中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (33): 5327-5333.doi: 10.12307/2023.724
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
山楂叶总黄酮调控星形胶质细胞治疗脊髓损伤的分子机制
马瑞鑫1,刘 槃2,张 琼3,曾高峰3,宗少晖1,2
- 广西医科大学,1再生医学与医用生物资源开发应用省部共建协同创新中心,3公共卫生学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;2 广西医科大学第一附属医院脊柱骨病外科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Molecular mechanism of total flavonoids of hawthorn leaves regulating astrocytes to repair spinal cord injury
Ma Ruixin1, Liu Pan2, Zhang Qiong3, Zeng Gaofeng3, Zong Shaohui1, 2
- 1Collaborative Innovation Center of Regenerative Medicine and Medical BioResource Development and Application Co-constructed by the Province and Ministry, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spinal Osteopathy, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3School of Public Health, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
山楂叶总黄酮:是从蔷薇科植物山里红的干燥叶中提取的天然黄酮类化合物,在抗炎症、抗氧化损伤、防止神经退行性病变、预防神经系统疾病和防止中风等方面有较好的效果。脊髓损伤:是由于各种不同致病因素引起脊髓结构和功能的损伤,可导致严重的运动、感觉和自主神经功能障碍,其主要原因是神经元的损失。在治疗过程中,神经元的修复至关重要,避免因神经元损失后不可再生导致永久性功能丧失。
背景:星形胶质细胞对脊髓损伤后神经元的修复具有重要作用,有研究证明山楂叶总黄酮可促进大鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复,山楂叶总黄酮是否影响星形胶质细胞促进神经元修复仍不清楚。
目的:探索山楂叶总黄酮调控星形胶质细胞治疗脊髓损伤的分子机制。
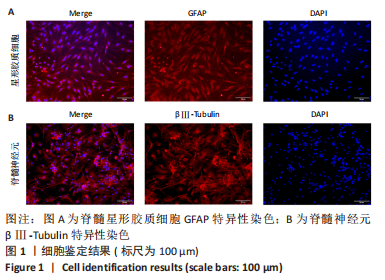
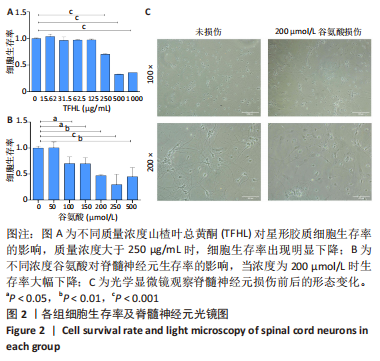
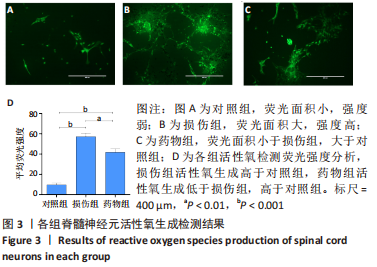
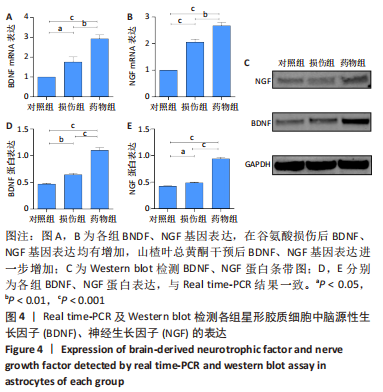
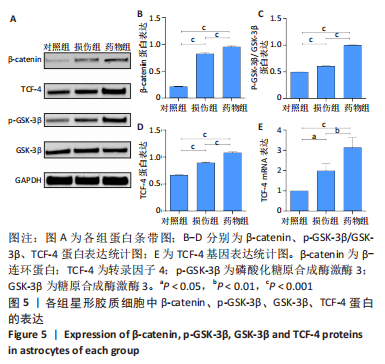
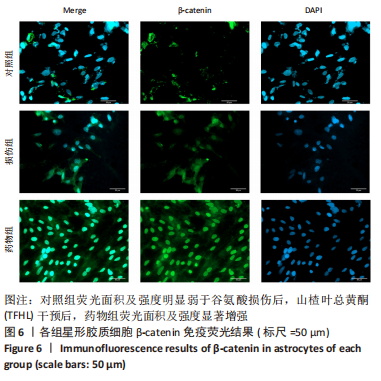
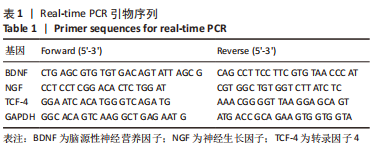
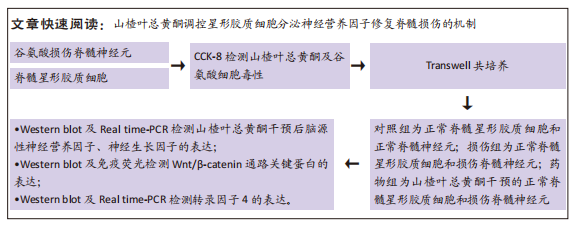
方法:构建脊髓星形胶质细胞与脊髓神经元 transwell共培养模型,对照组为正常脊髓星形胶质细胞和正常脊髓神经元;损伤组为正常脊髓星形胶质细胞和损伤脊髓神经元;药物组为125 μg/mL山楂叶总黄酮干预的正常脊髓星形胶质细胞和损伤脊髓神经元。荧光探针DCFH-DA检测脊髓神经元内活性氧的生成;实时荧光定量PCR检测脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子、转录因子4的表达;Western blot检测脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子、Wnt/β-catenin通路关键蛋白GSK-3β、phsopho-GSK-3β(ser9)、β-catenin及转录因子4的表达;免疫荧光观察Wnt/β-catenin通路关键蛋白β-catenin的表达。
结果与结论:①损伤组活性氧生成远高于对照组(P < 0.001);药物组活性氧生成低于损伤组(P < 0.01),高于对照组(P < 0.001);②药物组脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子基因及蛋白表达高于对照组与损伤组(P < 0.01);③与对照组、损伤组相比,药物组phsopho-GSK-3β(ser9)蛋白表达增加(P < 0.001),β-catenin蛋白表达增加(P < 0.001),转录因子4基因及蛋白表达增加(P < 0.01);④结果表明,山楂叶总黄酮可以减轻脊髓神经元的氧化损伤,激活星形胶质细胞Wnt/β-catenin通路,结合转录因子4启动转录,促进其分泌神经营养因子,实现对脊髓神经元的修复。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2162-0391 (马瑞鑫)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: