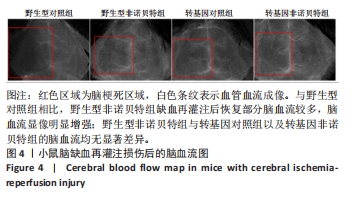
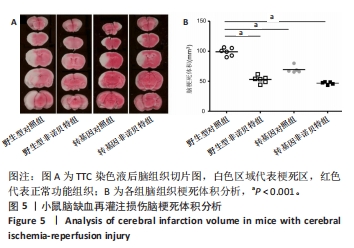
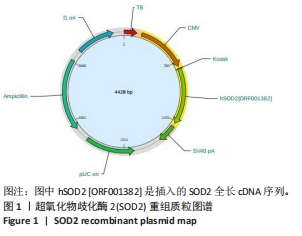
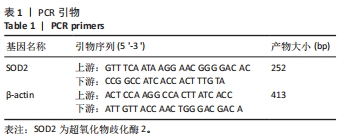
[1] AJOOLABADY A, WANG S, KROEMER G, et al. Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: From molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;225:107848.
[2] YUAN Q, YUAN Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Anti-cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury of polysaccharides: A review of the mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111303.
[3] SU X T, WANG L, MA SM, et al. Mechanisms of Acupuncture in the Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Treating Ischemic Stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:7875396.
[4] ZHU G, WANG X, CHEN L, et al. Crosstalk Between the Oxidative Stress and Glia Cells After Stroke: From Mechanism to Therapies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:852416.
[5] KOWALCZYK P, SULEJCZAK D, KLECZKOWSKA P, et al. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress-A Causative Factor and Therapeutic Target in Many Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13384.
[6] YOO J, JEONG IK, AHN KJ, et al. Fenofibrate, a PPARalpha agonist, reduces hepatic fat accumulation through the upregulation of TFEB-mediated lipophagy. Metabolism. 2021;120:154798.
[7] GUO X, DANG W, LI N, et al. PPAR-alpha Agonist Fenofibrate Ameliorates Sjogren Syndrome-Like Dacryoadenitis by Modulating Th1/Th17 and Treg Cell Responses in NOD Mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022;63(6):12.
[8] JIN L, HUA H, JI Y, et al. Anti-inflammatory role of fenofibrate in treating diseases. Biomol Biomed. 2023;23(3):376-391.
[9] SHEHATA A HF, AHMED A-S F, ABDELREHIM A B, et al. The impact of single and combined PPAR-α and PPAR-γ activation on the neurological outcomes following cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Life Sci. 2020;252:117679.
[10] 杨锡彤, 秦燕, 杜小珊, 等. PPARα调控SOD2表达的机制研究[J].大理大学学报,2018,3(2):27-31.
[11] BULLOCK JJ, MEHTA SL, LIN Y, et al. Hyperglycemia-enhanced ischemic brain damage in mutant manganese SOD mice is associated with suppression of HIF-1alpha. Neurosci Lett. 2009;456(2):89-92.
[12] LI M, TANG H, LI Z, et al. Emerging Treatment Strategies for Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Neuroscience. 2022;507:112-124.
[13] LIU M, SUN X, CHEN B, et al. Insights into Manganese Superoxide Dismutase and Human Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15893.
[14] SCHIEBER M, CHANDEL NS. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 2014;24(10):R453-462.
[15] KLAFKE JZ, DA SILVA MA, ROSSATO MF, et al. Acute and chronic nociceptive phases observed in a rat hind paw ischemia/reperfusion model depend on different mechanisms. Pflugers Arch. 2016;468(2): 229-241.
[16] LIU Y, ZHANG L, LIANG J. Activation of the Nrf2 defense pathway contributes to neuroprotective effects of phloretin on oxidative stress injury after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 351(1-2):88-92.
[17] ZHAO B, JIANG X. hsa-miR-518-5p/hsa-miR-3135b Regulates the REL/SOD2 Pathway in Ischemic Cerebral Infarction. Front Neurol. 2022;13:852013.
[18] YANG X, LI X, ZHONG C, et al. Circular RNA circPHKA2 Relieves OGD-Induced Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Injuries through Competitively Binding miR-574-5p to Modulate SOD2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:3823122.
[19] TOWNSEND K, LAFFAN J, HAYMAN G. Carboxymethylcellulose excipient allergy: a case report. J Med Case Rep.2021;15(1): 565.
[20] MONTAIGNE D, BUTRUILLE L, STAELS B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18(12): 809-823.
[21] TAHRI-JOUTEY M, ANDREOLETTI P, SURAPUREDDI S, et al. Mechanisms Mediating the Regulation of Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation by PPARalpha. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(16):8969.
[22] LEE D, TOMITA Y, NEGISHI K, et al. Pemafibrate, a potent selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α modulator, a promising novel treatment for ischemic retinopathy? Neural Regen Res. 2023; 18(7):1495-1496.
[23] MANDALA A, CHEN W J, ARMSTRONG A, et al. PPARalpha agonist fenofibrate attenuates iron-induced liver injury in mice by modulating the Sirt3 and beta-catenin signaling. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021;321(4):G262-G269.
[24] ZHAO J, WANG G, HAN K, et al. Mitochondrial PKM2 deacetylation by procyanidin B2-induced SIRT3 upregulation alleviates lung ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):594.
[25] BESSON VC, CHEN XR, PLOTKINE M, et al. Fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonist, exerts neuroprotective effects in traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett. 2005;388(1):7-12.
[26] LIU Q, ZHANG X, CHENG R, et al. Salutary effect of fenofibrate on type 1 diabetic retinopathy via inhibiting oxidative stress-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;376(2):165-177.
[27] MO Z, ZENG Z, LIU Y, et al. Activation of Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway as a Promising Therapeutic Candidate for Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:914537.
[28] SHI S, WANG M, LIU X, et al. Scalp Electroacupuncture Promotes Angiogenesis after Stroke in Rats by Activation of Wnt/beta-Catenin Signal Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022: 1649605.
[29] WANG LP, PAN J, LI Y, et al. Oligodendrocyte precursor cell transplantation promotes angiogenesis and remyelination via Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in a mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022;42(5):757-770.
[30] QIU CW, LIU ZY, ZHANG FL, et al. Post-stroke gastrodin treatment ameliorates ischemic injury and increases neurogenesis and restores the Wnt/beta-Catenin signaling in focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 2019;1712:7-15.
[31] SONG F, MAO YJ, HU Y, et al. Acacetin attenuates diabetes-induced cardiomyopathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and energy metabolism via PPAR-alpha/AMPK pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;922:174916.
[32] LI LX, YIN LH, GAO M, et al. MiR-23a-5p exacerbates intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting oxidative stress via targeting PPAR alpha. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;180:114194. |