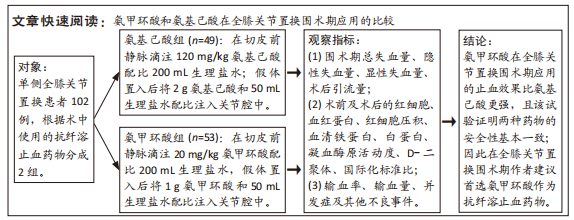
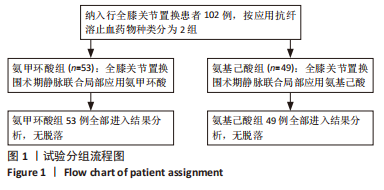
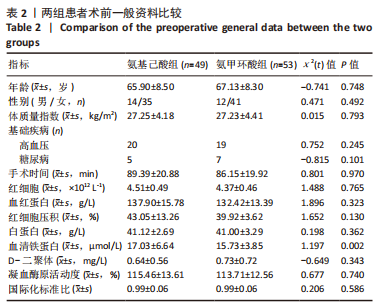
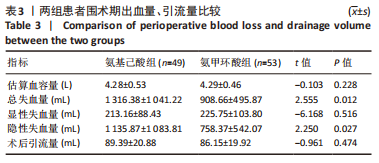
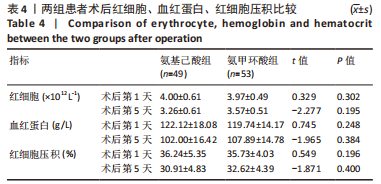
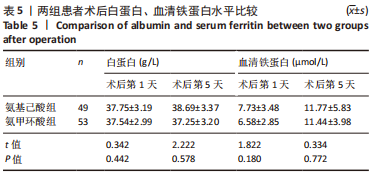
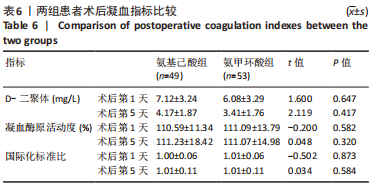
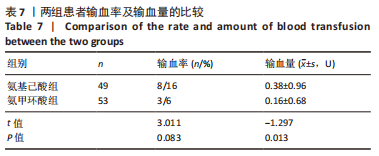
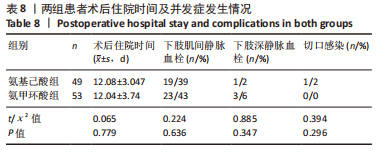
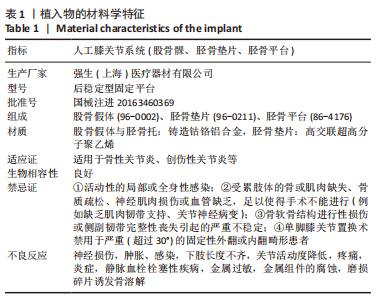
[1] 郑创史, 邱钊禹. 超声波检查在膝骨关节炎早期诊断中的应用价值分析[J]. 内科, 2017,12(5):654-656.
[2] 宁吉喆. 第七次全国人口普查主要数据情况[J]. 中国统计,2021(5):4-5.
[3] 姚美华, 许文娟, 沈微烨. 快速康复外科理念在膝关节单髁置换术患者中的应用[J]. 齐鲁护理杂志,2018,24(20):68-71.
[4] 王成龙, 唐玉梅, 尹东, 等. 尿路感染及无症状性菌尿与人工关节置换术后假体周围感染关系的研究进展[J]. 广东医学,2018,39(17):2672-2674.
[5] MIYAZAKI S, YOSHINAGA S, TSURUTA K, et al. Total Knee Arthroplasty Improved Locomotive Syndrome in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study Focused on Total Clinical Decision Limits Stage 3. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:3919989.
[6] 朱法政, 王沐, 蔡楠楠, 等. 帕瑞昔布钠对膝骨性关节炎患者全膝关节置换术后膝关节功能及血清炎性反应的影响[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2019,39(7):1471-1475.
[7] LAWRIE CM, SCHWABE M, PIERCE A, et al. The cost of implanting a cemented versus cementless total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019; 101-b(7_Supple_C):61-63.
[8] GARCIA D. Hybrid Strategy to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism after Joint Arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):762-763.
[9] 莫小汕, 滕居赞, 李彪, 等. 氨甲环酸在骨科围手术期中的应用研究进展[J]. 黑龙江中医药,2018,47(1):94-96.
[10] SPAHN DR. Anemia and patient blood management in hip and knee surgery: a systematic review of the literature. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(2):482-495.
[11] ARTHI PN, JALAKANDAN B, GUNASEELAN S. Effect of prophylactic tranexamic acid on blood conservation in Indian women undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. Int J Rep Contr Obstet Gynecol. 2018. doi: 10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20183415.
[12] ESTCOURT LJ, DESBOROUGH M, BRUNSKILL SJ, et al. Antifibrinolytics (lysine analogues) for the prevention of bleeding in people with haematological disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;3(3):Cd009733.
[13] DEVEREAUX PJ, MARCUCCI M, PAINTER TW, et al. Tranexamic Acid in Patients Undergoing Noncardiac Surgery. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(21):1986-1997.
[14] PORTER SB, WHITE LJ, OSAGIEDE O, et al. Tranexamic Acid Administration Is Not Associated With an Increase in Complications in High-Risk Patients Undergoing Primary Total Knee or Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case-Control Study of 38,220 Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(1):45-51.e3.
[15] WU J, ZHOU YQ, DENG JH, et al. Ideal intraarticular application dose of tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized and controlled study. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(21):1353.
[16] TSUKADA S, KUROSAKA K, NISHINO M, et al. Intraoperative Intravenous and Intra-Articular Plus Postoperative Intravenous Tranexamic Acid in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(8):687-692.
[17] BRAVO D, JOSEPHSON AM, BRADASCHIA-CORREA V, et al. Temporary inhibition of the plasminogen activator inhibits periosteal chondrogenesis and promotes periosteal osteogenesis during appendicular bone fracture healing. Bone. 2018;112:97-106.
[18] HARLEY BJ, BEAUPRé LA, JONES CA, et al. The effect of epsilon aminocaproic acid on blood loss in patients who undergo primary total hip replacement: a pilot study. Can J Surg. 2002;45(3):185-190.
[19] AKGÜL T, BÜGET M, SALDUZ A, et al. Efficacy of preoperative administration of single high dose intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: A prospective clinical study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(4):429-431.
[20] PACHAURI A, ACHARYA KK, TIWARI AK. The effect of tranexamic acid on hemoglobin levels during total knee arthroplasty. Am J Ther. 2014;21(5): 366-370.
[21] PARK D, CHOI YH, CHO KH, et al. 3-h drain clamping is not effective to reduce total blood loss after primary total knowledge. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2020;32(1):33.
[22] TILLE E, MYSLIWIETZ J, BEYER F, et al. Intraarticular use of tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rate after primary total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):341.
[23] CHEN L, YU Y. Exercise and Osteoarthritis. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020;1228: 219-231.
[24] KOLASINSKI SL, NEOGI T, HOCHBERG MC, et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(2):149-162.
[25] ROTHBAUER F, ZERWES U, BLEß HH, et al. Prevalence of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty//BLEß HH, KIP M. White Paper on Joint Replacement: Status of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Care in Germany. Berlin (Germany); Springer Copyright 2018, The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s). 2018:15-39.
[26] CHOU SH, SHIH CL. Efficacy of different platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of mild-moderate knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(6):e14068.
[27] TAI TW, LIN CJ, JOU IM, et al. Tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(7):1121-1130.
[28] GOOD L, PETERSON E, LISANDER B. Tranexamic acid decreases external blood loss but not hidden blood loss in total knee replacement. Br J Anaesth. 2003;90(5):596-599.
[29] 李宏波, 旦锋, 阮文辉, 等. 关节腔内注射氨甲环酸对人工膝关节置换术后患者引流量与血红蛋白及凝血功能水平的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2018,7(4):261-265.
[30] LU X, LIN J. Low molecular weight heparin versus other anti-thrombotic agents for prevention of venous thromboembolic events after total hip or total knee replacement surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):322.
[31] KOSTER A, FARAONI D, LEVY JH. Antifibrinolytic Therapy for Cardiac Surgery: An Update. Anesthesiology. 2015;123(1):214-221.
[32] 杨鹏, 马俊, 曾俊峰, 等. 氨基己酸与氨甲环酸用于全髋关节置换术的随机对照研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(3):214-218.
[33] HUNT BJ. The current place of tranexamic acid in the management of bleeding. Anaesthesia. 2015;70 Suppl 1:50-53,e18.
[34] LI G, SUN TW, LUO G, et al. Efficacy of antifibrinolytic agents on surgical bleeding and transfusion requirements in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(1):140-54.
[35] MORALES-AVALOS R, RAMOS-MORALES T, ESPINOZA-GALINDO AM,
et al. First Comparative Study of the Effectiveness of the Use of Tranexamic Acid against ε-Aminocapróic Acid via the Oral Route for the Reduction of Postoperative Bleeding in TKA: A Clinical Trial. J Knee Surg. 2021;34(4): 383-405.
[36] BOESE CK, CENTENO L, WALTERS RW. Blood Conservation Using Tranexamic Acid Is Not Superior to Epsilon-Aminocaproic Acid After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(19):1621-1628.
[37] 张晋, 杨自权. 氨甲环酸和ε-氨基己酸在髋膝关节置换术中止血疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2022,35(5):484-90.
[38] DUNCAN CM, GILLETTE BP, JACOB AK, et al. Venous thromboembolism and mortality associated with tranexamic acid use during total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(2):272-276.
[39] DONG Q, ZHANG Y, SUN X, et al. The effectiveness and safety of aminocaproic acid for reducing blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;52:156-163.
[40] 鲁超, 郭浩, 郝阳泉, 等. 多途径应用氨甲环酸降低全髋关节置换术围术期失血的前瞻性随机对照研究[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(2): 140-144.
[41] LIU Q, GENG P, SHI L, et al. Tranexamic acid versus aminocaproic acid for blood management after total knee and total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;54(Pt A):105-112. |