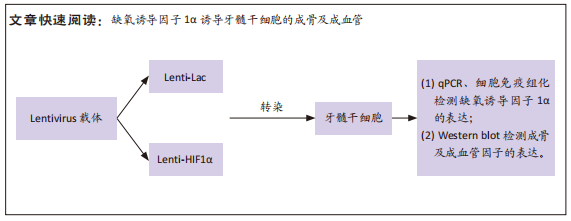
1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验,组间比较采用单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2018年3月至2020年6月在滨州医学院附属医院完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 细胞 选取2018年10月至2019年8月滨州医学院附属医院口腔颌面外科15例12-18岁患者因正畸治疗需要拔除的健康、完整的双尖牙,取所选离体牙牙髓组织进行原代培养。实验通过滨州医学院附属医院伦理委员会审核,所有患者及监护人均知情同意。
1.3.2 实验试剂及仪器 胎牛血清(FBS500-S,澳大利亚AusGeneX公司);DMEM培养基(KL-P0032,德国Merck/Sigma公司);实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)试剂盒(K1002S,美国Promega公司);MTT溶液(N/A-896,美国 Ameko 公司);缺氧诱导因子1α、β-actin 引物均由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成;血管内皮生成因子抗体、基质细胞衍生因子1抗体、胎盘生长因子抗体、促血管生成素2抗体、人骨形态发生蛋白2抗体、骨钙蛋白抗体、Runt相关转录因子2抗体、GAPDH抗体(Abcam公司);辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗兔抗体(0295G-HRP,美国Santa公司);恒温培养箱(MIR-162-PC/MIR-262-PC,日本松下公司);qRT-PCR仪(ABI 7500,美国Applied Biosystems公司);酶标仪(Model550)、化学发光成像系统(ChemiDocXRS)购自美国Bio-Rad公司。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 牙髓干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定
(1)牙髓干细胞分离:选取临床上12-18岁患者因正畸治疗需要拔除的健康、完整的双尖牙,将牙齿置于4 ℃预冷的PBS(含5%100 U/mL青霉素,100 U/mL链霉素)中冲洗两三分钟,转移至超净工作台,于无菌条件下劈开牙冠及牙根,取出牙髓,弃根尖约2 mm的牙髓组织。在PBS(含2% 100 U/mL青霉素,100 U/mL链霉素)浸润下将剩余牙髓组织充分剪碎,置于含有Ⅰ型胶原酶(3 mg/mL)和Dispase(4 mg/mL)的消化液中,置于培养箱中消化一两个小时,期间每5-10 min拿出来振荡1次,组织松散后反复吹打,使其彻底分散;取出离心管,加入含血清的DMEM培养基终止消化,用70 μm筛子过滤细胞悬液,1 000 r/min离心5 min,弃上清,收集组织,用DMEM培养基(含体积分数为20%的胎牛血清,2 mmol/L谷胺酰氨,100 U/mL青霉素,100 U/mL链霉素)重悬,接种于25 mm2的培养瓶中,在体积分数为5%CO2细胞培养箱37 ℃标准条件下培养,每两三天更换1次培养液,倒置显微镜下观察细胞生长情况及细胞形态,当细胞生长至70%-80%汇合状态时,按1∶3消化传代。
(2)牙髓干细胞培养:采用有限稀释法克隆化培养牙髓干细胞。将牙髓干细胞用Dispase(4 mg/mL)消化一两分钟,加入含血清的DMEM培养基终止消化,吹打混匀,制备成单细胞悬液。细胞计数,将细胞悬液依次稀释至1×108 L-1,1×106 L-1,1×103 L-1,将末次稀释的细胞悬液5 mL接种至60 mm培养皿中,放入CO2培养箱静置培养1周,待集落形成,进行单个集落的分离。
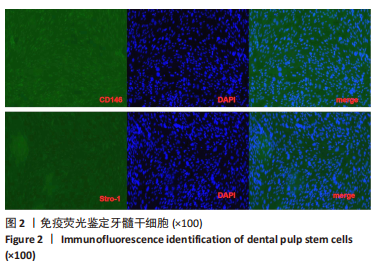
(3)牙髓干细胞鉴定:应用免疫荧光技术检测牙髓干细胞标记物Strol-1、CD146。将已消毒的20 mm盖玻片置于90 mm培养皿中,取15 mL细胞浓度为2×107 L-1的细胞悬液接种于培养皿中进行细胞爬片,5 d后进行免疫细胞化学染色鉴定,PBS清洗标本3次,每次1 min,冰丙酮固定15 min,空气干燥5 min,PBS清洗标本3次,每次2 min,0.5%Triton X-100(DPBS配)孵育1次20 min,PBS清洗标本3次,每次2 min,体积分数为3%H2O2孵育15 min,DPBS清洗标本3次,每次2 min,封闭血清孵育20 min,加入一抗2 ℃孵育过夜,PBS清洗标本3次,每次5 min,二抗工作液37 ℃孵育30 min,PBS清洗标本3次,每次5 min,DAB显色约5 min,蒸馏水洗2次,每次1 min,苏木素复染1 min,自来水洗30 min,树胶封固,荧光显微镜观察。
1.4.2 慢病毒载体构建、病毒包装及滴度测定 根据GENEBANK中缺氧诱导因子1α基因合成过表达载体,通过重组后构建慢病毒载体Lenti-LacZ和Lenti-HIF-1α(载体信息为:HIF1A:Human,基因 ID3091,NM_001530,载体元件信息:Ubi-MCS-3FLAG-SV40-EGFP-IRES-puromycin)。使用Invitrogen的慢病毒包装,将慢病毒载体Lenti-LacZ和Lenti-HIF-1α分别和包装质粒Packaging Mix共转染293T细胞,包装得到病毒进行滴度测定。将收集到的慢病毒液10倍比滴度稀释后感染牙髓干细胞,观察各稀释度孔病毒感染情况并计数,根据可数的最小梯度稀释孔的荧光细胞数目计算慢病毒滴度。
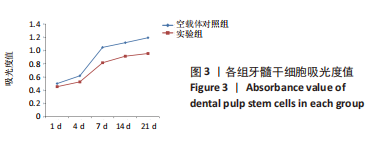
1.4.3 MTT法检测细胞活性 用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM配成单细胞悬液,将牙髓干细胞分为2组:不做任何处理的对照组和过表达慢病毒转染的实验组,以每孔5×103个牙髓干细胞接种到96孔板,每孔体积200 μL;在CO2培养箱中分别培养1,4,7,14,21 d后,每孔加MTT溶液20 μL,继续孵育4 h,终止培养,小心吸弃孔内培养上清液,每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜,振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解;选择490 nm波长,在酶联免疫监测仪上测定各孔光吸收值,记录结果,以时间为横坐标,吸光度值(A值)为纵坐标绘制细胞生长曲线。
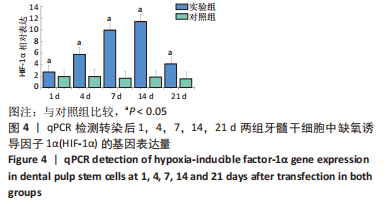
1.4.4 缺氧诱导因子1α基因转染后牙髓干细胞中缺氧诱导因子1α的表达 将状态良好,处于对数生长期的牙髓干细胞用0.25%胰酶消化后离心,用DMEM培养基将细胞沉淀悬浮成单细胞悬液,细胞计数后按照每孔2×105个细胞接种于6孔板中,待细胞生长至70%-80%融合度时,按照测定的最佳感染复数值加入相应体积的慢病毒转染牙髓干细胞。对照组为空载组,不进行慢病毒转染。
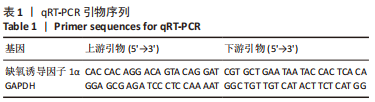
转染后1,4,7,14,21 d收集细胞,提取总RNA,反转录合成cDNA,采用qRT-PCR法检测缺氧诱导因子1α mRNA表达水平,内参基因为GAPDH,相对表达量以2-ΔΔCt法表示。反应程序:95 ℃、10 min,95 ℃、10 s,55 ℃、25 s,72 ℃、2 min,循环40次;72 ℃、10 min。引物序列见表1。
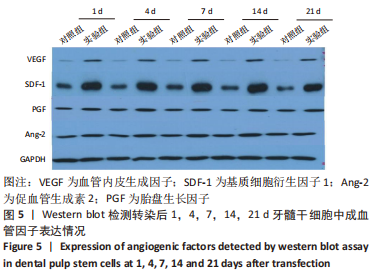
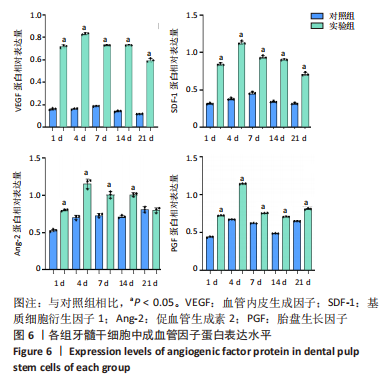
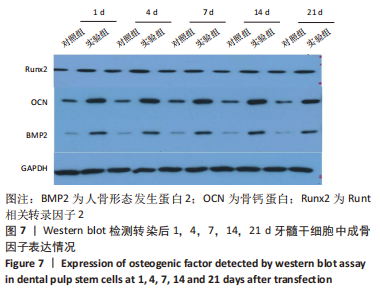
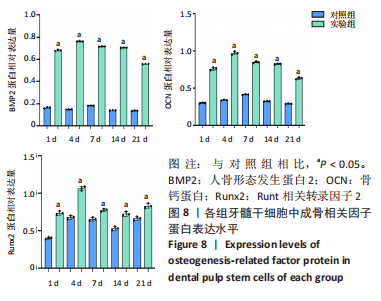
1.4.5 蛋白印迹法检测缺氧诱导因子1α基因转染后牙髓干细胞成骨及成血管因子的表达 转染后1,4,7,14,21 d收集细胞,PBS洗涤,提取各组细胞总蛋白并采用BCA法测定蛋白浓度。配制SDS-PAGE凝胶,向蛋白样品中加入1/5体积的5×SDS电泳样品缓冲液,100℃加热3-5 min,离心10 min,取上清作SDS-PAGE电泳分离;电泳、转膜、封闭液室温平摇1 h,分别加血管内皮生成因子抗体、基质细胞衍生因子1抗体、促血管生成素2抗体、胎盘生长因子抗体、人骨形态发生蛋白2抗体、骨钙蛋白抗体、Runt相关转录因子2抗体、GAPDH抗体(1∶500稀释),4 ℃孵育过夜,TBST洗涤,加辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗兔二抗(1∶5 000稀释),室温孵育1 h,加化学发光底物,Tanon 600图像分析系统拍摄图像并分析条带灰度,目的蛋白相对表达量=目的蛋白灰度值/内参GAPDH灰度值。
1.5 主要观察指标 牙髓干细胞中标记物Strol-1、CD14的表达,缺氧诱导因子1α mRNA表达量,成骨及成血管因子蛋白表达量。
1.6 统计学分析 所有数据以x±s表示。统计学分析采用SPSS10.0软件(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA),采用ANOVA方差分析。P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经通过滨州医学院附属医院生物统计学专家审核。