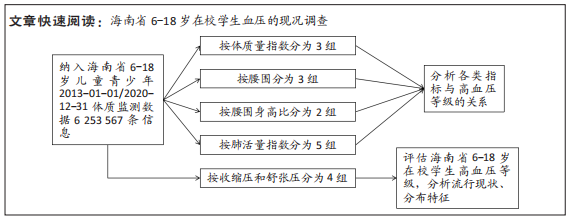
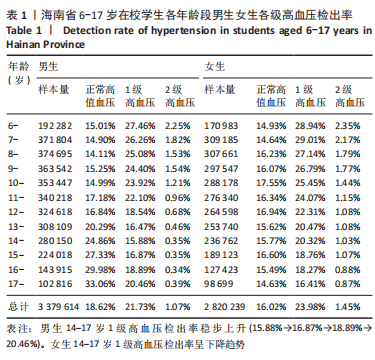
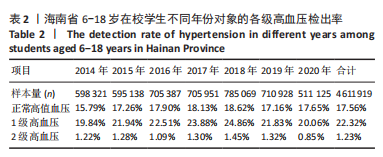
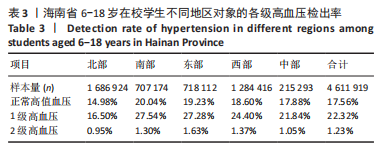
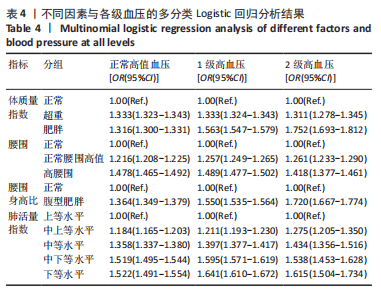
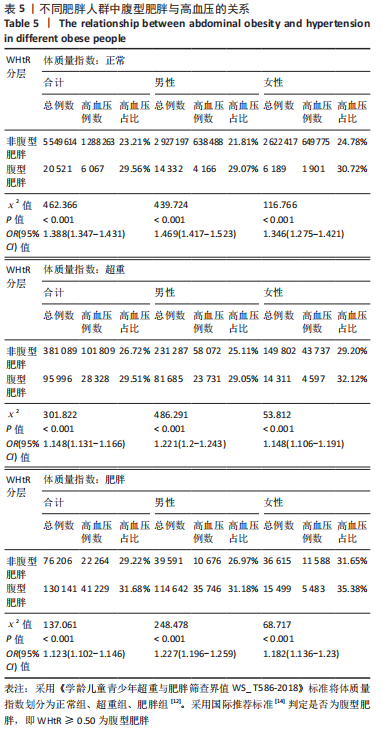
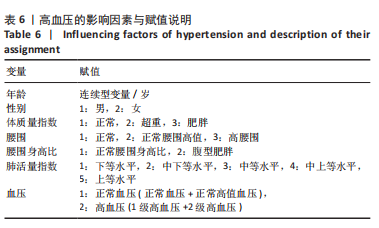
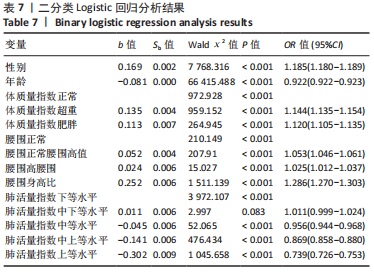
[1] 马丽媛,王增武,樊静,等.《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2021》关于中国高血压流行和防治现状[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(30): 3715-3720.
[2] YANG L, MAGNUSSEN CG, YANG L, et al. Elevated blood pressure in childhood or adolescence and cardiovascular outcomes in adulthood: a systematic review. Hypertension. 2020;75(4):948-955.
[3] MEER R, BOATENG D, KLIPSTEIN-GROBUSCH K, et al. Incidence and correlates of high blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: the Birth to Twenty study. J Hypertens. 2022;40(2):274-282.
[4] 刘宏彦,冷俊宏,王蕾棽.肥胖对儿童青少年健康影响的研究进展[J].中国城乡企业卫生,2022,37(2):38-41.
[5] WANG L, SONG L, LIU B, et al. Trends and status of the prevalence of elevated blood pressure in children and adolescents in China:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019; 21(11):88.
[6] 董彦会,邹志勇,王政和,等.中国2014年7-18岁儿童青少年血压偏高流行的区域分析[J].中华流行病学杂志,2017,38(7):931-937.
[7] HU J, SHEN H, WU JZ, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure and high normal blood pressure among 7- to 17-year-old children and adolescents in developed regions, China from 2014 to 2017: using new national blood pressure reference for Chinese children and adolescents. J Hum Hypertens. 2019;33(5):400-410.
[8] YE X, YI Q, SHAO J, et al. Trends in prevalence of hypertension and hypertension phenotypes among chinese children and adolescents over two decades (1991-2015). Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:627741.
[9] 欧阳范献,卜平凤,周家仍,等.海口市初中生的年龄、性别、身高分布特点及12-14岁组高血压现患率调查[J].海南医学,2016, 27(14):2385-2388.
[10] 范晖,闫银坤,米杰.中国3-17岁儿童性别、年龄别和身高别血压参照标准[J].中华高血压杂志,2017,25(5):428-435.
[11] 刘力生,吴兆苏,王继光,等.中国高血压防治指南2018年修订版[J].心脑血管病防治,2019,19(1):1-44.
[12] 国家卫生健康委员会.学龄儿童青少年超重与肥胖筛查: WS /T 586—2018[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2018. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2018/03/20180330094031236.pdf.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会.7岁-18岁儿童青少年高腰围筛查界值[S].中华人民共和国卫生行业标准WS/T611-2018.2018. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2018/07/20180704145130574.pdf.
[14] ASHWELL M, GIBSON S. A proposal for a primary screening tool: ‘Keep your waist circumference to less than half your height’. BMC Med. 2014;12:207.
[15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会、中国国家标准化管理委员会. 儿童青少年发育水平的综合评价:GB/T 31178-2014[S]. 2014. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/ewebeditor/uploadfile/2015/04/20150407151300845.pdf.
[16] 卫生部教育部关于印发《中小学生健康体检管理办法》的通知.中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2008(35):30-33.
[17] 教育部国家体育总局关于实施《国家学生体质健康标准》的通知.中华人民共和国教育部公报,2007(Z2):22-23.
[18] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会,高血压联盟(中国),中华医学会心血管病学分会,等.中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J].中国心血管杂志,2019,24(1):24-56.
[19] SILBERSTEIN J, GWYNN L, MATHEW MS, et al. Evidence to support universal blood pressure screening in school-based clinical settings. J Sch Health. 2020;90(6):474-481.
[20] 陈少萍.从中国高血压人群特点看优化联合治疗方案[C].第六届全国药学服务与研究学术论坛论文集,2015:66-75.
[21] MARTINA K, MARTINA M, NIKOLINA H, et al. Estimation of daily salt intake in children with essential hypertension. J Hypertension. 2022. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000836920.43945.2b.
[22] 任杰,张迎修,郭晓雷,等.2011年山东省青少年人群盐与高血压相关知识、态度和行为分析[J].中华高血压杂志,2014,22(2):146-150.
[23] 史文丽.青春期更要合理饮食控制体质量[J].青春期健康,2022, 20(4):22-25.
[24] 赵锦平,杨云娟,常利涛,等.云南省中小学生血压分布及影响因素分析[J].中国健康教育,2019,35(9):775-779, 785.
[25] 张华琴,马云,沈丽,等.中国12-17岁儿童青少年体格测量指标与血压偏高的关联分析[J].中国儿童保健杂志,2020,28(6):618-622.
[26] YANG Y, DONG B, WANG S, et al. Prevalence of high blood pressure subtypes and its associations with BMI in Chinese children: a national cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):598.
[27] 刘贝贝,满青青,李裕倩,等.中国东部地区青少年肥胖类型及其与血压的关系[J].卫生研究,2021,50(2):210-216.
[28] 黄贵民,侯冬青,高爱钰,等.北京市6-16岁儿童青少年睡眠状况与高血压的关联分析[J].中华预防医学杂志,2018,52(11):1136-1139.
[29] 朱金玉,李燕,牛桂林.南阳市儿童青少年血压升高现状及影响因素[J].中国卫生工程学,2021,20(2):248-249, 251.
[30] 吴容,尤映彬,吴龙飞,等.深圳市某区6-9岁儿童体脂成分与高血压和血脂异常的关系[J].疾病预防控制通报,2022,37(2):17-21.
[31] 刘冰,杨硕,吴晓刚,等.吉林省高年级小学生血压偏高现状及影响因素分析[J].中国健康教育,2021,37(9):778-782.
[32] 刘忠慧,徐渴,孙志颖,等.天津市儿童青少年肥胖与血压现状及关系[J].公共卫生与预防医学,2021,32(1):76-80.
[33] 胡佳,韩迪,丁子尧,等.基于不同血压标准的苏州市儿童青少年血压偏高率比较[J].中国学校卫生,2019,40(12):1870-1872, 1876.
[34] 张良恺,张艳青,张茜,等.基于不同标准判定的儿童血压偏高与颈动脉内中膜增厚的关联[J].中华预防医学杂志,2020,54(12): 1396-1401.
[35] 唐努,陈亚军,谭蔚清,等.基于不同血压参照标准的儿童高血压检出率比较[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2019,23(2):162-167.
[36] 张莹,王培安,刘兆琴,等.徐州地区青少年中学生高血压流行病学调查[J].中华高血压杂志,2021,29(7):661-667.
[37] 韩迪,沈明珠,施冰,等.苏州市中小学生非同日3时点血压测量结果[J].预防医学,2022,34(2):109-113.
[38] 王欢,张高辉,羊柳,等.血压测量次数对藏族青少年血压偏高检出率的影响分析[J].中华流行病学杂志,2020,41(9):1440-1444.
[39] 黄渊秀,胡劲松,黄霜,等.长沙市儿童青少年血压偏高现况及其影响因素[J].公共卫生与预防医学,2019,30(4):117-120.
[40] 陆萍,马蓉蓉,尹嘉.泰安市城区7-16岁儿童青少年血压现状及相关影响因素分析[J].健康教育与健康促进,2020,15(5):527-529.
[41] MATSUOKA S, AWAZU M. Masked hypertension in children and young adults. Pediatr Nephrol. 2004;19(6):651-654.
[42] LURBE E, THIJS L, TORRO MI, et al. Sexual dimorphism in the transition from masked to sustained hypertension in healthy youths. Hypertension. 2013;62(2):410-414.
[43] DONG Y, JAN C, ZOU Z, et al. Effect of overweight and obesity on high blood pressure in chinese children and adolescents. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(9):1503-1512.
[44] LURBE E, AGABITI-ROSEI E, CRUICKSHANK JK, et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J Hypertension. 2016;34(10): 1887-1920.
[45] 宁曼,何海燕.浅谈儿童高血压的影响因素及防治[J].中国妇幼卫生杂志,2016,7(5):70-74.
[46] 刘洋.儿童青少年高血压及其与体质量关联的Meta分析[D].衡阳:南华大学,2017.
[47] 骆晓燕.儿童青少年单纯性肥胖症与代谢综合征[J].实验与检验医学,2021,39(1):211-213.
[48] 朱维维,姚庆兵,杨帆,等.2020年扬州市儿童青少年血压偏高现状及其与超重和肥胖关系分析[J].现代医药卫生,2022,38(11): 1850-1853.
[49] 吴海霞,吴伟志,高明月.中山火炬开发区儿童青少年高血压现状及其与肥胖的相关分析[J].智慧健康,2021,7(14):188-190.
[50] 王一琳,徐佩茹,艾比白·艾尔肯.新疆沙湾县学龄期儿童肥胖和血压的相关性[J].中国妇幼保健,2021,36(19):4513-4516.
[51] 范晖,康利,刘宇丹.儿童期体质量状态及其变化与血压偏高发生风险的关系[J].现代预防医学,2021,48(5):819-823.
[52] JUONALA M, MAGNUSSEN CG, BERENSON GS, et al. Childhood adiposity, adult adiposity, and cardiovascular risk factors. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(20):1876-1885.
[53] UMER A, KELLEY GA, COTTRELL LE, et al. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: a systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. 2017;17(1):683.
[54] ZHANG T, ZHANG H, LI Y, et al. Temporal relationship between childhood body mass index and insulin and its impact on adult hypertension: the bogalusa heart study. Hypertension. 2016;68(3):818-823.
[55] SINGH AS, MULDER C, TWISK JW, et al. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes Rev. 2008;9(5):474-488.
[56] 王明明,侯亚苹,娄小焕,等.儿童青少年期和成年期腹型肥胖的联合效应对成年期高血压的影响研究[J].中华预防医学杂志,2019, 53(7):680-685. |