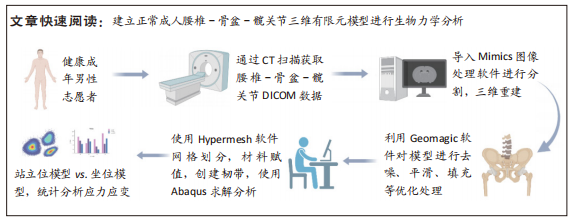
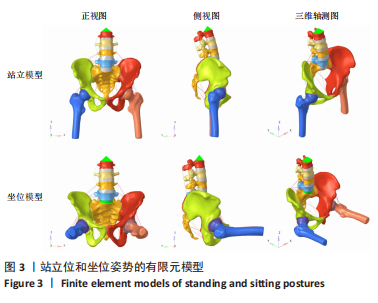
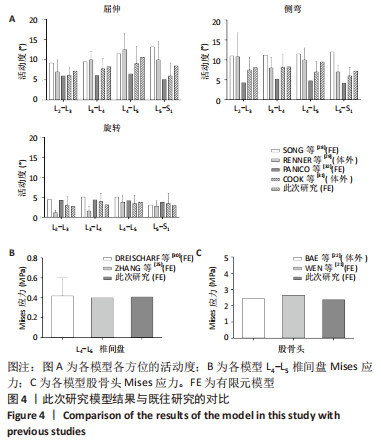
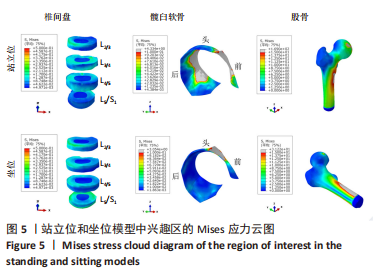
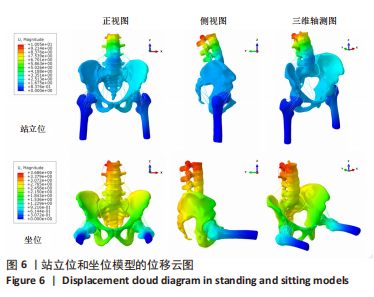
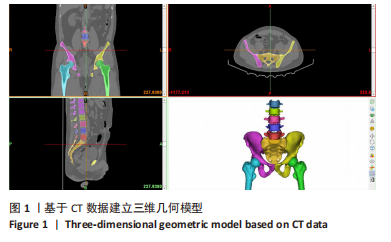
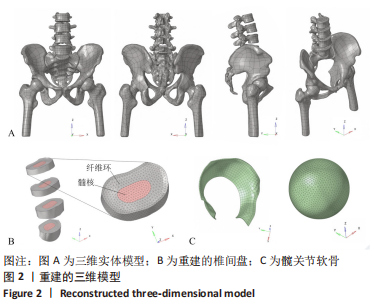
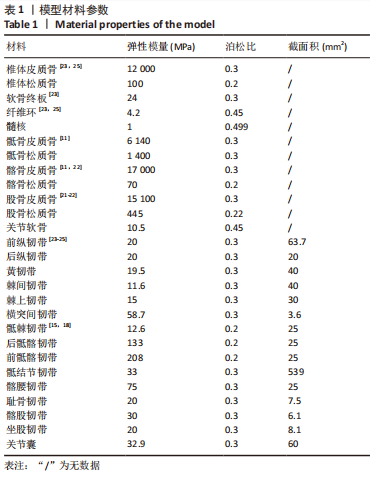
[1] OFFIERSKI CM,MACNAB I. Hip-spine syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(3):316-321.
[2] VASWANI R, WHITE AE, FEINGOLD J, et al. Hip-Spine Syndrome in the Nonarthritic Patient. Arthroscopy. 2022;38(10):2930-2938.
[3] OKUZU Y, GOTO K, OKUTANI Y, et al. Hip-Spine Syndrome: Acetabular Anteversion Angle Is Associated with Anterior Pelvic Tilt and Lumbar Hyperlordosis in Patients with Acetabular Dysplasia: A Retrospective Study. JB JS Open Access. 2019;4(1):e0025.
[4] ANAND N, COHEN RB, COHEN J, et al. The Influence of Lordotic cages on creating Sagittal Balance in the CMIS treatment of Adult Spinal Deformity. Int J Spine Surg. 2017;11:23.
[5] AN VVG, PHAN K, SIVAKUMAR BS, et al. Prior Lumbar Spinal Fusion is Associated With an Increased Risk of Dislocation and Revision in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(1):297-300.
[6] WYATT MC, KUNUTSOR SK, BESWICK AD, et al. Outcomes following primary total hip arthroplasty with pre-existing spinal fusion surgery. Bone Joint J. 2020;102-b(6):664-670.
[7] MALKANI AL, HIMSCHOOT KJ, ONG KL, et al. Does Timing of Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Prior to or After Lumbar Spine Fusion Have an Effect on Dislocation and Revision Rates? J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(5): 907-911.
[8] NESSLER JM, MALKANI AL, SACHDEVA S, et al. Use of dual mobility cups in patients undergoing primary total hip arthroplasty with prior lumbar spine fusion. Int Orthop. 2020;44(5):857-862.
[9] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[10] 潘爱星, 刘玉增, 海涌, 等. 腰椎皮质骨螺钉联合椎弓根螺钉固定对融合节段应力影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2022, 32(1): 67-74.
[11] SHI D, WANG F, WANG D, et al. 3-D finite element analysis of the influence of synovial condition in sacroiliac joint on the load transmission in human pelvic system. Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(6):745-753.
[12] VAFAEIAN B, ZONOOBI D, MABEE M, et al. Finite element analysis of mechanical behavior of human dysplastic hip joints: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):438-447.
[13] NEWELL E, DRISCOLL M. Investigation of physiological stress shielding within lumbar spinal tissue as a contributor to unilateral low back pain: A finite element study. Comput Biol Med. 2021;133:104351.
[14] KIAPOUR A, MASSAAD E, JOUKAR A, et al. Biomechanical analysis of stand-alone lumbar interbody cages versus 360 degrees constructs: an in vitro and finite element investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2021:1-9.
[15] 刘慧, 张喜林, 周楠, 等. 步态仿真下腰椎间盘退变合并骶髂关节紊乱的有限元分析[J]. 医用生物力学,2017,32(1):46-53.
[16] SONG Y, SHAO C, YANG X, et al. Biomechanical study of anterior and posterior pelvic rings using pedicle screw fixation for Tile C1 pelvic fractures: Finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2022;17(8):e0273351.
[17] ROUSSOULY P, GOLLOGLY S, BERTHONNAUD E, et al. Classification of the normal variation in the sagittal alignment of the human lumbar spine and pelvis in the standing position. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(3):346-353.
[18] WANG W, PEI B, WU S, et al. Biomechanical responses of human lumbar spine and pelvis according to the Roussouly classification. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0266954.
[19] HEY HWD, TEO AQA, TAN KA, et al. How the spine differs in standing and in sitting-important considerations for correction of spinal deformity. Spine J. 2017;17(6):799-806.
[20] DE CARVALHO DE, SOAVE D, ROSS K, et al. Lumbar spine and pelvic posture between standing and sitting: a radiologic investigation including reliability and repeatability of the lumbar lordosis measure. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2010;33(1):48-55.
[21] WEN PF, GUO WS, ZHANG QD, et al. Significance of Lateral Pillar in Osteonecrosis of Femoral Head: A Finite Element Analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(21):2569-2574.
[22] BAE JY, KWAK DS, PARK KS, et al. Finite element analysis of the multiple drilling technique for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2528-2537.
[23] ZHU J, SHEN H, CUI Y, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Coflex-F and Pedicle Screw Fixation: Finite Element Analysis of Static and Vibration Conditions. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2339-2349.
[24] LIU J, HE X, NIU B, et al. Biomechanical properties of a novel nonfusion artificial vertebral body for anterior lumbar vertebra resection and internal fixation. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):2632.
[25] ZHANG NZ, XIONG QS, YAO J, et al. Biomechanical changes at the adjacent segments induced by a lordotic porous interbody fusion cage. Comput Biol Med. 2022;143:105320.
[26] WEN P, ZHANG Y, HAO L, et al. The effect of the necrotic area on the biomechanics of the femoral head - a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):211.
[27] DU CF, CAI XY, GUI W, et al. Does oblique lumbar interbody fusion promote adjacent degeneration in degenerative disc disease: A finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2021;128:104122.
[28] SONG M, SUN K, LI Z, et al. Stress distribution of different lumbar posterior pedicle screw insertion techniques: a combination study of finite element analysis and biomechanical test. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1): 12968.
[29] RENNER SM, NATARAJAN RN, PATWARDHAN AG, et al. Novel model to analyze the effect of a large compressive follower pre-load on range of motions in a lumbar spine. J Biomech. 2007;40(6):1326-1332.
[30] DREISCHARF M, ZANDER T, SHIRAZI-ADL A, et al. Comparison of eight published static finite element models of the intact lumbar spine: predictive power of models improves when combined together. J Biomech. 2014;47(8):1757-1766.
[31] COOK DJ, YEAGER MS, CHENG BC. Range of motion of the intact lumbar segment: a multivariate study of 42 lumbar spines. Int J Spine Surg. 2015;9:5.
[32] PANICO M, BASSANI T, VILLA TMT, et al. The Simulation of Muscles Forces Increases the Stresses in Lumbar Fixation Implants with Respect to Pure Moment Loading. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:745703.
[33] ZHANG S, CHEN Y, REN R, et al. Quantitative study on the biomechanical mechanism of sacroiliac joint subluxation: A finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(5):1223-1235.
[34] 司高,李彤,于淼,等. 成人脊柱侧凸患者长节段脊柱融合术后髋关节疼痛与脊柱-骨盆-髋关节参数的相关性分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(11):989-994.
[35] YANG DS, LI NY, MARIORENZI MC, et al. Surgical Treatment of Patients With Dual Hip and Spinal Degenerative Disease: Effect of Surgical Sequence of Spinal Fusion and Total Hip Arthroplasty on Postoperative Complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(10):E587-E593.
[36] MENON RG, ZIBETTI MVW, PENDOLA M, et al. Measurement of Three-Dimensional Internal Dynamic Strains in the Intervertebral Disc of the Lumbar Spine With Mechanical Loading and Golden-Angle Radial Sparse Parallel-Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;54(2):486-496.
[37] ZHOU Z, NI HJ, ZHAO W, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy via Transforaminal Approach Combined with Interlaminar Approach for L4/5 and L5/S1 Two-Level Disc Herniation. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):979-988.
[38] 刘彩银, 欧阳文辉, 黄俊远. 基于有限元分析骨盆前后倾斜对髋关节应力的影响[J]. 赣南医学院学报,2022,42(1):12-15.
[39] PIERANNUNZII L. Femoroacetabular impingement: question-driven review of hip joint pathophysiology from asymptomatic skeletal deformity to end-stage osteoarthritis. J Orthop Traumatol. 2019;20(1):32.
[40] MALLOY P, WICHMAN DM, GARCIA F, et al. Impaired Lower Extremity Biomechanics, Hip External Rotation Muscle Weakness, and Proximal Femoral Morphology Predict Impaired Single-Leg Squat Performance in People With FAI Syndrome. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(11):2984-2993.
[41] THUMMALA AR, XI Y, MIDDLETON E, et al. Does surgery change pelvic tilt: an investigation in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip, dysplasia, and femoroacetabular impingement. Bone Joint J. 2022;104-B(9): 1025-1031. |