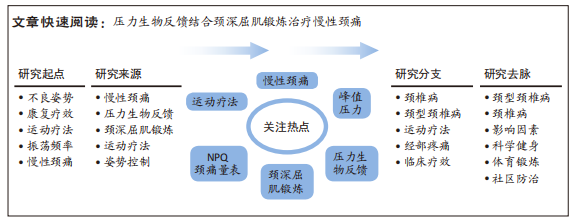
[1] WU A, DONG W, ZENG X, et al. Neck pain is the leading cause of disability burden in China: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(9):777.
[2] LV Y, TIAN W, CHEN D, et al. The prevalence and associated factors of symptomatic cervical Spondylosis in Chinese adults: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1): 325.
[3] Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743-800.
[4] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[5] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, HOY D, et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neck pain in the general population, 1990-2017: systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMJ. 2020;368:m791.
[6] ZHANG Y, DENG G, ZHANG Z, et al. A cross sectional study between the prevalence of chronic pain and academic pressure in adolescents in China (Shanghai) . BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):219.
[7] WANG T, ZHAO Y-L, HAO LX, et al. Prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms among industrial employees in a modern industrial region in Beijing, China. Chin Med J. 2019;132(7):789-797.
[8] KAMPER SJ, HENSCHKE N, HESTBAEK L, et al. Musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents. Braz J Phys Ther. 2016;20(3):275-284.
[9] MURPHY AC, MULDOON SF, BAKER D, et al. Structure, function, and control of the human musculoskeletal network. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(1): e2002811-e.
[10] XIAOLONG S, XUHUI Z, JIAN C, et al. Weakness of the neck extensors, possible causes and relation to adolescent idiopathic cervical kyphosis. Med Hypotheses. 2011;77(3):456-459.
[11] ALPAYCI M, ŞENKöY E, DELEN V, et al. Decreased neck muscle strength in patients with the loss of cervical lordosis. Clin Biomech(Bristol, Avon). 2016;33:98-102.
[12] 李智斐, 张家立, 钟远鸣, 等. 颈部肌肉四方抗阻静力功能锻炼预防CSM初步观察[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2011,19(7):30-32.
[13] 张家立, 王东洋. 颈部肌四方抗阻静力功能锻炼和“以头书凰”防治早期CSM疗效对比[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2016,7(5):15-17.
[14] 王雪强, 王于领, 张志杰, 等. 运动疗法治疗颈痛的中国专家共识[J].上海体育学院学报,2020,44(1):59-69.
[15] HARRIS KD, HEER DM, ROY TC, et al. Reliability of a measurement of neck flexor muscle endurance. Phys Ther. 2005;85(12):1349-1355.
[16] YIP CH, CHIU TT, POON AT. The relationship between head posture and severity and disability of patients with neck pain. Man Ther. 2008;13(2): 148-154.
[17] KIM JY, KWAG KI. Clinical effects of deep cervical flexor muscle activation in patients with chronic neck pain. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016; 28(1):269-273.
[18] TSIRINGAKIS G, DIMITRIADIS Z, TRIANTAFYLLOY E, et al. Motor control training of deep neck flexors with pressure biofeedback improves pain and disability in patients with neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;50:102220.
[19] CRASTO CFB, MONTES AM, CARVALHO P, et al. Pressure biofeedback unit to assess and train lumbopelvic stability in supine individuals with chronic low back pain. J Phys Ther Sci. 2019;31(10):755-759.
[20] IQBAL ZA, RAJAN R, KHAN SA, et al. Effect of deep cervical flexor muscles training using pressure biofeedback on pain and disability of school teachers with neck pain. J Phys Ther Sci.2013;25(6):657-661.
[21] KANG DY. Deep cervical flexor training with a pressure biofeedback unit is an effective method for maintaining neck mobility and muscular endurance in college students with forward head posture. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015;27(10):3207-3210.
[22] BALTHILLAYA GM, PARSEKAR SS, GANGAVELLI R, et al. Effectiveness of posture-correction interventions for mechanical neck pain and posture among people with forward head posture: protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2022;12(3):e054691.
[23] PICKERING PM, OSMOTHERLY PG, ATTIA JR, et al. An examination of outcome measures for pain and dysfunction in the cervical spine: a factor analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(7):581-588.
[24] YLINEN J, NIKANDER R, NYKäNEN M, et al. Effect of neck exercises on cervicogenic headache: a randomized controlled trial. J Rehabil Med. 2010;42(4):344-349.
[25] SOUTHERST D, NORDIN MC, CôTé P, et al. Is exercise effective for the management of neck pain and associated disorders or whiplash-associated disorders? A systematic review by the Ontario Protocol for Traffic Injury Management (OPTIMa) Collaboration. Spine J. 2016; 16(12):1503-1523.
[26] PANJABI MM. The stabilizing system of the spine. Part I. Function, dysfunction, adaptation, and enhancement. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(4): 383-389; discussion 97.
[27] PANJABI MM. The stabilizing system of the spine. Part II. Neutral zone and instability hypothesis. J Spinal Disord. 1992;5(4):390-396; discussion 7.
[28] RöIJEZON U, JULL G, DJUPSJöBACKA M, et al. Deep and superficial cervical muscles respond differently to unstable motor skill tasks. Hum Mov Sci. 2021;80:102893.
[29] SCHOMACHER J, FALLA D. Function and structure of the deep cervical extensor muscles in patients with neck pain. Man Ther. 2013;18(5): 360-366.
[30] OXLAND TR. Fundamental biomechanics of the spine--What we have learned in the past 25 years and future directions. J Biomech. 2016;49(6):817-832.
[31] TRELEAVEN J, JULL G, STERLING M. Dizziness and unsteadiness following whiplash injury: characteristic features and relationship with cervical joint position error. J Rehabil Med. 2003;35(1):36-43.
[32] FALLA DL, JULL GA, HODGES PW. Patients with neck pain demonstrate reduced electromyographic activity of the deep cervical flexor muscles during performance of the craniocervical flexion test. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(19):2108-2114.
[33] HIDES JA, STOKES MJ, SAIDE M, et al. Evidence of lumbar multifidus muscle wasting ipsilateral to symptoms in patients with acute/subacute low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994;19(2):165-172.
[34] FALLA D, JULL G, HODGES PW. Feedforward activity of the cervical flexor muscles during voluntary arm movements is delayed in chronic neck pain. Exp Brain Res. 2004;157(1):43-48.
[35] CAGNIE B, DICKX N, PEETERS I, et al. The use of functional MRI to evaluate cervical flexor activity during different cervical flexion exercises. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104(1):230-235.
[36] RUBINI EC, COSTA AL, GOMES PS. The effects of stretching on strength performance. Sports Med. 2007;37(3):213-224.
[37] CHIU TT, LAM TH, HEDLEY AJ. A randomized controlled trial on the efficacy of exercise for patients with chronic neck pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):E1-7.
[38] BLOMGREN J, STRANDELL E, JULL G, et al. Effects of deep cervical flexor training on impaired physiological functions associated with chronic neck pain: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):415.
[39] AMIRI ARIMI S, MOHSENI BANDPEI MA, JAVANSHIR K, et al. The Effect of Different Exercise Programs on Size and Function of Deep Cervical Flexor Muscles in Patients With Chronic Nonspecific Neck Pain: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;96(8):582-588.
|