中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (32): 5236-5241.doi: 10.12307/2022.910
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨膜牵张技术用于糖尿病足治疗的理论基础及临床结果验证
刘 杰 1,2,5,花奇凯1,5,李山郎3,余 杰1,苏宏杰1,2,4,5,丁 毅1,5,赵永鑫1,2,5,苏永锋1,5,陈 炎1
- 1广西医科大学第一附属医院骨关节外科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;2广西医科大学再生医学与医用生物资源开发应用协同创新中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;3右江民族医学院附属医院运动医学科,广西壮族自治区百色市 533000;4广西医科大学再生医学研究中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;5广西壮族自治区糖尿病足保肢工程研究中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Periosteum distraction for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcer: theoretical basis and clinical verification
Liu Jie1, 2, 5, Hua Qikai1, 5, Li Shanlang3, Yu Jie1, Su Hongjie1, 2, 4, 5, Ding Yi1, 5, Zhao Yongxin1, 2, 5, Su Yongfeng1, 5, Chen Yan1
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University; 2Collaborative Innovation Center of Regenerative Medicine and Medical Biological Resources Development and Application, Guangxi Medical University; 3Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Youjiang Medical College for Nationalities; 4Guangxi Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Guangxi Medical University; 5Guangxi Diabetic Foot Limb Salvage Engineering and Research Center
摘要:
文题释义:
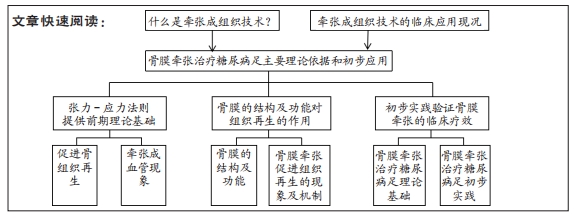
张力-应力法则:也称牵张成组织原理,即对任何活组织进行缓慢、持续及稳定的牵张,可以使其进入细胞增生和生物合成功能激活的状态,最终再生新的组织。
糖尿病足:是糖尿病患者由于肢体远端血管、神经病变等导致机体缺血和缺乏正常的神经自我保护机制,引发足部的感染、溃疡和(或)深层组织破坏,是糖尿病患者最严重的并发症之一。
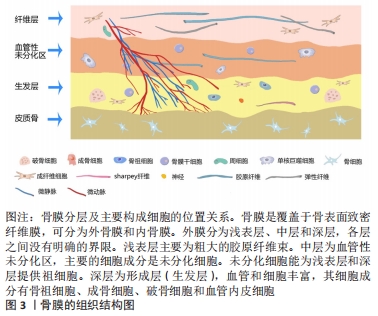
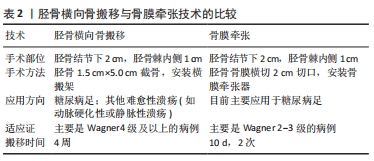
背景:骨膜牵张也具有促进成骨和微血管生成作用,但能否用于治疗糖尿病足目前尚未明确。
目的:对骨膜牵张促进骨和血管再生的研究进展进行综述,以明确该技术用于糖尿病足治疗的理论基础,并介绍其在治疗糖尿病足中的初步应用。
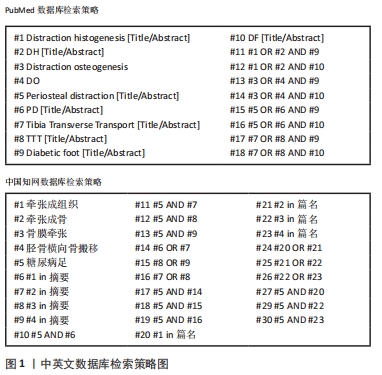
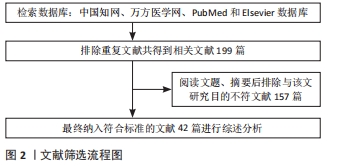
方法:计算机检索万方医学网、中国知网、PubMed及Elsevier数据库收录的相关文献,中文检索词为:“牵张成组织技术、牵张成骨、胫骨横向骨搬移与糖尿病足、骨膜牵张、骨膜牵张成骨、骨膜牵张与糖尿病足”;英文检索词为“Distraction histogenesis,Distraction osteogenesis,Tibia transverse transport and diabetic foot,Periosteal distraction osteogenesis,Periosteal distraction and diabetic foot”。最终纳入42篇文献进行综述分析。
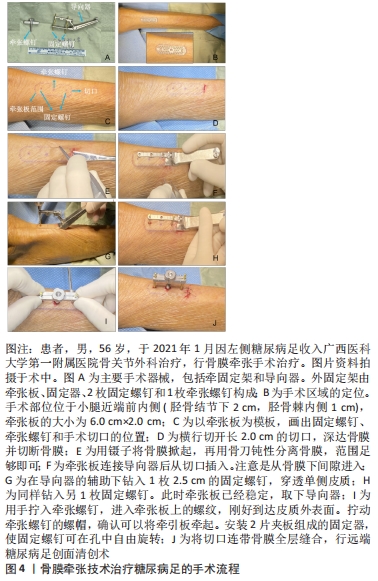
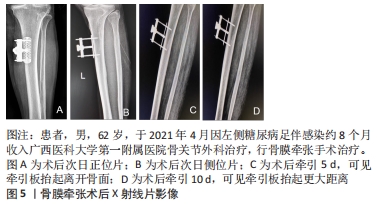
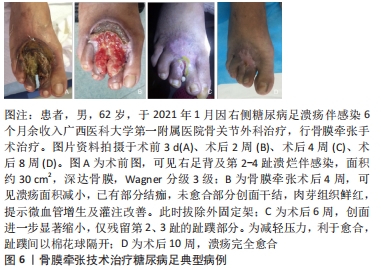
结果与结论:①基于Ilizarov张力-应力法则或牵张成组织原理,牵张成骨技术已用于治疗骨缺损、骨不连等疾病,而牵张成骨伴随的成血管原理催生了胫骨横向骨搬移技术,该技术已经成功应用于治疗包括糖尿病足在内的下肢难愈性溃疡,取得良好的治疗效果。②研究发现对骨膜进行持续、稳定、缓慢的牵张可以促进骨和血管再生,即骨膜牵张成骨和成血管现象,该现象的机制可能与骨膜的结构和成分有关。③目前关于骨膜牵张的研究主要聚焦于其成骨功能,且主要停留在动物实验阶段而极少用于人体。与胫骨横向骨搬移促进血管再生从而用于治疗糖尿病足类似,骨膜牵张促进血管再生也可能用于治疗糖尿病足,此即骨膜牵张用于治疗糖尿病足的理论基础。④该课题组已初步将骨膜牵张用于临床治疗糖尿病足,且治疗效果良好,该文章通过展示用于骨膜搬移的器械、手术方法及典型病例。初步结果显示,由于骨膜牵张技术不需要截骨,手术操作要比胫骨横向骨搬移更加简单,手术时间更短;因为骨膜牵张技术缺少对胫骨钻孔和骨搬移的操作,缺乏对胫骨髓腔的“开窗减压”作用及骨组织的搬移,可能促血管生成和创面愈合的效果要弱于胫骨横向骨搬。未来还需对骨膜牵张促进骨和血管再生的具体机制以及手术适应证及禁忌证等进一步研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5009-3776 (刘杰) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5962-5713 (陈炎)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: