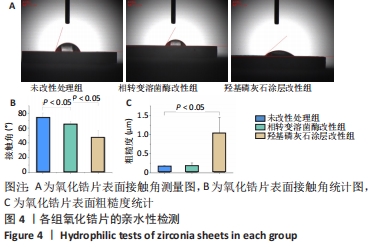
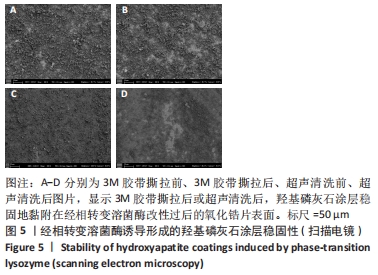
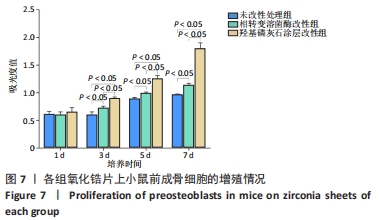
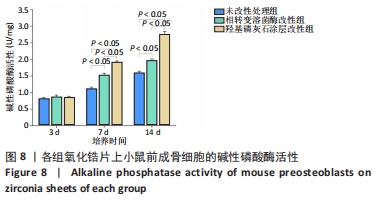
[1] KOHAL RJ, KLAUS G, STRUB JR. Zirconia-implant-supported all-ceramic crowns withstand long-term load: a pilot investigation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(5):565-571.
[2] PICONI C, MACCAURO G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999;20:1-25.
[3] YOSHINARI M. Future prospects of zirconia for oral implants -A review. Dent Mater J. 2020;39(1):37-45.
[4] SURMENEV RA. A review of plasma-assisted methods for calcium phosphate-based coatings fabrication. Surf Coat Technol. 2012;206(8-9): 2035-2056.
[5] LE NIHOUANNEN D, SAFFARZADEH A, AGUADO E, et al. Osteogenic properties of calcium phosphate ceramics and fibrin glue based composites. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(2):225-235.
[6] POINERN GE, BRUNDAVANAM RK, MONDINOS N, et al. Synthesis and characterisation of nanohydroxyapatite using an ultrasound assisted method. Ultrason Sonochem. 2009;16(4):469-474.
[7] ZHOU H, LEE J. Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(7):2769-2781.
[8] 凯康.牙科种植体表面改性的研究进展[J].临床医药文献电子杂志, 2019,6(102):196-198.
[9] KIM HW, KOH YH, LI LH, et al. Hydroxyapatite coating on titanium substrate with titania buffer layer processed by sol-gel method. Biomaterials. 2004;25(13):2533-2538.
[10] WU Z, YANG P. Simple Multipurpose Surface Functionalization by Phase Transited Protein Adhesion. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2015;2(2):1-11.
[11] MALOLLARI KG, DELPARASTAN P, SOBEK C, et al. Mechanical Enhancement of Bioinspired Polydopamine Nanocoatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(46):1-26.
[12] GU J, MIAO S, YAN Z, et al. Multiplex Binding of Amyloid-like Protein Nanofilm to Different Material Surfaces. Colloid Interface Sci Commun. 2018;22:42-48.
[13] HA Y, YANG J, TAO F, et al. Phase-Transited Lysozyme as a Universal Route to Bioactive Hydroxyapatite Crystalline Film. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(4):1-12.
[14] LI C, QIN R, LIU R, et al. Functional amyloid materials at surfaces/interfaces. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(3):462-472.
[15] GU J, SU Y, LIU P, et al. An Environmentally Benign Antimicrobial Coating Based on a Protein Supramolecular Assembly. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(1):198-210.
[16] FURLONG RJ, OSBORN JF. Fixation of hip prostheses by hydroxyapatite ceramic coating. J Bone Joint Surg. 1991;73(5):741-745.
[17] CHO Y, HONG J, RYOO H, et al. Osteogenic responses to zirconia with hydroxyapatite coating by aerosol deposition. J Dent Res. 2015;94(3): 491-499.
[18] PARK JW, JANG JH, LEE CS, et al. Osteoconductivity of hydrophilic microstructured titanium implants with phosphate ion chemistry. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(6):2311-2321.
[19] DRELICH J, MELLER JD. The Effect of Solid Surface Heterogeneity and Roughness on the Contact AngleDrop (Bubble) Size Relationship. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1994;164(1):252-259.
[20] GILJEAN S, BIGERELLE M, ANSELME K, et al. New insights on contact angle/roughness dependence on high surface energy materials. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257(22):9631-9638.
[21] GAHLERT M, GUDEHUS T, EICHHORN S, et al. Biomechanical and histomorphometric comparison between zirconia implants with varying surface textures and a titanium implant in the maxilla of miniature pigs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18(5):662-668.
[22] SANTANDER S, ALCAINE C, LYAHYAI J, et al. In vitro osteoinduction of human mesenchymal stem cells in biomimetic surface modified titanium alloy implants. Dent Mater J. 2012;31(5):843-850.
[23] RUPP F, SCHEIDELER L, REHBEIN D, et al. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterials. 2004;25(7-8):1429-1438.
[24] DELIGIANNI DD, KATSALA N, LADAS S, et al. Effect of surface roughness of the titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V on human bone marrow cell response and on protein adsorption. Biomaterials. 2001;22:1241-1251.
[25] WANG D, HA Y, GU J, et al. 2D Protein Supramolecular Nanofilm with Exceptionally Large Area and Emergent Functions. Adv Mater. 2016; 28(34):7414-7423.
[26] STONE A, HERRING DH. Practical Considerations for Successful Hardness Testing. Mater Test Charact. 2006;73:83-85.
[27] AMNA T. Valorization of Bone Waste of Saudi Arabia by Synthesizing Hydroxyapatite. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018;186(3):779-788.
[28] KIM J, KANG IG, CHEON KH, et al. Stable sol-gel hydroxyapatite coating on zirconia dental implant for improved osseointegration. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(7):81.
[29] KIM JJ, LEE JK. Bioactivity Improvement of Zirconia Substrate by Hydroxyapatite Coating Using Room Temperature Spray Processing. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021;21(8):4151-4156.
[30] MACAN J, SIKIRIĆ MD, DELUCA M, et al. Mechanical properties of zirconia ceramics biomimetically coated with calcium deficient hydroxyapatite. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;111:104006.
[31] AZARI A, NIKZAD S, YAZDANI A, et al. Deposition of crystalline hydroxyapatite nano-particle on zirconia ceramic: a potential solution for the poor bonding characteristic of zirconia ceramics to resin cement. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(7):111.
[32] TORSTRICK FB, LIN ASP, POTTER D, et al. Porous PEEK improves the bone-implant interface compared to plasma-sprayed titanium coating on PEEK. Biomaterials. 2018;185:106-116.
[33] 王铮,丁茜,高远,等.氧化锆多孔表面显微形貌对成骨细胞增殖及分化的影响[J/OL].2021-12-16. https://www.doc88.com/p-31273042813382.html?r=1
[34] CHEVALIER J, LOH J, GREMILLARD L, et al. Low-temperature degradation in zirconia with a porous surface. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(7):2986-2993.
[35] PEZZOTTI G, YAMADA K, SAKAKURA S, et al. Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of Advanced Ceramic Composite for Hip Prosthesis. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;91(4):1199-2206.
[36] SANON C, CHEVALIER J, DOUILLARD T, et al. A new testing protocol for zirconia dental implants. Dent Mater. 2015;31(1):15-25.
[37] ALTMANN B, RABEL K, KOHAL RJ, et al. Cellular transcriptional response to zirconia-based implant materials. Dent Mater. 2017;33(2):241-255.
[38] TUNA T, WEIN M, SWAIN M, et al. Influence of ultraviolet photofunctionalization on the surface characteristics of zirconia-based dental implant materials. Dent Mater. 2015;31(2):e14-24.
[39] NAKAZAWA M, YAMADA M, WAKAMURA M, et al. Activation of Osteoblastic Function on Titanium Surface with Titanium-Doped Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticle Coating: An In Vitro Study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(4):779-791.
[40] LI X, ZOU Q, LI W, et al. Intracellular Interaction of Hydroxyapatite-Based Nanocrystals with Uniform Shape and Traceable Fluorescence. Inorg Chem. 2018;57(21):13739-13748.
|