liu Yinghui. Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 202-210.
2.2 类器官技术 类器官的生成与工程生物材料和类器官培养方法息息相关,该文将从工程生物材料和类器官培养方法两方面对类器官的形成进行阐述。
2.2.1 工程生物材料 细胞黏附配体、基质几何形状和力学性能是影响细胞增殖、分化和成熟的主要参数,为开发先进可靠的类器官,工程生物材料优化了基质的生物、化学和物理特性,使得大多数用于细胞培养的工程基质和水凝胶具有机械弹性。用于3D细胞培养和类器官的工程生物材料按照其几何结构分类可以分为纤维基质、大孔基质和高度交联的水凝胶。纤维基质(如脱细胞细胞外基质和水凝胶)含有纤维蛋白,其孔隙与细胞的天然体积大小相近;高度交联水凝胶(如聚乙二醇和海藻酸盐)的孔网目尺寸小于细胞尺度,在无其他形式的材料重塑或降解情况下,小网目尺寸可能会抑制细胞的增殖和分化,因此大孔基质材料应运而生。大孔基质的孔隙比天然细胞大,如微带交联成水凝胶大孔支架(形成的大孔约300 μm)可使得人类脂肪来源干细胞扩散到2D和3D培养物中,而在具有小大孔(约100 μm)的支架中细胞可与多个微带发生更直接的细胞间相互作用[5]。CHRISNANDY等[6]报道的一系列合成水凝胶为促进精细的体外形态发生提供了有前途的多功能基质,它们通过可逆氢键介导的动态重排促进广泛的类器官形态发生,这些应激松弛的可调基质通过增加对称性破坏和潘氏细胞形成依赖于yes关联蛋白1(YAP1)来促进肠干细胞上皮细胞中的有效隐窝出芽。GJOREVSKI等[7]报道了微加工阵列能够均匀产生隐窝绒毛状上皮,即通过水凝胶力学和水凝胶微纳加工的原位光图案化,从外在控制肠道干细胞的自组织过程,这是完全由“随机”自组织驱动的、基于干细胞的指导器官发生方法,该研究也验证了组织的当前形状可以帮助模式化和指定组织的发育过程,从而确定组织的未来形状,该研究的类器官培养物可用于回答现有类器官和动物模型无法解决的问题,并且促使类器官技术转化为实际应用。
2.2.2 类器官培养方法 体外建立三维类器官的常规方法有如下几种:①3D简单培养:在培养皿中的脱细胞细胞外基质(如小鼠肉瘤、胶原蛋白等)上生成类器官,尽管已被广泛应用,但存在缺乏营养物质和气体交换以及废物清除、缺乏类器官的可重复性和均匀性等问题,使其不适用于大型药物筛选或高通量评估。②利用旋转生物反应器从胚状体中产生类器官:这种方法常用于视网膜和脑类器官的生成。胚状体是多能干细胞的体外分化模型。生物反应器是指用于在体外增强细胞和组织3D培养的任何设备,虽然生物反应器能提高营养供给,但通常受到类器官大小的限制。CAI等[8]基于智能声流体的微型生物反应器培养人脑类器官,所用的微型生物反应器由3个组件组成,通过声螺旋相涡旋方法实现非接触式旋转的转子;用于实时跟踪旋转动作的摄像头;基于强化学习的控制器,用于旋转操作的闭环调节。在模拟和实验环境中,该微型生物反应器可以实现孔板中转子的自动旋转,可以出色地控制转子的旋转模式、方向和速度,而不受转子质量、液体体积和工作温度波动的影响,并且在长期培养过程中稳定地保持类器官的旋转速度、增强类器官的神经分化和均匀性,这种生物反应器在自动化、鲁棒性和准确性方面具有更优越的性能,凸显了新型智能系统在微流控实验中的潜力。③气液界面法:该方法中细胞的顶层暴露在空气中,细胞的基底表面与液体介质(即类器官中的培养基)接触,主要用于生成肾脏和肠道类器官。④“新型”类器官技术:随着新技术的发展,Tracewell小室、微流控芯片等多方面技术对类器官技术进行了改造,“新型”类器官技术已应用于建立类器官,例如:微流控生物反应器由一个或多个入口、一系列小通道和腔室以及一个或多个出口组成,可以改善营养物质的输送和交换,允许阵列生产大小可控的培养区域,从而产生更均匀的类器官和球状体;在微流体装置中设置传感器和执行器,以实现精确的监测和控制,调节关键参数(包括细胞-细胞和细胞-脱细胞细胞外基质相互作用、流体流动交换、组织模式和电刺激)以较大程度减少批次间差异,增加组织相似性;通常使用微加工技术(例如基于光刻的成型)进行定制设计,具有从毫米到微米级的小型建筑特征,为培养器械的几何形状提供广泛的可能性,为高度专业化的应用提供了有前途的动态平台[9]。SALMON等[10]使用3D打印微流控芯片设计神经血管类器官,开发基于人类多能干细胞来产生以空间决定的与血管细胞相互作用的类器官,这种基于3D打印的平台旨在与任何类器官系统兼容,是一种简单且极具成本效益的类器官血管化方法。该平台为理解和操纵组织特异性类器官与脉管系统的共同开发开辟了新途径。WRIGHT等[11]报道了使用原代人肠道类器官建立96-孔transwell系统以捕获多个定量通路读数,通过对候选疗法进行定量评估,表征并确认了正常人肠道分化模式和屏障功能,使用各种定量读数确定了肿瘤坏死因子α(IBD的核心驱动因素)通路拮抗剂以剂量依赖性方式挽救了肿瘤坏死因子α引起的损伤,表明该系统适用于屏障调节因子的定量评估,适合提供关键功能数据以支持转化靶点和药物发现工作。
2.3 类器官临床应用方向及预期发展与受益 类器官已在药效评价研究(临床前模型)、传染病研究、肿瘤研究及精准治疗、再生医学等领域得到应用。
2.3.1 药效评价研究(临床前模型) 类器官技术具有成本低、时间短、生理相关度更高等优势,在体外培养体系中长期保持生理及遗传信息稳定下广泛扩增获得的类器官将更接近于临床实践情形,类器官模型可以增加筛选出具有更大生理和临床相关性药物的成功率,加速确定对患者最有益的药物,加速药物的临床应用。
(1)肠道类器官:由于小肠上皮细胞含有大量的药物代谢酶和外源加工蛋白,小肠在人体进行药物和外源物质的代谢、消化、营养吸收等过程中起极其重要的作用[12]。EVANS等[13]首先提出肠内培养的概念,将肠道类器官定义为体外生长的小肠绒毛、黏膜固有层和完整的隐窝结构。肠道类器官是体外研究肠道干细胞和肠上皮细胞的较好工具[14],其特点是由多种肠细胞组成、中空腔花瓣状结构、能稳定低温保存和复苏、能够长期自我更新[15]。SATO等[16]基于前人对肠道干细胞生长微环境的研究,分离肠道隐窝,培养LGR5基因表达的肠道干细胞,成熟后按比例(1∶5)进行传代培养,发现在连续传代培养> 1.5年中依然可保持基因型及生理功能的稳定。因此,肠道类器官模型在疾病建模研究中可用于探索传染病和癌症发生的确切机制,肠道类器官模型也可用于疾病发生机制研究,如营养物质对肠道健康干预机制、幽门螺旋杆菌感染发病机制、GII.4型人诺如病毒在人肠道组织中的增殖和转录机制[17];肠道类器官模型也可作为系统来识别生物活性微生物产品,评估它对宿主上皮的潜在作用;对于基因缺陷疾病,肠道类器官模型可用于基因组编辑技术集成的研究、细胞的治疗和药物输送工具。
(2)肾脏类器官:肾的功能单位由肾小球和肾小管组成。“转运扩增肾元祖细胞”可在发育过程中产生哺乳动物肾脏的所有肾元,但由于它们数量有限、体外扩增能力差、难以在人体中获得,减缓了肾脏发育和疾病的基础研究和转化研究。LI等[18]研究发现,在适当3D培养条件下可通过干细胞体外培养产生肾脏类器官,例如支持小鼠和人类胎儿肾元祖细胞、人类诱导多能干细胞的肾元祖细胞的长期扩增,所获得的扩大肾元祖细胞在体外和体内都保持了基因组稳定性、分子同质性和肾形成潜力。另外,据此培养方式获得的非肾细胞具有基因靶向性,可以形成类肾素器官,植入体内后与宿主循环系统功能结合,通过过滤产生尿样代谢物。总之,这些发现为研究人类肾脏发生、肾脏疾病建模和诊断以及药物发现提供了技术平台。
(3)肝脏和胆囊类器官:肝脏是细胞组成复杂、生理功能丰富、结构精密、相关疾病高发的器官,既是外源毒性物质作用靶器官也是最重要的解毒器官,肝脏类器官可应用于疾病模型、药物筛选和肝脏再生等诸多应用场景。2013年,TAKEBE等[19]模拟肝脏发育早期的细胞谱系制备类似人肝芽组织的3D聚合物,主要是通过将肝细胞、人脐静脉内皮细胞和人间充质干细胞共培养,将获得的肝类器官移植入小鼠体内后具有良好的血管生成功能,虽然这些体外培养的肝芽组织缺乏胆管结构,该研究在2013年仍被《Science》评为十大突破之一。SHINOZAWA等[20]建立了一个基于人肝类器官(HLO)的筛选模型,即开发一种可重复的方法,从具有可重复胆汁转运功能的多能干细胞系可储存前肠祖细胞中产生人肝类器官,通过组织学和超微结构评估微观解剖结构,并且测试存活率、胆汁淤积和线粒体毒性,预测238种市售药物对肝的毒性(特异性88.9%,敏感性88.7%),获得了基于人肝类器官的药物诱导性肝损伤检测被转化为基于384孔的高速实时成像平台。
胆管组织包括肝内胆管和肝外胆管,是一个复杂的三维网络系统。胆囊颈部和底部都存在具有前体/干细胞特性的胆管上皮细胞群[21-22]。陈智闻等[21]通过分离人来源胆囊组织上皮细胞,运用3D培养体系将细胞嵌入基质胶中进行3D培养并加入增强其繁殖能力的小分子(CHIR-99021和blebbistatin),所获得的胆囊类器官有胆管类上皮细胞特征。人胆囊类器官培养体系的建立为胆管疾病的治疗与建模提供了新思路[23]。胆管细胞类器官已被建立用于研究正常的胆管细胞生物学和原发性硬化性胆管炎,并且测试类器官在体外形成胆管和胆囊组织的潜力。类器官培养系统已发展成为肝脏和胆道研究的前沿技术,如在胃肠道类器官建立的基础上,从富含亮氨酸的小鼠重复蛋白G蛋白偶联受体5阳性肝祖细胞产生肝胆类器官培养物;从肝细胞和胆管细胞开发3D肝胆类器官培养物,以模拟人类和动物的肝胆健康和疾病。目前,肝细胞类器官已被用于研究阿拉吉勒综合征、脂肪肝疾病、威尔逊病、乙型肝炎病毒感染和囊性纤维化[24]。
(4)肺类器官:人体气道上皮是吸入空气污染物的主要毒性靶区,肺是病原体感染和损伤的重要靶器官。病原体包括细菌(铜绿假单胞菌、肺炎链球菌、结核分歧杆菌等)、病毒(流感病毒、人副流感病毒、呼吸道合胞病毒及新型冠状病毒(SARS-CoV-2)等)、真菌、支原体、衣原体以及寄生虫等。肺类器官可源于祖细胞或干细胞等,成熟的肺上皮干细胞可直接进行体外培养,为肺生理、病理,尤其是感染性肺系病的防治研究提供有效研究工具。利用上皮基底细胞中表达的YP450代谢酶制成的肺类器官,为体外吸入毒理学研究的理想模型,基于该细胞的肺类器官气管结构的出现,是肺类器官构建成功的重要标志[1]。商业化肺3D组织模型网EpiAirwayTM包含基底细胞、杯状细胞和纤毛细胞,由正常人气管/支气管上皮细胞培养形成的、高度分化的假复层上皮组织模型,该产品具有良好的均一性和重复性。EpiAirwayTM与人肺组织高度相似,能模拟人类真实的肺部结构及功能,在预测中/低毒性呼吸道刺激物的毒性效应时优于动物测试[1,25]。
(5) 脑类器官:人脑的复杂性极高,采用体内原位模型进行研究耗时长、成本高昂且成功率低;采用动物模型研究人类大脑功能不能准确再现脑肿瘤微环境,脑类器官能高度模拟脑原位组织的生理结构和功能,可研究肿瘤组织在脑内的特性,被广泛用于恶性肿瘤的研究[26]。2016年,HUBERT等[27]开发了直接从胶质母细胞瘤标本中衍生的肿瘤类器官培养系统,该方法将肿瘤细胞混悬在基质胶中培养并保持稳定和存活。这些类器官再现了体内肿瘤的低氧梯度和肿瘤干细胞的异质性、不同的分子特性,这也允许了肿瘤细胞层次结构的研究。
类器官和胎儿组织之间显著的转录相似性为大脑类器官作为人类皮质发育模型提供了依据。EIRAKU 等[28]建立了神经外胚层类器官,这些类器官中的神经元表现出新生皮质脑组织的特性,在神经上皮细胞受到刺激后可表现出特定的脑区功能特性,重现了早期皮质发生过程中的时空调控。2015年,KIRWAN等[29]构建了模拟体内皮质网络发育和功能的人大脑皮质神经网络,可用于人类前脑神经网络生理学机制的研究。
(6)心脏类器官:心脏是外源化学物毒性的重要靶器官之一,全球范围内多发的心血管疾病是导致死亡的主要原因,体外药物诱导心脏毒性试验是药物发现和临床应用的关键步骤,而心血管疾病的研究主要局限于传统的二维细胞和动物模型[30]。人类心脏类器官是复杂的多细胞聚集物,由于心脏类器官的血管化和结构复杂性,人类心脏类器官最近才被开发[31],其研究进展也相对较少。心脏类器官的3D类器官细胞来源于原代组织或重编程分化细胞类型(人类多能干细胞、胚胎干细胞)或人诱导多能干细胞的成体干细胞[32-34]。自组织型心脏类器官和工程心脏组织类器官、心脏微组织等可用于疾病模型的构建和疾病机制研究(如先天性心脏病、缺血性心肌病、遗传性心脏病、心律失常)、心脏毒性监测、药物筛选与评价、再生医学与移植等。
TAKEDA等[35]开发了一种通过在细胞表面涂覆细胞外基质成分在短时间内构建3D人工组织的方法,将3D人工心脏组织用于药物心脏毒性体外测试,通过纤维连接蛋白和明胶纳米膜包覆单颗人诱导性多能干细胞来源心肌细胞衍生生成诱导性多能干细胞来源心肌细胞3D心脏组织,组织学上该3D心脏组织显示肌细胞和细胞外基质蛋白(如纤维连接蛋白、Ⅰ/Ⅲ型胶原和层粘连蛋白)中有肌节结构,在体外表现出对阿霉素敏感的细胞毒性和对人类hERG相关基因通道阻断剂/异丙肾上腺素的响应灵敏性,hERG型钾通道阻滞剂E-4031和异丙肾上腺素呈剂量依赖的方式诱导钙瞬变和细胞收缩力显著变化,表明其在药物诱导的心脏毒性试验或药物筛选系统中可用于发现药物。尽管类器官存在批次间的可见性和异质性、无法概括天然器官的高保真度、成熟度和功能有限等局限性,人类心脏类器官在这些领域仍极具潜力[36]。
(7)皮肤类器官:皮肤为人体的第一道屏障,对人体起到物理保护、免疫防御、体温调节、分泌排泄等多种重要作用,也是最易损伤的器官,烧伤是最常见的皮肤损伤,因此创面的愈合和修复研究也愈加受到重视[37]。合适的动物模型是皮肤刺激评价、创面愈合机制和评价药物治疗创面修复效果的基础,但存在实验周期长、成本高、实验结果外推至人类不确定等缺点,并且在毒理学测试方面需要评估的化合物数量庞大,因此其他方法正被大力推动来取代动物实验,如基于细胞的体外方法、高通量方法、创新技术(基于诱导多能干细胞和类器官的方法,器官型共培养系统和微流控“多器官”芯片)[38]。
LIU等[39]构建了一个含有毛细血管网络的无支架双层组织工程皮肤,通过将真皮成纤维细胞与真皮微血管内皮细胞以2∶1的比例共培养,成纤维细胞与内皮细胞相互作用形成纤维层,共培养20 d后可观察到毛细血管样结构,然后将上皮细胞播种在纤维片上以组装双层组织,苏木精-伊红染色显示7 d后组织工程皮肤表皮呈层状,免疫染色显示上皮促进了毛细血管样结构的形成,透射电镜分析显示毛细血管样结构为典型的微血管。2009年3月,欧盟提出停止化妆品安全性评价的动物实验,并已根据欧盟新化妆品法规EC 1223/2009将3D皮肤模型用于化妆品安全性评价[40],皮肤模型有EpiskinTM模型和 Epikutis? 3D表皮模型。EpiSkin?模型是一个完全分化的三维皮肤模型,包括重建的表皮和功能角质层,该模型是通过在胶原底物上培养成人非转化人角质形成细胞而获得的具有3D结构的人表皮模型,具有功能角质层的表皮。EpiSkin?按照质量参考标准ISO 9001生产,获得的表皮组织具有可追溯性和可重复性,每个生产批次的组织在放行前都对细胞活力、屏障功能和形态进行了质量控制,已被广泛应用于皮肤腐蚀性体外实验[41]。Epikutis?体外重组3D表皮模型为国内第一款用于皮肤测试的模型,已被应用于化学品皮肤刺激检测、纳米材料透皮行为、皮肤毒性研究的模型[42-44]。
(8)生殖系统类器官:类器官在男性生殖系统(如睾丸)和女性生殖系统(如子宫和卵巢)中也建立了应用[45]。对于男性生殖系统,BAERT等[46]的研究结果表明,无论是否有生物支架的支持,原代人睾丸细胞都能够自组织成人类睾丸类器官,即多细胞组织替代物。尽管缺乏睾丸特有的形状,但这些微型组织窝藏着精原细胞、生态位细胞,并且保留了特定的功能。人类睾丸类器官可能有助于开发仿生睾丸模型,这将对研究和开发不孕不育的临床治疗以及与药物发现和毒理学相关的筛选产生巨大影响。
对于女性生殖系统,子宫内膜/黏膜在整个月经周期和怀孕期间经历动态变化,尽管子宫内膜作为植入部位的营养支持很重要,但没有长期培养系统可以在体外重现子宫内膜功能,来自子宫内膜和蜕膜的单细胞可以产生功能齐全的类器官。TURCO等[47]建立了人类成体干细胞衍生类器官培养物的条件,以生成正常和蜕膜化人子宫内膜的三维培养物,这些类器官长期扩增、遗传稳定,并且在用生殖激素治疗后进行区分,转录分析证实类器官与原发组织有很大的相似性。子宫内膜类器官暴露于妊娠信号后可发展出早期妊娠的特征。恶性子宫内膜类器官为研究子宫内膜异位症和子宫内膜癌等常见疾病以及早期妊娠生理学提供了基础。
2.3.2 传染病研究 严重急性呼吸系统综合征等病毒以及细菌、寄生虫和真菌每年在全世界造成超过1 000万人死亡,死因包括下呼吸道感染、腹泻病、肺结核、艾滋病毒/艾滋病、疟疾、热带疾病(恰加斯病和血吸虫病等),再加上耐药细菌(如耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌)带来的额外威胁,需要对传染病保持警惕。知晓传染性病原体的疾病发展的潜在机制可更好地设计预防措施[48-49],例如:腹泻病仍是世界上最大的健康问题之一,利用肠道类器官模拟肠道感染,既能研究宿主-病原体的相互作用又能寻找治疗靶点[50]。人肠道类器官可通过在三维培养中扩增分离的患者来源肠上皮干细胞来产生[51]。近年来,人肠道类肠道越来越多地被用作研究宿主-病原体相互作用的疾病模型,特别是在缺乏强大细胞系统(如轮状病毒和诺如病毒)的病毒感染情况下[52]。人肠道类肠道在细胞外基质支架中以11D形式生长,并且在培养中长期保持体内生理学的各个方面,与传统转化的肠上皮细胞系相比具有多种优势:仅包含未转化的人类细胞、包含多种细胞类型、维持肠道区域特异性培养的差异、可分化为位于绒毛或隐窝区域的细胞群、维持宿主的遗传特性等[53],已成功用于培养人轮状病毒和诺如病毒感染模型[54]。另外,中国科学家采用类器官研究病毒对人体的致病机制,为病毒致病机制研究和药物开发提供了新模型[55]。
2.3.3 肿瘤研究及精准治疗 肿瘤的发生发展是多阶段、多步骤、多因素的复杂过程,类器官模型能够在体外稳定保存母体肿瘤的遗传、蛋白质组学、形态学和药型特征的能力,同时还可提供前所未有的基因组和操作环境,使用与原始肿瘤具有相似特征的个性化肿瘤模型可能会更准确地预测患者的药物反应,如对放化疗、靶向药物、免疫细胞治疗等有效性的反应。尽管最近在类器官方案方面进行了创新,但由于包括癌症组织来源和后续加工、培养基配方与动物源性三维基质在内的几个方面未标准化,目前的癌症类器官培养技术本质上是不受控制和不可重复的。鉴于癌症类器官有可能准确概括与患者特异性癌症相关的肿瘤内和肿瘤间生物学异质性,可实现肿瘤精准个体化治疗,建立可重复的平台以加速可转化为患者应用是必要的[56]。另外,建立肿瘤类器官样本库有利于进行肿瘤分子学背景与肿瘤生物学行为(如临床病理学特征、药物反应或耐药关系等)模式分析[57-58]。肝胆癌类器官已从冷冻和新鲜的人体组织中建立,并且用作药物测试平台和癌症样本的生物样本库。而且,基于CRISPR的基因修饰和暴露于传染因子的类器官已经用于生产致癌的类器官模型,这种患者特异性肿瘤的器官型模型正在彻底改变人们对癌症异质性及对个性化医疗的理解。
2.3.4 再生医学 再生医学是利用干细胞、生物相容性和生化因子在体外环境中构建与体内组织相似的生物组织的科学,用于研究疾病的机制和诊断过程以及可能的治疗方法,此外还用于开发体外生命支持系统或替换体内受损器官或修复损伤[59]。类器官自诞生以来应用于再生和器官移植的尝试从未中断过,如用于骨/软骨修复、外耳修复[60-61]、皮肤置换[62-63]、炎症性肠病的肠道类器官、肺器官、唾液类器官、肝脏类器官、胆道类器官、胰腺类器官、心脏类器官和泪腺类器官等[64-66]。全世界每年骨折、骨缺损和软骨损伤的患者数量庞大,打印骨生物已成为替代丢失或受损骨组织的可行替代方案[67],生物打印生产与天然组织结构相似的复杂3D支架也非常适合软骨组织工程。TARAFDER等[68-69]通过微波烧结和激光/金属打印开发了机械坚固的3D磷酸三钙支架,使用人成骨细胞和SD大鼠股骨缺损进行体外和体内研究,通过微波烧结3D打印控制孔径较传统烧结可提高抗压强度、增加细胞密度且具有优异的生物相容性和成骨性能,掺入锶(Sr2+)和镁(Mg2+)的磷酸三钙支架较纯磷酸三钙支架在骨形成、矿化、多尺度孔隙度以及骨钙素和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白水平方面均增加。在软骨再生研究方面,LEE等[70]使用基于挤出的生物打印机,使用层层组装打印生产具有人类胫骨髁解剖形状的聚己内酯和羟基磷灰石的复合材料,得到的复合支架尺寸为20 mm×15 mm×15 mm,具有关节再生和关节炎治疗的潜力。使用相同的工艺,LEE等[71]在没有细胞移植的情况下使用聚己内酯-羟基磷灰石聚合物再生兔滑膜关节的整个关节表面,以取代骨骼成熟兔的肱骨髁,并且注入转化生长因子β3的生物支架显示出全组织覆盖、更均匀的软骨细胞分布、更大的基质密度和关节软骨厚度。总之,与现有的再生疗法相比,基于类器官的再生医学具有以下优势:更易保护细胞;易获得,大多数组织可通过微创手术(如活检)轻松收集;获得程序简单,捐赠者无任何负担;可长期大规模繁殖;可分化成构成靶组织的特定细胞,再生治疗效果可最大限度提高;移植具有安全性;直接移植到病变部位,移动和分布到其他器官的风险较低;可最大限度地降低免疫排斥风险;移植程序安全且患者友好。尽管尚未应用于人类,类器官良好的治疗效果使其在再生医学中的应用备受期待[72-73]。
2.3.5 免疫类器官 免疫细胞的浓度在上皮细胞中最高(血液和淋巴器官除外),免疫细胞在上皮细胞中直接与上皮细胞相互作用,是人体与病原体感染环境的第一个接触点,上皮细胞与免疫细胞密切合作以维护体内平衡并对感染快速反应,不仅是预防和控制致病性感染的先决条件,也在防止过度免疫激活方面很重要。上皮类器官培养也可以整合到芯片上的器官平台中,从而建立更复杂的培养系统,也可以被操纵来反转它们的极性融合形成更接近原器官或原组织的管状结构。BOUFFI等[74]报道了一种新一代复杂的包括功能性免疫系统的肠道类器官,以帮助人类研究胃肠道疾病,这种类器官不仅能支持迁移的免疫组织,而且也能继续改善肠道自身的发育,并且具有识别外来抗原的能力。VOTANOPOULOS等[75]将从黑色素瘤患者获得的黑色素瘤和淋巴结生物样本转移到实验室,用生理盐水、抗生素和红细胞裂解缓冲液洗涤后,将生物样本解离并掺入基于细胞外基质的水凝胶系统中,生物制成三维混合黑色素瘤/淋巴结类器官。保持肿瘤异质性产生免疫增强的患者肿瘤类器官,平均免疫治疗7 d,即类器官组织与纳武利尤单抗、帕博利珠单抗、伊匹木单抗和达拉非尼/曲美替尼平行筛选72 h,测定记录相对药物疗效,在85%的患者中,肿瘤类器官对免疫治疗的反应与标本临床反应相似,证明了开发3D混合免疫增强肿瘤/淋巴结类器官允许个体患者的免疫系统和肿瘤细胞保持活力,用于研究个性化免疫治疗反应。
2.4 国内类器官器械类产品上市申报情况概述 目前国内类器官器械产品暂无上市申报情形,但有类器官相关辅助产品提交创新医疗器械特别审查程序并获得审批,如:胶原蛋白软骨再生载体/胶原基软骨修复基质。
胶原蛋白软骨再生载体/胶原基软骨修复基质一般由注射针、预灌封注射器以及预装在预灌封注射器中的胶原蛋白材料组成,仅含载体不含活体细胞。保留天然结构的胶原具有良好的温敏特性和自组装能力,于低温条件下与骨髓间充质干细胞混合后注入软骨缺损部位,通过温度变化形成凝胶并固定于缺损处;胶原基软骨诱导性基质为干细胞提供良好的黏附、增殖与分化的微环境,诱导其成软骨分化并有正常的功能表达,最终实现软骨的再生修复。该产品将自体骨髓浓缩物与动物源软骨修复基质相结合,应用于关节软骨缺损修复,预期用于无系统性感染的成年患者,与自体骨髓间充质干细胞复合,用于治疗由创伤、退变导致的局灶性膝关节软骨缺损患者。
2.5 国际监管部门关于3D打印类器官的应用研究
2.5.1 动物实验替代研究 2016年FDA通过的《21世纪医药法案》法律法规,授权了开发旨在促进新药研发的药物开发工具,包括生物标志物、临床结果评估、动物模型[76];2017年FDA推出预测毒理学路线图[77],强调FDA减少动物实验使用的目标,推进类器官技术作为新的替代方法以及非临床研究工具,从而努力取代、减少、改善对动物实验的依赖[78]。
3D打印类器官可以评估化妆品及食品中重金属对神经系统的毒性,利用微生理系统评估药物的预期效果[79],具体如下:①微生理系统:使用微型细胞培养平台,通过将细胞暴露于对其功能或病理生理重要的微环境,对人类或动物来源特定组织或器官的功能特征进行体外建模健康状况模拟。微生理系统设计可能旨在为培养的细胞提供和支持物理(例如,温度、pH值和氧气)/生化/电气/机械(例如,流动或拉伸)/结构/形态条件,并概括一组定义健康的特定属性或患病器官或组织功能。微生理系统平台可能包括单一培养物、多种细胞类型的共培养物、来自组织/器官的外植体的维护和/或包含类器官细胞形成。②器官芯片:是微生理系统的一个子集,由一个微型生理环境组成,设计用于产生和/或分析能够模拟指定/
目标器官水平反应的功能组织单元,可用于评估疾病检测或疫苗效力的可靠性、敏感性、特异性、体外替代体的可重复性。
2.5.2 预测药物临床试验研究 在对14家大型制药公司的调查发现,生产一种商业产品需要24种候选药物,而超过45%的失败发生在药物开发的3个临床阶段,表明药物开发过程中需要更好的临床前测试系统。药品评价和研究中心(Center for Drug Evaluation and Research,CDER)正在评估通过在临床前药物测试的早期检测药物效果,用以推进药物开发和评估。在药物评估的临床阶段之前,检测药物毒性的能力受到如下因素限制:临床前测试中使用的动物模型与临床试验中人类受试者之间的生理差异、药物对患者的影响与实验室检测中观察到的差异。目前,CDER评估重点主要集中在以下领域:开发用于改进药物对人体影响的临床前预测系统,测量药物对肝脏生理学影响的肝脏微生理系统,与其他器官系统相互连接的预测系统,成熟度增强的微工程单干细胞衍生心肌细胞,心脏细胞的功能性研究系统。上述方法也可能在临床试验有限或不可行的情况下使用,例如应对突发公共卫生事件的医学对策和评估治疗罕见疾病的疗法。
2.5.3 化妆品安全性评价替代研究 自2009年3月欧盟禁止动物实验用于化妆品安全性评价,EpiskinTM模型和Epikutis? 3D表皮模型已被开发使用。EpiskinTM模型可用于皮肤腐蚀性体外实验。EpiAirwayTM是一个商品化的肺3D组织模型网在测试预测强吸入毒性化学物质和预测中/低毒性呼吸道刺激物的毒性效应。但欧盟尚未开展类器官在其他领域的研究应用,也尚未有相关指南推出。
2.6 类器官研究的监管现状及监管风险
2.6.1 FDA关于类器官研究的监管现状 2016年FDA通过的《21世纪医药法案》法律法规,授权开发旨在促进新药研发的药物开发工具及启动新药创新科学和技术方法试点计划,2017年推出预测毒理学路线图推进类器官技术作为新的替代方法作为非临床研究工具[76-78]。
2.6.2 欧盟关于类器官研究的监管现状 欧盟于1997年制定了《用体外模型替代动物研究》的文件,2010年制定《保护用于科学目的动物的法律》(Directive 2010 /63/EU,现行版本为2019年修订版),以消除不同欧盟成员国在保护用于科学研究的动物方面的法律、法规和行政规定之间的差异[79]。2018年出台的《非基因毒性杂质鉴定反思文件(草案)》提到对杂质的安全性评估可针对性地使用体外方法(2D、3D细胞系统和微生理系统)[80]。2023年1月,欧盟发布的《非临床领域3年综合工作计划,包含2023年优先事项》制定了与类器官相关的具体监管行动[81],包括:起草“定义用于制药领域特定使用环境的器官芯片技术的监管接受标准的反思文件”;创建全球监管机构集群,为新方法学(3R,例如器官芯片)制定监管接受标准,并且协调欧盟和全球监管机构之间的观点和监管接受标准;专注于对特定重点微生理系统后续研讨会监管机构接受的方法确认。
2.6.3 中国关于类器官研究的监管现状 3D打印类器官研究涉及干细胞的提取、保存、应用,细胞治疗是Ⅲ类医疗技术。目前对于基因和细胞治疗产品,中国采用“双轨制”的框架进行监管,但人源类器官研究有其特殊性、复杂性和敏感性[82],因此除了评估其风险受益,伦理原则是否平衡与适度也需进行评估。目前,国家卫生健康委和国家药品监督管理局联合承担医疗机构开展干细胞临床研究的监管职责,中国相继推出和实施《干细胞临床研究管理办法(试行)》《涉及人的生物医学研究伦理审查办法》《国家限制类技术目录和临床应用管理规范》,并且2020年和2021年分别起草《人源性干细胞及其衍生细胞治疗产品临床试验技术指导原则》和《人源性干细胞产品药学研究与评价技术指导原则》并公开征求意见[83-85]。目前国家监管部门遵照上述临床管理原则及以《中华人民共和国药品管理法》为法律依据等开展专项监督检查,未来建议组织专业委员会制定相应的政策措施,优化法律和法规框架,细化相关规则和标准,逐步完善临床相关的监管体系并综合考虑伦理原则,为中国类器官产业创造更加良好的政策环境[86]。
2.6.4 类器官研究的风险
客观风险:新技术本身存在一定的客观风险,类器官作为药效评价研究(临床前模型)、传染病研究、肿瘤研究及精准治疗、再生医学方面一种新的研究方法,短期和远期是否安全有效、如何转化为临床应用都需要经过时间和实践的检验,仅有目前理论依据或探索研究可能存在风险和隐患[85]。
主观风险:类器官在应用阶段技术的推广、掌握过程都存在质量风险,中国人口众多,医务人员和研究机构人员数量庞大且水平参差不齐,易发生新技术的误用、滥用和谬用。
伦理风险:类器官临床应用在缩短生物医学创新周期的同时,与人体组织相关的伦理问题,如道德地位、知情同意商业化和利益共享等随之而来,中国应在法律和监管政策下健全科技伦理治理,强化伦理底线意识,提倡公众参与治理[87],遵循伦理原则:人的福祉、尊重、负责、透明、公众参与和利益共享[82]。
生物安全风险:类器官涉及遗传物质、微生物改造或利用等生物技术的研究和应用,国际环境复杂且形势严峻,易存在危及公众健康、损害遗传资源和生物资源、破坏生态系统和生物多样性等危害。
医疗管理风险:现有医疗管理体系对任何新技术使用所需的流程设置、人员安排、设施配套和建立应急措施都需进行调整,如何科学完善的管理、充分利用医疗资源、保证医疗安全都将会产生医疗管理风险[85,88]。
2.7 类器官用于监管工具的挑战与展望 目前类器官模型已在毒理学评价中应用,但在其他靶器官毒理学研究中的应用极为有限。利用类器官模型进行毒理学评价,需要满足可获得高产量类器官模型、可测量毒性终点和高通量测试体系等方面的需求[1]。现阶段相关研究还存在较多问题,具体如下:①尚未构建类器官应用方法学体系及其标准化工作。类器官培养过程暂无成熟的方法,也无标准化的程序,简单扩散过程在细胞大小和体积增加时不能为核心部分提供足够的氧气和营养,并且限制细胞代谢废物的排出,这导致制备的类器官通常缺乏基底、组织驻留免疫细胞和血管,限制了类器官的发育和成熟。②受试物的暴露途径、剂量和毒代动力学特征与体内相关性较难确认。由于类器官模型中的细胞呈3D生长和组织模式,并且采用的是特殊材料和器件体系,如何确定体外受试物暴露浓度、暴露途径、剂量和毒代动力学与体内的相关性,使得建立类器官毒理学模型具有困难。③剂量-效应关系评定。在动物/人体内产生毒性效应所需剂量,尚无法根据类器官毒理学研究结果利用体外体内外推法、计算毒理学模型直接估测。
| [1] 刘薇,梅玺丽,陈雨萌,等.3D类器官模型的研究进展及其在化学品毒理学评价中的应用展望[J].生态毒理学报,2021,16(4):32-42. [2] 赵冰.类器官在器官移植领域的应用前景[J].器官移植,2022,13(2): 169-175. [3] KRETZSCHMAR K, CLEVERS H. Organoids: modeling development and the stem cell niche in a dish. Dev Cell. 2016;38(6):590-600. [4] 周永杰,石毓君.类器官研究进展及展望[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2022,29(6):716-718. [5] HAN LH, TONG X, YANG F. Photo-crosslinkable PEG-based microribbons for forming 3D macroporous scaffolds with decoupled niche properties. Adv Mater. 2014;26:1757-1762. [6] CHRISNANDY A, BLONDEL D, REZAKHANI S, et al. Synthetic dynamic hydrogels promote degradation-independent in vitro organogenesis. Nat Mater. 2022;21(4):479-487. [7] GJOREVSKI N, NIKOLAEV M, BROWN TE, et al. Tissue geometry drives deterministic organoid patterning. Science. 2022;375(6576):eaaw9021. [8] CAI H, AO Z, WU Z, et al. Intelligent acoustofluidics enabled mini-bioreactors for human brain organoids. Lab Chip. 2021;21(11):2194-2205. [9] LICATA JP, SCHWAB KH, HAR-EL YE, et al. Bioreactor Technologies for Enhanced Organoid Culture. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14):11427. [10] SALMON I, GREBENYUK S, FATTAH ARA, et al. Engineering neurovascular organoids with 3D printed microfluidic chips. Lab Chip. 2022;22(8): 1615-1629. [11] WRIGHT CW, LI N, SHAFFER L, et al. Establishment of a 96-well transwell system using primary human gut organoids to capture multiple quantitative pathway readouts. Sci Rep. 2023;13:16357. [12] PECK BC, MAH AT, PITMAN WA, et al. Functional transcriptomics in diverse intestinal epithelial cell types reveals robust microR-NA sensitivity in intestinal stem cells to microbial status. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(7):2586-2600. [13] EVANS GS, FLINT N, SOMERS AS, et al. The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures. J Cell Sci. 1992;101(Pt1):219-231. [14] 邱广志,喻礼怀,张昌卫,等.肠道类器官模型的构建和应用研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2023,35(7):4231-4237. [15] DERRICOTT H, LUU L, FONG WY, et al. Developing a 3D intestinal epithelium model for livestock species. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;375(2):409-424. [16] SATO T, VRIES RG, SNIPPERT HJ, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459(7244): 262-265. [17] 林琳.GⅡ.4型人诺如病毒在人肠道类组织中的增殖及转录组研究[D].北京:中国疾病预防控制中心,2019. [18] LI Z, ARAOKA T, WU J, et al. 3D culture supports long-term expansion of mouse and human nephrogenic progenitors. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;19(4): 516-529. [19] TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013;499(7459): 481-484. [20] SHINOZAWA T, KIMURA M, CAI YQ, et al. High-fidelity drug-induced liver injury screen using human pluripotent stem in organoids. Nat Methods. 2017;14(11):1097-1106. [21] 陈智闻,陈费,刘畅,等.人胆囊类器官培养体系的建立与鉴定[J].海军军医大学学报,2023,44(4):402-408. [22] CARPINO G, CARDINALE V, RENZI A, et al. Activation of biliary tree stem cells within peribiliary glands in primary sclerosing cholangiti. J Hepatol. 2015; 63:1220-1228. [23] 袁波.胆囊良恶性肿瘤类器官培养体系的建立及鉴定[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,海军军医大学,2019. [24] SHIOTA J, SAMUELSON LC, RAZUMILAVA N. Hepatobiliary Organoids and Their Applications for Studies of Liver Health and Disease: Are We There Yet? Hepatology. 2021;74(4):2251-2263. [25] RISS T, KUPCHO K, SHULTZ J, et al. Measuring apoptosis in real-time by linking luciferase fragments to annexin V. Toxicol Lett. 2016;258:S56. [26] 邵云香,黄煜伦.大脑类器官在胶质母细胞瘤中的应用进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2020,47(4):453-458. [27] HUBERT CG, RIVERA M, SPANGLER LC, et al. A three-dimensional organoid culture system derived from human glioblastomas recapitulates the hypoxic gradients and cancer stem cell Heterogeneity of Tumors Found In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2016;76(8):2465-2477. [28] EIRAKU M, WATANABE K, MATSUO-TAKASAKI M, et al. Self-organized formation of polarized cortical tissues from ESCs and its active manipulation by extrinsic signals[. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(5):519-532. [29] KIRWAN P, TURNER-BRIDGER B, PETER M, et al. Development and function of human cerebral cortex neural networks from pluripotent stem cells in vitro. Development. 2015;142(18):3178-3187. [30] 卢国庆,孙正宇,康品方,等.心脏类器官的生物构建策略及应用进展[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2023,44(7):664-670. [31] TUVESON D, CLEVERS H. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science. 2019;364(6444):952-955. [32] ASHOK A, CHOUDHURY D, FANG Y, et al. Towards manufacturing of human organoids. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107460. [33] SHANKARAN A, PRASAD K, CHAUDHARI S, et al. Advances in development and application of human organoids. Biotech. 2021;11(6):257. [34] HOFER M, LUTOLF MP. Engineering organoids. Nat Rev Mater. 2021;6(5): 402-420. [35] TAKEDA M, MIYAGAWA S, FUKUSHIMA S, et al. Development of in vitro drug-induced cardiotoxicity assay by using three-dimensional cardiac tissues derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2018;24:56-67. [36] 刘昕彦,邵瑞,贺爽,等.类器官和立体细胞模型在中药心脏毒性评价中的应用前景[J].药学学报,2019,54(11):1888-1894. [37] 王美佳.皮肤类器官的构建及大面积皮肤损伤的修复研究[D].长春:长春理工大学,2022. [38] ZINK D, CHUAH JKC, YING JY. Assessing toxicity with human cell-based invitro methods. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(6):570-582. [39] LIU Y, LUO HL, WANG XW, et al. In vitro construction of scaffold-free bilayered tissue-engineered skin containing capillary networks. BioMed Res. Int. 2013;2013:561410. [40] 张艳云,李润芝,姜珊,等.三维表皮模型Epikutis®参考品的研制[J].药物分析杂志,2019,39(12):2117-2125. [41] ALÉPÉE N, GRANDIDIER MH, COTOVIO J, et al. Sub-categorisation of skin corrosive chemicals by the EpiSkinTM reconstructed human epidermis skin corrosion test method according to UN GHS: Revision of OECD Test Guideline 431. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014;28(2):131-145. [42] 刘洋,卢涛,周宙霖,等.HaCaT表皮模型作为皮肤刺激性体外替代实验的可行性研究[J].干细胞与组织工程,2017,31(10):1262-1266. [43] 张劲松,何立成,桑晶,等.EpiskinTM和Epikutis®模型在体外皮肤刺激性和腐蚀性检测应用中的比较[J].中国现代应用药学,2017,34(4): 524-526. [44] 姜珊,陈亮,吴美玉,等.金核/银壳纳米棒在三维表皮模型中的透皮行为和对组织活力的影响[J]. 药物分析杂志,2019,39(3):377-385. [45] 郭正昌,周波.类器官的研究现状及其作为临床前模型的应用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2022,57(3):500-503. [46] BAERT Y, DE KOCK J, ALVES-LOPES JP, et al. Primary human testicular cells self-organize into organoids with testicular properties. Stem Cell Rep. 2017; 8(1):30-38. [47] TURCO MY, GARDNER L, HUGHES J, et al. Long-term,hormone-re-sponsive organoid cultures of human endometrium in a chemically defined medium. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(5):568-577. [48] DE OLIVEIRA LF, MENDES FILHO D, MARQUES BL, et al. Organoids as a novel tool in modelling infectious diseases. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2023;144:87-96. [49] BLUTT SE, ESTES MK. Organoid models for infectious disease. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:167-182. [50] YIN Y, BIJVELDS M, DANG W, et al. Modeling rotavirus infection and antiviral therapy using primary intestinal organoids. Antiviral Res. 2015;123:120-131. [51] JANOWSKI AB, BAUER IK, HOLTZ LR, et al. Propagation of astrovirus VA1, a neurotropic human astrovirus, in cell culture. J Virol. 2017;91(19):e00740-17. [52] ETTAYEBI K, CRAWFORD SE, MURAKAMI K, et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell–derived human enteroids. Science. 2016;353(6306): 1387-1393. [53] VU DL, BOSCH A, PINTÓ RM, et al. Human astrovirus MLB replication in vitro: persistence in extraintestinal cell lines. J Virol. 2019;93(13):10-1128. [54] KOLAWOLE AO, MIRABELLI C, HILL DR, et al. Astrovirus replication in human intestinal enteroids reveals multi-cellular tropism and an intricate host innate immune landscape. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(10):e1008057. [55] ZHAO B, NI C, GAO R, et al. Recapitulation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and cholangiocyte damage with human liver ductal organoids. Protein Cell. 2020;11(10):771-775. [56] LESAVAGE BL, SUHAR RA, BROGUIERE N, et al. Next-generation cancer organoids. Nat Mater, 2022;21(2):143-159. [57] DROST J, CLEVERS H. Organoids in cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018; 18(7):407-418. [58] ABOULKHEYR ES H, MONTAZERI L, AREF AR, et al. Personalized cancer medicine: an organoid approach. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(4):358-371. [59] BERTHIAUME F, MAGUIRE TJ, YARMUSH ML. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: history, progress, and challenges. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2011;2:403-430. [60] SUGIMOTO S, KOBAYASHI E, FUJII M, et al. An organoid-based organ repurposing approach to treat short bowel syndrome. Nature. 2021; 592(7852):99-104. [61] SAMPAZIOTIS F, MURARO D, TYSOE OC, et al. Cholangiocyte organoids can repair bile ducts after transplantation in the human liver. Science. 2021; 371(6531):839-846. [62] CUBO N, GARCIA M, DEL CANIZO JF, et al. 3D bioprinting of functional human skin: production and in vivo analysis. Biofabrication. 2016;9(1):015006. [63] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, LU WF, FUH JY. 3D bioprinting of skin: a state-of-the-art review on modelling, materials, and processes. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032001. [64] JANG J, PARK HJ, KIM SW, et al. 3D printed complex tissue construct using stem cell-laden decellularized extracellular matrix bioinks for cardiac repair. Biomaterials. 2017;112:264-274. [65] ZHANG YS, ARNERI A, BERSINI S, et al. Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials. 2016;110:45-59. [66] CHOI WH, BAE DH, YOO J. Current status and prospects of organoid-based regenerative medicine. BMB Rep. 2023;56(1):10-14. [67] LI J, HE L, ZHOU C, et al. 3D printing for regenerative medicine: From bench to bedside. MRS Bull. 2015;40(2):145-154. [68] TARAFDER S, BALLA VK, DAVIES NM, et al. Microwave‐sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regener Med. 2013;7(8):631-641. [69] TARAFDER S, DAVIES NM, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. 3D printed tricalcium phosphate bone tissue engineering scaffolds: effect of SrO and MgO doping on in vivo osteogenesis in a rat distal femoral defect model. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(12):1250-1259. [70] LEE CH, MARION NW, HOLLISTER S, et al. Tissue Formation and Vascularization in Anatomically Shaped Human Joint Condyle Ectopically in Vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(12):3923-3930. [71] LEE CH, COOK JL, MENDELSON A, et al. Regeneration of the articular surface of the rabbit synovial joint by cell homing: a proof of concept study. Lancet. 2010;376(9739):440-448. [72] 郭贝贝,胡慧丽.类器官在发育与再生中的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1111-1119. [73] 李潇萌,管若羽,高建军,等.类器官在再生医学中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1120-1131. [74] BOUFFI C, WIKENHEISER-BROKAMP KA, CHATURVEDI P, et al. In vivo development of immune tissue in human intestinal organoids transplanted into humanized mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41(6):824-831. [75] VOTANOPOULOS KI, FORSYTHE S, SIVAKUMAR H, et al. Model of Patient-Specific Immune-Enhanced Organoids for Immunotherapy Screening: Feasibility Study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:1956-1967. [76] FDA.Drug development tool (DDT)qualification programs. 2023-04-06[2023-07-03]. https: //www.Fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-development-tool-ddt-qualification-programs. [77] FDA. FDA’s predictive toxicology roadmap. 2017-12-30 [2023-07-03]. https://www. Fda. Gov/science-research/About-science-research-fda/fdas-predictive-toxicology-Roadmap. [78] 傅丽霞,张秀莉,庞晓丛,等.类器官和器官芯片在新药评价中的应用及国内外监管现状分析[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2023,39(18):2724-2730. [79] UNION E. Directive 2010/63 /EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes Text with EEA relevance. 2019-06-26[2023-07-03]. https://eur-lex.Europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj. [80] EMA. Reflection paper on the qualification of non - genotoxic impurities. 2018 -11- 15[2023 -07-03].https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-qualification-non-genotoxic-impurities_en.pdf. [81] EMA. Consolidated 3 - year work plan for the Non - clinical domainincluding the priorities for 2023.2023-01-26[2023-07-03]. https://www.ema. europa.eu/en/documents/otherlconsolidated-3-year-work-plan-non-clinical-do-main-including-priorities-2023_en. pdf. [82] 罗会宇,马永慧.人源类器官的应用前景,伦理风险与治理建议[J].科技导报,2022,40(8): 6-13. [83] 高建超.关于我国细胞治疗产业发展现况和监管思路的浅见(上)[J].中国医药生物技术,2019,14(3):193-198. [84] 高建超.关于我国细胞治疗产业发展现况和监管思路的浅见(下)[J]. 中国医药生物技术,2022,14(4):289-293. [85] 刘家伟,冯佳佳,孔维华,等.我国生物医药领域中生物医学新技术发展及管理现状的思考[J].医学新知,2023,33(2):136-142. [86] 郑颖,邓诗碧,陈方.干细胞与再生医学技术发展态势研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(4):111-119. [87] 乐晶晶.类器官应用的伦理问题及治理对策研究[D].厦门:厦门大学, 2020. [88] 杨练,冯海洋,许苑晶.3D打印医疗应用及中心建设现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):2110-2115. |
| [1] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [3] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [4] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [5] | 喻 婷, 吕冬梅, 邓 浩, 孙 涛, 程 钎. 淫羊藿苷预处理增强人牙周膜干细胞对M1型巨噬细胞的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [6] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [7] | 胡涛涛, 刘 兵, 陈 诚, 殷宗银, 阚道洪, 倪 杰, 叶凌霄, 郑祥兵, 严 敏, 邹 勇. 过表达神经调节蛋白1的人羊膜间充质干细胞促进小鼠皮肤创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [8] | 金 凯, 唐 婷, 李美乐, 谢裕安. 人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基及外泌体对肝癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [9] | 李帝均, 酒精卫, 刘海峰, 闫 磊, 李松岩, 王 斌. 明胶三维微球装载人脐带间充质干细胞修复慢性肌腱病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [10] | 娄 国, 张 敏, 付常喜. 8周运动预适应增强脂肪干细胞治疗心肌梗死大鼠的效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [11] | 刘 琪, 李林臻, 李玉生, 焦泓焯, 杨 程, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清促进3种细胞共培养体系中软骨细胞增殖和干细胞成软骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [12] | 艾克帕尔·艾尔肯, 陈晓涛, 吾凡别克·巴合提. 成骨诱导人牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体促进炎症微环境下人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [13] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [14] | 谢刘刚, 崔书克, 郭楠楠, 李遨宇, 张菁瑞. 干细胞治疗阿尔茨海默病的研究热点与前沿[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [15] | 彭洪成, 彭国璇, 雷安毅, 林 圆, 孙 红, 宁 旭, 尚显文, 邓 进, 黄明智. 血小板衍生生长因子BB参与生长板损伤修复的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
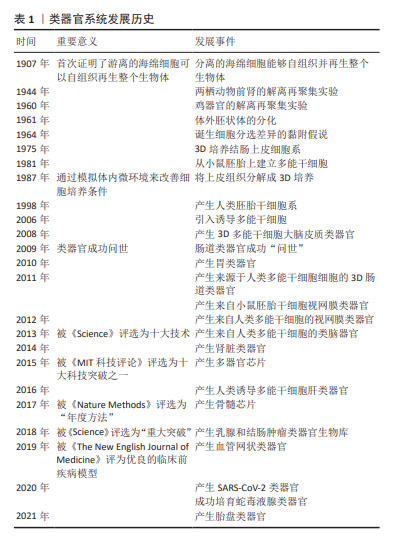
类器官培养技术自2009年肠道类器官成功“问世”以来迅速发展,在生物医学领域逐步成为最具突破性的领域。类器官技术曾分别被《Nature Methods》和《Science》杂志评选为“年度方法”和“年度重大突破”,2021年,中国的“十四五”计划将类器官列入重点研发计划[4]。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2023年9月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索时间范围重点为2010年1月至2023年9月,同时纳入少数远期经典及特别相关文献。
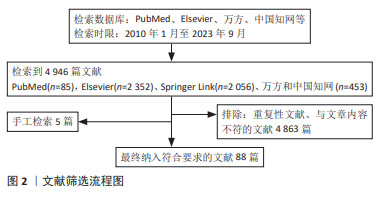
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Elsevier、Springer Link、万方数据和中国知网数据库,以及国家药品监督管理局及FDA网站。
1.1.4 检索词 以“类器官,干细胞,疾病模型,3D打印技术,医疗领域”为中文检索词,以“organoid,stem cell,disease model,3D printing technology,medical field”为英文检索词分别进行检索。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述及荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 对于文献中的高价值参考文献,先阅读文题,再以标题进行检索,阅读摘要或全文。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed 数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.1.8 检索文献量 初检文献4 946篇。
1.2 入选标准1.2.1 纳入标准 类器官与临床应用相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 文献内容与主题无关的文章,重复性研究。
1.3 数据提取和质量评估 检索获得4 946篇文章,其中英文文献4 493篇、中文文献453篇,排除重复文献及与文章相关性低的文献,结合手工检索及远期经典文献,最终纳入88篇文献进行综述分析,包括中文文献26篇、英文文献62篇,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
类器官:是由干细胞经体外3D培养产生的“类似”器官样、具有自我更新和组装能力以及结构和功能与来源组织或器官高度相似的微型器官,类似于组织器官。
疾病模型:是通过对疾病的生理、病理机制进行系统性建模,模拟疾病的发生发展和治疗效果变化的模型。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
3D类器官具有类似于生理组织并在一定程度上模仿器官功能的特点,使其成为从基础发育/干细胞研究到个性化医疗等应用的出色模型。尽管该领域研究近年来迅速扩大,但许多类器官的可能性仍然只是在原理验证水平上显示,尚未得到广泛应用。类器官在以下领域已得到应用:药效评价研究(临床前模型),包括肠道类器官、肾脏类器官、肝脏类器官、胆囊类器官、肺类器官、脑类器官、心脏类器官、皮肤类器官、生殖系统类器官等;传染病研究;肿瘤研究及精准治疗;再生医学;免疫类器官。全球范围内目前均无完善的法规体系,但各国监管机构均在进行相关研究。在国内,类器官医疗器械产品虽暂无已上市产品,但与其相关的再生医学产品已有突破性进展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||