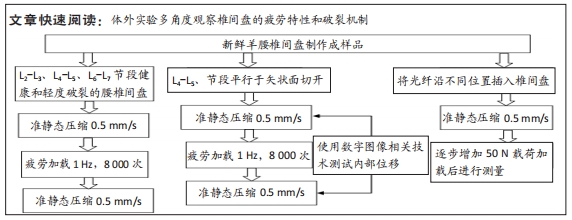
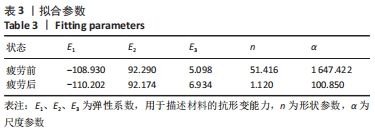
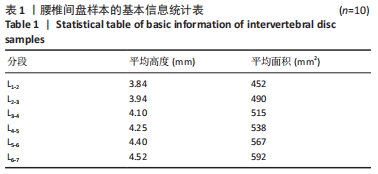
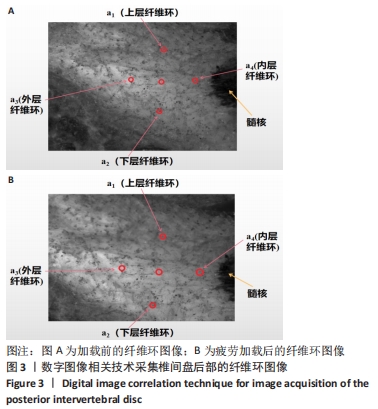
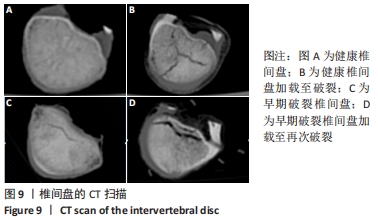
[1] 解志锋,刘清,刘冰,等. 腰椎间盘疲劳损伤的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):339-343.
[2] 杨立杰,欧阳林,陈鼎伟,等.下腰疼痛的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(33):5267-5271.
[3] MIXTER WJ, BARR JS. Rupture of the Intervertebral Disc with Involvement of the Spinal Canal. New Eng J Med. 1934;211(5):210-215.
[4] 欧阳钧,钱蕾,孙培栋. 脊柱生物力学研究的回顾与展望[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(2):169-176.
[5] ZANG CQ, ZHANG T, GAO L, et al. Ratcheting Behavior of Intervertebral Discs Under Cyclic Compression: Experiment and Prediction. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):895-902.
[6] YANSGISAWA O, OSHIKAWA T, MATSUNAGA N, et al. Acute Physiological Response of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs to High-load Deadlift Exercise. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2021;20(3):290-294.
[7] O’NEILL SFD, FIDELMAN JM, HAARUP LS, et al. Low prevalence of end plate junction failure in danish patients with lumbar disc herniation. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):17652.
[8] 孙尚,赵振达,蒋嫒,等. 力学刺激在椎体软骨终板退变中的作用及机制[J]. 医用生物力学,2021,36(4):652-657.
[9] 李宛青. 椎间盘组织结构特点及椎间盘突出症[J]. 生物学杂志, 1998,15(3):26-27.
[10] 张玉文,郭媛,张绪树,等. 兔脊柱节段压缩的生物力学研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2020,35(3):325-330,363.
[11] MIKUCKYT S, OSTAEVIIUS V. Experimental Investigation of an Influence of Coupled Compressive Loading on Porcine Spine Specimens. Mechanika. 2021;27(1):40-44.
[12] 梁仁,卢长巍,吴毅华. 腰椎间盘退行性变及损伤的生物力学研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2015,19(2):201-207.
[13] TAKEOKA Y, YURUBE T, NISHIDA K. Gene Therapy Approach for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: An Update. Neurospine. 2020;17(1): 3-14.
[14] GHEZELBASH F, SHIRAZI-ADL A, BAGHANI M, et al. On the modeling of human intervertebral disc annulus fibrosus: Elastic, permanent deformation and failure responses. J Biomech. 2020;102:109463.
[15] PARKINSON RJ, CALLAGHAN JP. The role of dynamic flexion in spine injury is altered by increasing dynamic load magnitude. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2009;24(2):148-154.
[16] CASAROLI G, VILLA T, BASSANI T, et al. Numerical Prediction of the Mechanical Failure of the Intervertebral Disc under Complex Loading Conditions. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(1):31.
[17] WADE KR, SCHOLLUM ML, RPBERTSON PA, et al. A more realistic disc herniation model incorporating compression, flexion and facet-constrained shear: a mechanical and microstructural analysis. Part I: Low rate loading. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(10):2616-2628.
[18] SHAN Z, WADE KR, SCHOLLUM ML, et al. A more realistic disc herniation model incorporating compression, flexion and facet-constrained shear: a mechanical and microstructural analysis. Part II: high rate or ‘surprise’ loading. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(10):2629-2641.
[19] LI K, ZHANG SJ, DU CF, et al. Effect of Strain Rates on Failure of Mechanical Properties of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Under Flexion. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(6):1980-1989.
[20] YANG X, CHENG X, LUAN Y, et al. Creep experimental study on the lumbar intervertebral disk under vibration compression load. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(8):858-867.
[21] MA K, CHEN S, LI Z, et al. Mechanisms of endogenous repair failure during intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019; 27(1):41-48.
[22] UMALE S, YOGANANDAN N. Mechanisms of Cervical Spine Disc Injury under Cyclic Loading. Asian Spine J. 2018;12(5):910-918.
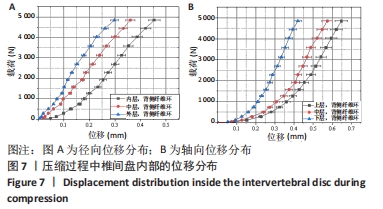
[23] LIU Q, LIU B, ZHANG KP, et al. Effect of Fatigue Load on Internal Mechanical Properties of the Intervertebral Disc. Int J Morphol. 2020;38(6):1597-1605.
[24] BERGER-ROSCHER N, CASAROLI G, RASCHE V, et al. Influence of Complex Loading Conditions on Intervertebral Disc Failure. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(2):E78-E85.
[25] SCHOLLUM ML, WADE KR, ROBERTSON PA, et al. A Microstructural Investigation of Disc Disruption Induced by Low Frequency Cyclic Loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(3):E132-E142.
[26] SUBRAMANI AV, WHITLEY PE, GARIMELLA HT, et al. Fatigue damage prediction in the annulus of cervical spine intervertebral discs using finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2020;23(11):773-784.
[27] KAPLAN JT, NEU CP, DRISSI H, et al. Cyclic loading of human articular cartilage: The transition from compaction to fatigue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;65:734-742.
[28] AZARNOOSH M, SSTOFFEL M, MARKERT B. A study of the damage behaviour of porcine intervertebral discs in a bioreactor environment. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;77:727-733.
[29] ÂNGELO A, PEIXINHO N, PINHO M, et al. The intradiscal failure pressure on porcine lumbar intervertebral discs: an experimental approach. Mechan Sci. 2015; 6(2):255-263.
[30] LEPAGE EC, STOKER AM, KUROKI K, et al. Effects of cyclic compression on intervertebral disc metabolism using a whole-organ rat tail model. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(9):1945-1954.
[31] KALINOWSKI A, KARAM LZ, PEGORINI V, et al. Optical Fiber Bragg Grating Strain Sensor for Bone Stress Analysis in Bovine During Masticatory Movements. IEEE Sens J. 2017;17(8):2385-2392.
[32] WILKE HJ, KETTLER A, WENGER KH, et al. Anatomy of the sheep spine and its comparison to the human spine. Anat Rec. 1997;247(4):542-555.
[33] CASAROLI G, VILLA T, GALBUSERA F. Finite element comparison between the human and the ovine lumbar intervertebral disc. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2018;7(4):510-519.
[34] QASIM M, NATARAJAN RN, AN HS, et al. Damage accumulation location under cyclic loading in the lumbar disc shifts from inner annulus lamellae to peripheral annulus with increasing disc degeneration. J Biomech. 2014;47(1):24-31.
[35] 刘清,刘冰,李琨,等. 体温环境下腰椎间盘疲劳损伤的力学性能研究[J]. 医用生物力学,2019,34(S1):54.
[36] PAVLOVIĆ T,ŠTEFANČIĆ K, ROŽANKOVIĆ M, et al. Ventrolateral disc herniation causes psoas muscle compression: A case report. Radiol Case Rep. 2019;15(2):136-140.
[37] NOGUCHI M, GOOYERS CE, KARAKOLIS T, et al. Is intervertebral disc pressure linked to herniation? An in-vitro study using a porcine model. J Biomech. 2016;49(9):1824-1830.
[38] PELOQUIN JM, ELLIOTT DM. A comparison of stress in cracked fibrous tissue specimens with varied crack location, loading, and orientation using finite element analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;57: 260-268.
[39] WOGNUM S, HUYGHE JM, BAAIJENS FP. Influence of osmotic pressure changes on the opening of existing cracks in 2 intervertebral disc models. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(16):1783-1788.
[40] HUSSEIN AI, MASON ZD, MORGAN EF. Presence of intervertebral discs alters observed stiffness and failure mechanisms in the vertebra. J Biomech. 2013;46(10):1683-1688.
[41] DENNISON CR, WILD PM, WILSON DR, et al. A minimally invasive in-fiber Bragg grating sensor for intervertebral disc pressure measurements. Measur Sci Technol. 2008;19(8):085201.
[42] KARPIńSKI, ROBERT, JAWORSKI, et al. The influence of the nucleus pulposus on the stress distribution in the natural and prosthetic intervertebral disc. MATEC Web of Conferences. 2019. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/201925207006
[43] SCHMIDT H, SHIRAZI-ADL A. Temporal and spatial variations of pressure within intervertebral disc nuclei. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;79:309-313.
|