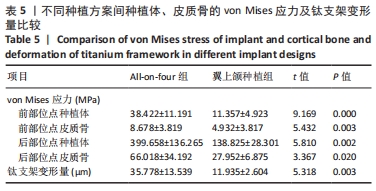
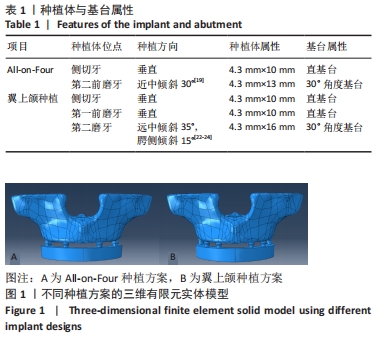
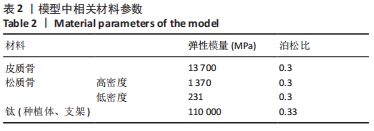
[1] LEUNG M, ALGHAMDI R, GUALLART I F, et al. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Procedures: A Systematic Literature Review. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2021;41(3): e121-e128.
[2] KIM J, LIM Y, KIM B, et al. How Do Parameters of Implant Primary Stability Correspond with CT-Evaluated Bone Quality in the Posterior Maxilla? A Correlation Analysis. Materials. 2021;14(2):270.
[3] TESTORI T, WEINSTEIN T, TASCHIERI S, et al. Risk factors in lateral window sinus elevation surgery. Periodontology 2000. 2019;81(1):91-123.
[4] RAGUCCI GM, ELNAYEF B, SUÁREZ-LÓPEZ DEL AMO F, et al. Influence of exposing dental implants into the sinus cavity on survival and complications rate: a systematic review. Int J Implant Dent. 2019;5(1):6.
[5] DEL FABBRO M, TESTORI T, KEKOVIC V, et al. A Systematic Review of Survival Rates of Osseointegrated Implants in Fully and Partially Edentulous Patients Following Immediate Loading. J Clin Med. 2019; 8(12):2142.
[6] GUTIÉRREZ MUÑOZ D, OBRADOR ALDOVER C, ZUBIZARRETA-MACHO Á, et al. Survival Rate and Prosthetic and Sinus Complications of Zygomatic Dental Implants for the Rehabilitation of the Atrophic Edentulous Maxilla: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biology. 2021;10(7):601.
[7] SIGNORINI L, FAUSTINI F, SAMARANI R, et al. Immediate fixed rehabilitation supported by pterygoid implants for participants with severe maxillary atrophy: 1-Year postloading results from a prospective cohort study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(1):67-75.
[8] MALÓ P, DE ARAÚJO NOBRE M, LOPES A, et al. The All-on-4 concept for full-arch rehabilitation of the edentulous maxillae: A longitudinal study with 5-13 years of follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(4): 538-549.
[9] STELLA JP, WARNER MR. Sinus slot technique for simplification and improved orientation of zygomaticus dental implants: a technical note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000;15(6):889-893.
[10] MALÓ P, RANGERT B, NOBRE M. All-on-4 immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous maxillae: a 1-year retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2005; 7 Suppl 1:S88-S94.
[11] 周磊,岳新新.All-on-Four技术在口腔种植领域中的应用进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(1):1-7.
[12] KWON T, BAIN PA, LEVIN L. Systematic review of short- (5-10 years) and long-term (10 years or more) survival and success of full-arch fixed dental hybrid prostheses and supporting implants. J Dent. 2014; 42(10):1228-1241.
[13] BALSHI TJ, WOLFINGER GJ, BALSHI SF. Analysis of 356 pterygomaxillary implants in edentulous arches for fixed prosthesis anchorage. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999;14(3):398-406.
[14] ZHONG J, GUAZZATO M, CHEN J, et al. Effect of different implant configurations on biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported mandibular monolithic zirconia fixed prostheses. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;102:103490.
[15] MALÓ P, NOBRE MD, LOPES A. The rehabilitation of completely edentulous maxillae with different degrees of resorption with four or more immediately loaded implants: a 5-year retrospective study and a new classification. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2011;4(3):227-243.
[16] DI STEFANO DA, AROSIO P, PERROTTI V, et al. Correlation between Implant Geometry, Bone Density, and the Insertion Torque/Depth Integral: A Study on Bovine Ribs. Dent J (Basel). 2019;7(1):25.
[17] VAN STEENBERGHE D, JACOBS R, DESNYDER M, et al. The relative impact of local and endogenous patient-related factors on implant failure up to the abutment stage. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13(6):617-622.
[18] OZAN O, KURTULMUS-YILMAZ S. Biomechanical Comparison of Different Implant Inclinations and Cantilever Lengths in All-on-4 Treatment Concept by Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;33(1):64-71.
[19] LIU X, PANG F, LI Y, et al. Effects of Different Positions and Angles of Implants in Maxillary Edentulous Jaw on Surrounding Bone Stress under Dynamic Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Comput Math Methods Med. 2019;2019:8074096.
[20] WANG X, ZHANG T, YANG E, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Grafted and Nongrafted Maxillary Sinus Augmentation in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla with Three-Dimensional Finite Element Method. Scanning. 2020;2020:8419319.
[21] YALÇıN M, KAYA B, LACIN N, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of the Effect of Endosteal Implants with Different Macro Designs on Stress Distribution in Different Bone Qualities. Int J Oral Max Impl. 2019;34(3):E43-E50.
[22] RODRÍGUEZ X, RAMBLA F, DE MARCOS LOPEZ L, et al. Anatomical study of the pterygomaxillary area for implant placement: cone beam computed tomographic scanning in 100 patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(5):1049-1052.
[23] ARAUJO RZ, SANTIAGO JÚNIOR JF, CARDOSO CL, et al. Clinical outcomes of pterygoid implants: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(4):651-660.
[24] IHDE S, PAKA U, JARZB S, et al. Three-Dimensional Determination of the Fusion Zone between the Distal Maxilla and the Pterygoid Plate of the Sphenoid Bone and Considerations for Implant Treatment Procedure. Appl Sci. 2021;11(1):30.
[25] 王璨,顾卫平,蒋煜彬,等.不同种植设计对下颌无牙颌应力影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):573-578.
[26] MERICSKE-STERN R, ASSAL P, MERICSKE E, et al. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995;10(3):345-353.
[27] 董海东,汤春波,周储伟,等.6颗种植体支持的上颌无牙颌固定义齿应力分布研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(5):659-663.
[28] LISIAK-MYSZKE M, MARCINIAK D, BIELIŃSKI M, et al. Application of Finite Element Analysis in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery-A Literature Review. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;13(14):3063.
[29] CICCIÙ M. Bioengineering Methods of Analysis and Medical Devices: A Current Trends and State of the Art. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2020;13(3):797.
[30] SCHULLER-GÖTZBURG P, ENTACHER K, PETUTSCHNIGG A, et al. Sinus elevation with a cortical bone graft block: a patient-specific three-dimensional finite element study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012; 27(2):359-368.
[31] OLIVEIRA H, BRIZUELA VELASCO A, RÍOS-SANTOS J, et al. Effect of Different Implant Designs on Strain and Stress Distribution under Non-Axial Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(13):4738.
[32] MIYAMOTO I, TSUBOI Y, WADA E, et al. Influence of cortical bone thickness and implant length on implant stability at the time of surgery--clinical, prospective, biomechanical, and imaging study. Bone. 2005;37(6):776-780.
[33] LEKHOLM U, ZARB GA. Patient selection and preparation. Tissue Integrated Prostheses. Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co. Inc., 1985: 199-209.
[34] OKUMURA N, STEGAROIU R, KITAMURA E, et al. Influence of maxillary cortical bone thickness, implant design and implant diameter on stress around implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthodont Res. 2010;54(3):133-142.
[35] SUGIURA T, YAMAMOTO K, HORITA S, et al. The effects of bone density and crestal cortical bone thickness on micromotion and peri-implant bone strain distribution in an immediately loaded implant: a nonlinear finite element analysis. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2016;46(3):152-165.
[36] AYALI A, ALTAGAR M, OZAN O, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the All-on-4, M-4, and V-4 techniques in an atrophic maxilla: A 3D finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2020;123:103880.
[37] BECKER W, HUJOEL PP, BECKER BE, et al. Osteoporosis and implant failure: an exploratory case-control study. J Periodontol. 2000;71(4): 625-631.
[38] HAKIM SG, GLANZ J, OFER M, et al. Correlation of cone beam CT-derived bone density parameters with primary implant stability assessed by peak insertion torque and periotest in the maxilla. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47(3):461-467.
[39] DRAGO C, HOWELL K. Concepts for Designing and Fabricating Metal Implant Frameworks for Hybrid Implant Prostheses. J Prosthodont. 2012;21(5):413-424.
[40] 王稚英,李瑞飘.无牙颌即刻负重种植义齿风险因素的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(9):821-826.
[41] FISCHER K, STENBERG T. Prospective 10-year cohort study based on a randomized, controlled trial (RCT) on implant-supported full-arch maxillary prostheses. part II: prosthetic outcomes and maintenance. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013;15(4):498-508.
[42] RASMUSSEN EJ. Alternative prosthodontic technique for tissue-integrated prostheses. J Prosthet Dent. 1987;57(2):198-204.
[43] TAYLOR TD. Prosthodontic Complications Associated with Implant Therapy. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 1991;3(4):979-991.
[44] GHERLONE E, CAPPARÉ P, VINCI R, et al. Conventional Versus Digital Impressions for “All-on-Four” Restorations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(2):324-330.
[45] SIGNORINI L, FAUSTINI F, SAMARANI R, et al. Immediate fixed rehabilitation supported by pterygoid implants for participants with severe maxillary atrophy: 1-Year postloading results from a prospective cohort study. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;126(1):67-75.
[46] SANTIAGO JUNIOR JF, VERRI FR, ALMEIDA DADF, et al. Finite element analysis on influence of implant surface treatments, connection and bone types. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;63:292-300.
[47] SCHNEIDER D, MARQUARDT P, ZWAHLEN M, et al. A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry. Clin Oral Implan Res. 2009;20( Suppl 4):73-86.
[48] BRÅNEMARK PI, SVENSSON B, VAN STEENBERGHE D. Ten-year survival rates of fixed prostheses on four or six implants ad modum Brånemark in full edentulism. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1995;6(4):227-231.
[49] BALAJI VR, LAMBODHARAN R, MANIKANDAN D, et al. Pterygoid Implant for Atrophic Posterior Maxilla. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2017;9(Suppl 1): S261-S263.
|