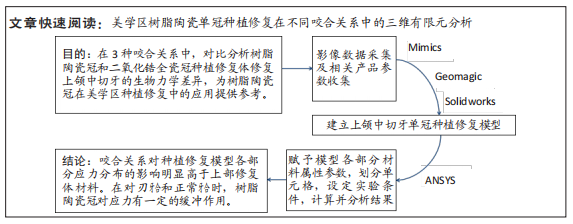
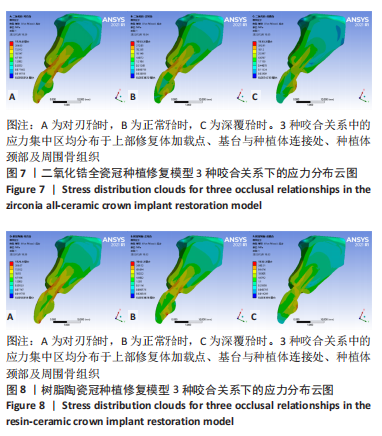
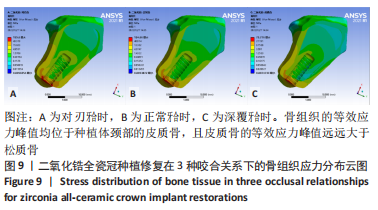
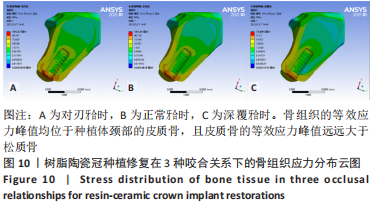
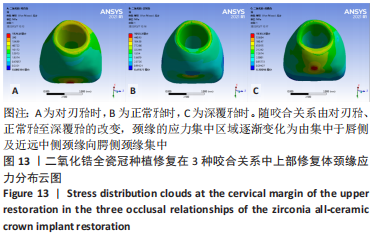
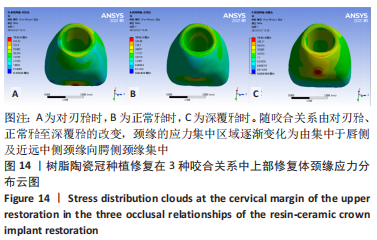
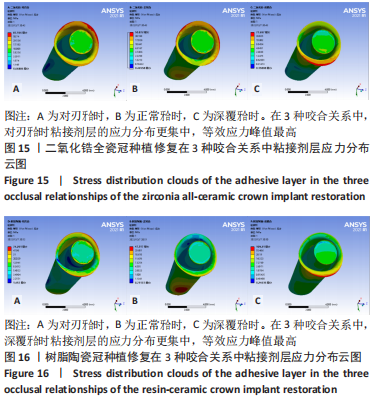
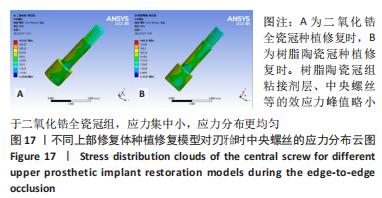
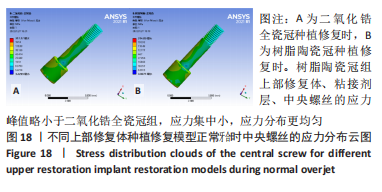
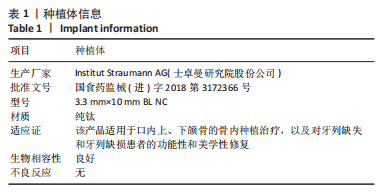
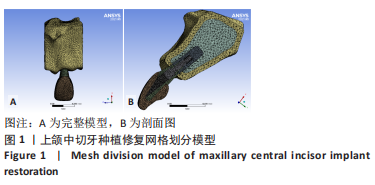
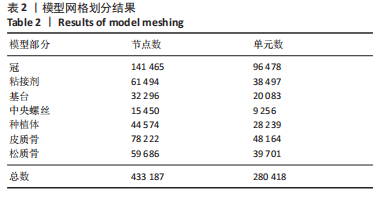
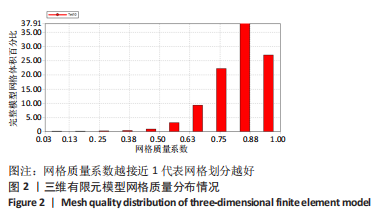
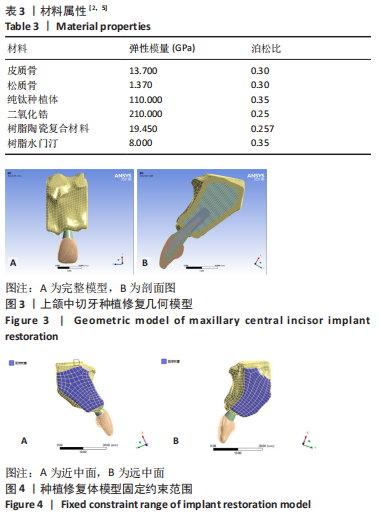
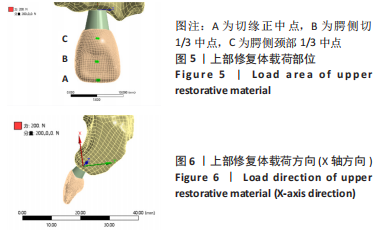
[1] 全泉.口腔种植修复对前牙牙列缺损患者修复成功率及对患者预后的影响[J].中国医药指南,2021,19(27):52-54.
[2] 洪煜锐,李阳,骆伟燕,等.树脂陶瓷复合材料单冠美学区种植修复的三维有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2020,29(3):262-266.
[3] Rammelsberg P, Lorenzo Bermejo J, Kappel S, et al. Long-term performance of implant-supported metal-ceramic and all-ceramic single crowns. J Prosthodont Res. 2020;64(3):332-339.
[4] 郭馨蔚,张志民,赵洪岩.CAD/CAM陶瓷材料的分类及研究进展[J].口腔生物学, 2019,10(2):109-113.
[5] 白布加甫·叶力思,热娜古丽·买合木提,艾孜买提江·赛依提,等.上颌中切牙联冠种植修复体在不同咬合方式中的应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):567-572.
[6] 肖严,熊康,权菲菲.不同咬合状态下上颌中切牙全瓷冠修复的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(12):1806-1811.
[7] Zucchelli G, Tavelli L, Stefanini M, et al. Classification of facial peri-implant soft tissue dehiscence/deficiencies at single implant sites in the esthetic zone. J Periodontol. 2019;90(10):1116-1124.
[8] 陈菊仙,张蕊.天然上颌中切牙与种植体应力规律的三维有限元分析[J].中外医学研究,2018,16(7):67-69.
[9] 陈恩,李守宏.种植修复后基台或中央螺丝折断的原因及预防[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(6):375-378.
[10] Alqutaibi AY, Alnazzawi AA, Algabri R, et al.Clinical performance of single implant-supported ceramic and metal-ceramic crowns: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;26(3): 369-376.
[11] 林志明,陈宏柏,彭秀燕.两种冠修复材料对牙周状况及龈沟液中TWEAK、RANKL水平的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(8):467-470.
[12] Nejatidanesh F, Abbasi M, Savabi G, et al. Five year clinical outcomes of metal ceramic and zirconia-based implant-supported dental prostheses: a retrospective study. J Dent. 2020;100:103420.
[13] Cantó-Navés O, Medina-Galvez R, Marimon X, et al. A 3D Finite Element Analysis Model of Single Implant-Supported Prosthesis under Dynamic Impact Loading for Evaluation of Stress in the Crown, Abutment and Cortical Bone Using Different Rehabilitation Materials. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(13):3519.
[14] 中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会.树脂陶瓷复合材料椅旁计算机辅助设计与辅助制作修复技术指南[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2022,57(9):895-898.
[15] 刘丽杨,郭佳杰,杜亚鑫,等.3种可切削树脂陶瓷复合材料机械性能比较[J].上海口腔医学,2019,28(1):25-29.
[16] 李佳,曾剑玉,张思佳.冷热老化和循环加载后单冠材料影响种植体周围骨应力时间传导的光弹分析[J].北京口腔医学,2018,26(5):250-255.
[17] 姜澜.可切削树脂复合陶瓷CAD/CAM高嵌体修复根管治疗后牙缺损的临床观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2020,13(22):159-160.
[18] Lambert H, Durand JC, Jacquot B, et al. Dental biomaterials for chairside CAD/CAM: State of the art. J Adv Prosthodont. 2017;9(6):486-495.
[19] Bergamo ETP, Yamaguchi S, Coelho PG, et al. Survival of implant-supported resin-matrix ceramic crowns: in silico and fatigue analyses. Dent Mater. 2021;37(3):523-533.
[20] 李杰森.树脂基陶瓷在种植牙冠修复厚度设计的研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2021.
[21] Miura S, Kasahara S, Yamauchi S, et al. Effect of finish line design on stress distribution in bilayer and monolithic zirconia crowns: a three‐dimensional finite element analysis study. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018;126(2):159-165.
[22] Hosseini-Faradonbeh SA, Katoozian HR. Biomechanical evaluations of the long-term stability of dental implant using finite element modeling method: a systematic review. J Adv Prosthodont. 2022;14(3):182-202.
[23] 胡建,章非敏,戴宁,等.不同基底冠材料对上颌中切牙全瓷冠受载应力分布的影响[J].口腔生物医学,2013,4(2):74-78.
[24] 陈垂史,李阳.牙种植术中机械并发症发生原因及处理体会[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2019,24(2):82-85.
[25] Staedt H, Heimes D, Lehmann KM, et al. Does the Modification of the Apical Geometry of a Dental Implant Affect Its Primary Stability? A Comparative Ex Vivo Study. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(7):1728.
[26] 姜佳杨.美学区即刻与早期种植软硬组织变化的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2022.
[27] Zandim-Barcelos DL, Carvalho GG, Sapata VM, et al. Implant-based factor as possible risk for peri-implantitis. Braz Oral Res. 2019;33(suppl 1):e067.
[28] Zupancic Cepic L, Frank M, Reisinger A, et al. Biomechanical finite element analysis of short-implant-supported, 3-unit, fixed CAD/CAM prostheses in the posterior mandible. Int J Implant Dent. 2022;8(1):8.
[29] 万林子,孙蕾,吴熙凤,等.天然上颌中切牙与种植体应力规律的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(16):2545-2550.
[30] 安尼卡尔·安尼瓦尔,帕丽黛姆·图尔迪,阿迪力·麦木提敏,等.上颌前牙区不同种植修复体在不同咬合受力下的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(16):2531-2536.
[31] Krejci I, Daher R. Stress distribution difference between Lava Ultimate full crowns and IPS e.max CAD full crowns on a natural tooth and on tooth-shaped implant abutments. Odontology. 2017;105(2):254-256.
[32] 张思佳,曾剑玉,李佳,等.三种单冠对种植体周围骨应力分布影响的光弹分析[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2018,53(1):30-35.
[33] Ercal P, Taysi AE, Ayvalioglu DC, et al. Impact of peri-implant bone resorption, prosthetic materials, and crown to implant ratio on the stress distribution of short implants: a finite element analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021;59(4):813-824.
[34] 邹英楠,王屹博,丁超,等.动态载荷下牙半切与种植体联合修复的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):178-183. |