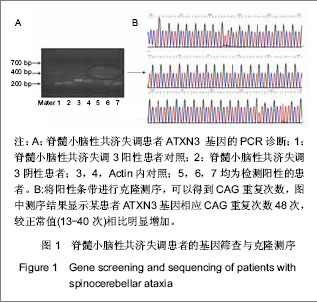
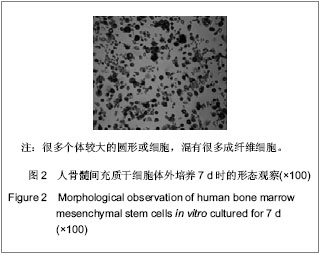
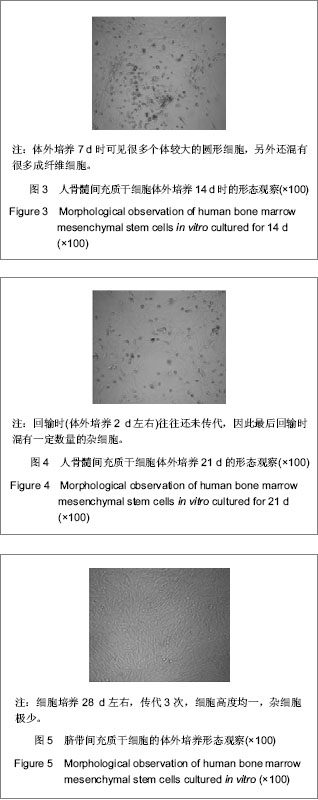
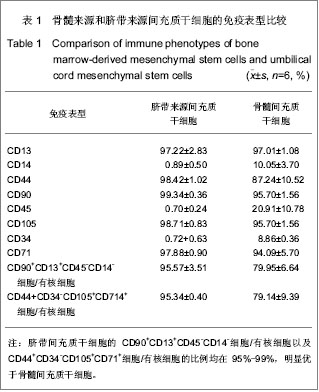
| [1] Koch P, Breuer P, Peitz M, et al.Excitation-induced ataxin-3 aggregation in neurons from patients with Machado-Joseph disease. Nature. 2011;480(7378):543-546. [2] Paulson H.Machado-Joseph Disease: from first descriptions to new perspectives. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;103:437-449.[3] D'Abreu A, França MC Jr, Paulson HL, et al. New insights into the pathoanatomy of spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (Machado-Joseph disease). Curr Opin Neurol. 2008;21(2): 111-116.[4] Yamada M, Sato T, Tsuji S, Takahashi H. CAG repeat disorder models and human neuropathology: similarities and differences. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;115(1):71-86.[5] Zhang L, Tan X, Dong C, et al.In vitro differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs), derived from Wharton's jelly, into choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2012;30(6): 471-477. [6] Datta I, Mishra S, Mohanty L, et al.Neuronal plasticity of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stromal cells to the dopaminergic cell type compared with human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8):918-932.[7] Zhang HT, Fan J, Cai YQ, et al. Human Wharton's jelly cells can be induced to differentiate into growth factor-secreting oligodendrocyte progenitor-like cells.Differentiation. 2010; 79(1):15-20.[8] Peng J, Wang Y, Zhang L, et al. Human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into a Schwann-cell phenotype and promote neurite outgrowth in vitro. Brain Res Bull. 2011;84(3):235-243.[9] Ding DC, Shyu WC, Lin S Z. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(1):5-14.[10] Caimi PF, Reese J, Lee Z, et al. Emerging therapeutic approaches for multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(6):505-513. [11] Lin YC, Ko TL, Shih YH,et al.Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery after ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2011;42(7):2045-2053.[12] Lim JY, Jeong CH, Jun JA,et al.Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells after intrathecal administration by lumbar puncture in a rat model of cerebral ischemia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;22:2(5):38. [13] Kim ES, Ahn SY, Im GH, et al.Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates severe brain injury by permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in newborn rats.Pediatr Res. 2012;72(3):277- 284. [14] Schira J, Gasis M, Estrada V, et al.Significant clinical, neuropathological and behavioural recovery from acute spinal cord trauma by transplantation of a well-defined somatic stem cell from human umbilical cord blood. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 2): 431-446.[15] Hu SL, Luo HS, Li JT, et al. Functional recovery in acute traumatic spinal cord injury after transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(11):2181-2189. [16] Matsuse D, Kitada M, Kohama M,et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells differentiate into functional Schwann cells that sustain peripheral nerve regeneration.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2010;69(9):973-985.[17] Pang KM, Sung MA, Alrash-dan MS, et al. Trans-plantation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord versus human umbilical cord blood for peripheral nerve regenera-tion. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(11):838-845.[18] Seo Y, Yang SR, Jee MK, et al.Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against neuronal cell death and ameliorate motor deficits in Niemann Pick type C1 mice. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(7):1033-1047. [19] Chang YK, Chen MH, Chiang YH, et al.Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation ameliorates motor function deterioration of spinocerebellar ataxia by rescuing cerebellar Purkinje cells.J Biomed Sci. 2011 Aug 8;18:54.[20] Jones J, Jaramillo-Merchán J, Bueno C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells rescue Purkinje cells and improve motor functions in a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia. Neurobiol Dis. 2010; 40(2):415-423. [21] Jones J, Jaramillo-Merchán J, Bueno C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells rescue Purkinje cells and improve motor functions in a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia Neurobiol Dis. 2010; 40(2):415-423. [22] Dey R, Kemp K, Gray E, et al.Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase Anti-oxidant Defences in Cells Derived from Patients with Friedreich's Ataxia. Cerebellum. 2012 Jul 24. [23] Kemp K, Mallam E, Hares K, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells restore frataxin expression and increase hydrogen peroxide scavenging enzymes in Friedreich ataxia fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26098. [24] Yang XF, Xu YF, Lü NW, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6(10): 785-789.[25] Dongmei H, Jing L, Mei X, et al. Clinical analysis of the treatment of spinocerebellar ataxia and multiple system atrophy-cerebellar type with umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(8):913-917.[26] Trouillas P,Takayanagi T,Hallett M,et al. International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale for pharmacological assessment of the cerebellar syndrome. The Ataxia Neuropharmacology Committee of the World Federation of Neurology. J NeurolSci 1997;145:205–211.[27] Matos CA, de Macedo-Ribeiro S, Carvalho AL. C Polyglutamine diseases: the special case of ataxin-3 and Machado-Joseph disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;95(1):26-48. [28] Dalous J, Larghero J, Baud O.Transplantation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells as a novel strategy to protect the central nervous system: technical aspects, preclinical studies, and clinical perspectives.Pediatr Res. 2012;71(4 Pt 2):482-490.[29] Taghizadeh RR, Cetrulo KJ, Cetrulo CL.Wharton's Jelly stem cells: future clinical applications.Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 4: S311-315. [30] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Zhou JR.Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord.Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):195-207.[31] Soleymaninejadian E, Pramanik K, Samadian E. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: cytokines and factors. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2012;67(1):1-8. [32] Momin EN, Mohyeldin A, Zaidi HA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: new approaches for the treatment of neurological diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;5(4):326-344. [33] Zhang MJ, Sun JJ, Qian L, et al.Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells enhance the expression of neurotrophic factors and protect ataxic mice. Brain Res. 2011; 1402:122-131. |