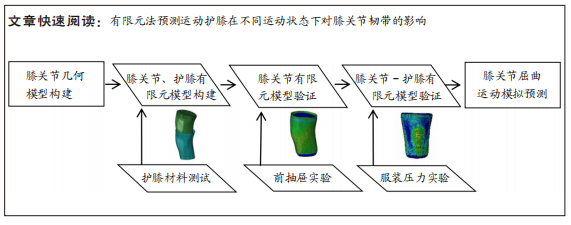
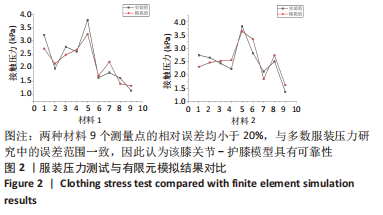
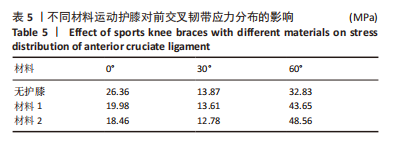
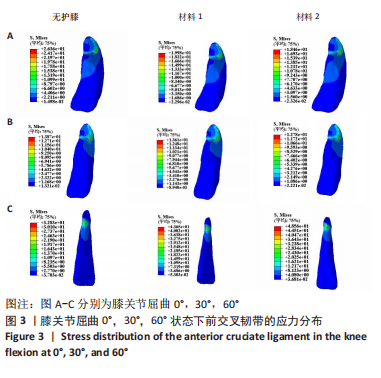
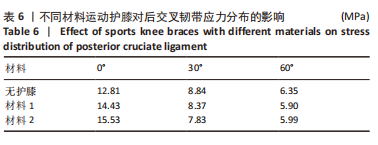
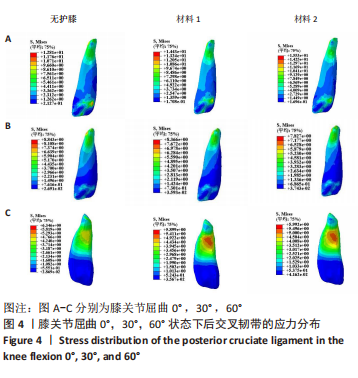
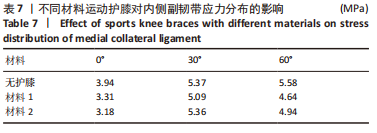
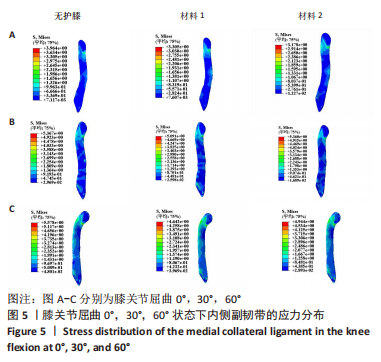
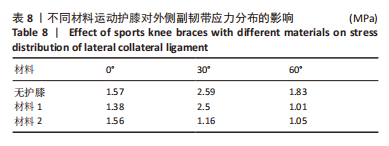
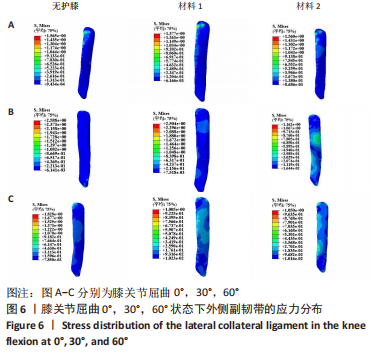
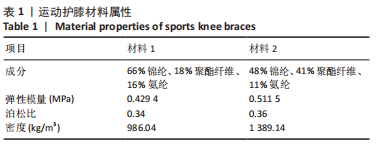
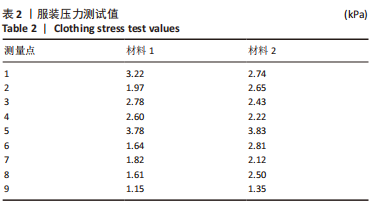
[1] MAJEWSKI M, SUSANNE H, KLAUS S. Epidemiology of athletic knee injuries: A 10-year study. Knee. 2006;13(3):184-188.
[2] POSCH M, SCHRANZ A, LENER M, et al. In recreational alpine skiing, the ACL is predominantly injured in all knee injuries needing hospitalisation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(6):1790-1796.
[3] BROPHY RH, WOJTYS EM, MACK CD, et al. Factors associated with the Mechanism of ACL tears in the National Football League: A Video-Based Analysis. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(11):23259671211053301.
[4] MANIAR N, VERHAGEN E, BRYANT AL, et al. Trends in Australian knee injury rates: An epidemiological analysis of 228,344 knee injuries over 20 years. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2022;21:100409.
[5] 陈凌娴,李俊,王敏.护膝防护性能及其功能设计研究进展[J].毛纺科技,2022,50(3):117-123.
[6] MOON J, KIM H, LEE J, et al. Effect of wearing a knee brace or sleeve on the knee joint and anterior cruciate ligament force during drop jumps: A clinical intervention study. Knee. 2018;25(6):1009-1015.
[7] 荆晓伟, 母应秀. 硅网支具对前交叉韧带损伤及膝关节稳定性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):505-510.
[8] ALTHOMALI OW. Influence of using knee sleeve and lateral wedge insole on knee loading among healthy individuals during stair negotiation. Gait Posture. 2022;92:103-109.
[9] VALLDECABRES R, DE BENITO AM, LITTLER G, et al. An exploration of the effect of proprioceptive knee bracing on biomechanics during a badminton lunge to the net, and the implications to injury mechanisms. Peer J. 2018;6:e6033.
[10] JIANG T, TIAN S, FAN X, et al. Kinematics and kinetics of lower-extremity joints in parachuting landing with backpack and knee brace. Med Eng Phys. 2020;86:1-7.
[11] BOTTONI G, HERTEN A, KOFLER P, et al. The effect of knee brace and knee sleeve on the proprioception of the knee in young non-professional healthy sportsmen. Knee. 2013;20(6):490-492.
[12] KRAMI M, QIAN Z, ZOU Z, et al. Subject-specific finite element modelling of the human foot complex during walking: sensitivity analysis of material properties, boundary and loading conditions. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(2):559-576.
[13] PENA E, CALVO B, MARTINEZ MA, et al. A three -dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1686-1701.
[14] 万超杰.人体大臂软组织活体力学特性分析[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2017.
[15] 何川,李彦林,张振光,等.不同屈曲状态下膝关节韧带生物力学的有限元分析[J].中国运动医学杂志,2015,34(7):662-669.
[16] 孙亚博. 基于有限元模拟的针织服装穿着压力分析[D].天津:天津工业大学,2021.
[17] GROOD ES, SUNTAY WJ. A joint coordinate system for the clinical description of three-dimensional motions: application to the knee. J Biomech Eng. 1983;105(2):136-144.
[18] SKINNER H. Current diagnosis and treatment in orthopedics.USA: McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing. 2006.
[19] 黎蒙. 女性羽毛球运动员头顶球单腿落地动作的膝关节生物力学有限元分析[D].上海:上海体育学院,2020.
[20] GABRIEL MT, WONG EK, WOO SLY, et al. Distribution of in situ forces in the anterior cruciate ligament in response to rotatory loads. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(1):85-89.
[21] SONG YH, DEBSKI RE, MUSAHL V, et al. A three -dimensional finite element model of the human anterior cruciate ligament: A computational analysis with experimental validation. J Biomech. 2004; 37(3):383- 390.
[22] 万超,郝智秀,温诗铸.前交叉韧带力学特性差异对膝关节有限元仿真结果的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(4):375-380.
[23] SHERMAN MF, LIEBER L, BONAMO JR, et al. The long-term followup of primary anterior cruciate ligament repair. Defining a rationale for augmentation. Am J Sports Med. 1991;19(3):243-255.
[24] YU A, YICK KL, NG SP, et al. Numerical simulation of pressure therapy glove by using Finite Element Method. Burns. 2016;42(1):141-151.
[25] 于洁.基于人体臂部模型的服装压测试与数值模拟[D].天津:天津工业大学,2019.
[26] CHEW KT, LEW HL, DATE E, et al. Current evidence and clinical applications of therapeutic knee braces. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2007; 86(8):678-686.
[27] COUDEYRE E, NGUYEN C, CHABAUD A, et al. A decision-making tool to prescribe knee orthoses in daily practice for patients with osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2018;61(2):92-98.
[28] 庞欣.高弹护膝纺织品的开发与压力性能分析[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2018.
[29] 沈妙音.抗菌热湿舒适性服用机织物的研究与开发[D].杭州:浙江理工大学,2021.
[30] 匡新谋,苏敏茹,李浩,等.预处理工艺对回收涤纶/锦纶/氨纶混合纤维改性聚丙烯力学性能影响[J].工程塑料应用,2020,48(9): 78-82.
[31] WIGGINS AJ, GRANDHI RK, SCHNEIDER DK, et al. Risk of Secondary Injury in Younger Athletes After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(7):1861-1876.
[32] ANDRIACCHI TP, MÜNDERMANN A, SMITH RL, et al. A framework for the in vivo pathomechanics of osteoarthritis at the knee. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(3):447-457.
[33] FOCKE A, STEINGREBE H, MÖHLER F, et al. Effect of Different Knee Braces in ACL-Deficient Patients. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:964.
[34] HOLDEN MA, CALLAGHAN M, FELSON D, et al. Clinical and cost-effectiveness of bracing in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis management: protocol for a multicenter, primary care, randomized, parallel-group, superiority trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(3):e048196.
[35] PIERRAT B, OULLION R, MOLIMARD J,et al. Characterisation of in-vivo mechanical action of knee braces regarding their anti-drawer effect.Knee. 2015;22(2):80-87.
[36] MOHD SHARIF NA, USMAN J, WAN SAFWANI WKZ, et al. Effects of simple knee sleeves on pain and knee adduction moment in early unilateral knee osteoarthritis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(11): 1132-1140.
[37] SINCLAIR J, TAYLOR PJ. Effects of a Prophylactic Knee Sleeve on Anterior Cruciate Ligament Loading During Sport-Specific Movements. J Sport Rehabil. 2019;28(1):1-7.
[38] BALTACI G, AKTAS G, CAMCI E, et al. The effect of prophylactic knee bracing on performance: balance, proprioception, coordination, and muscular power.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(10): 1722-1728.
[39] GIOTIS D, TSIARAS V, RISTANIS S, et al. Knee braces can decrease tibial rotation during pivoting that occurs in high demanding activities. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19:1347-1354.
[40] FLEMING BC, RENSTROM PA, BEYNNON BD, et al. The influence of functional knee bracing on the anterior cruciate ligament strain biomechanics in weightbearing and nonweightbearing knees. Am J Sports Med. 2000;28(6):815-824.
|