1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验,多组数据比较使用单因素方差分析,两两比较使用最小显著性差异法(LSD)。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2018年10-12月在南方医科大学南方医院脊柱脊髓损伤研究实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 成年雄性SD大鼠60只,体质量280-320 g,由南方医科大学实验动物中心提供,动物许可证号:SYXK(粤)2016-0167,饲养环境:湿度40%-47%,温度20-25 ℃,光照12 h阴暗12 h。
1.3.2 实验主要仪器设备 CO2细胞孵育箱、实验生物安全柜(Thermo公司,美国);细胞/组织超声粉碎仪(新芝公司,中国);蛋白电泳仪(Bio-Rad公司,美国);超净工作台(苏州超净仪器厂,中国);Instron E1000电磁伺服材料试验机(Instron公司,美国);YH-X-4A小动物手术显微镜(镇江亿华光学仪器有限公司,中国);小动物麻醉机(Matrix公司,美国);小动物立体定位仪(深圳瑞沃德生命科技公司,中国);组织冰冻切片机(Thermo Fisher Scientific 公司,美国);光学显微镜及成像系统、激光共聚焦荧光显微镜(Olympus公司,日本);多功能酶标仪(MD公司,美国);全自动化学发光成像分析系统,(上海Tanon公司,中国)。
1.3.3 细胞及实验主要试剂 大鼠肾上腺PC12细胞(ATCC细胞库,美国);兔抗大鼠STAT3多克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠NCK1多克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠Catalase多克隆抗体(均为Proteintech公司产品,美国);兔抗大鼠锰超氧化物歧化酶多克隆抗体、兔抗大鼠GAPDH多克隆抗体(均为Abcam公司产品,美国);信号转导和转录激活因子(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT)STAT3抑制剂(STATTIC)(Selleck公司,美国); 山羊抗兔二抗(北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司,中国);三羟乙基芦丁[上海阿拉丁(Aladdin)试剂有限公司,中国];荧光二抗FITC、荧光二抗TRITC、叔丁基过氧化氢(tert-butyl hydroperoxide,TBHP)、四甲基偶氮唑盐(MTT)(均为Sigma公司产品,美国);DCFH-DA荧光探针(Gibco公司,美国)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 实验方案 通过MTT方法检测梯度浓度TBHP和三羟乙基芦丁对PC12细胞活性的影响,然后通过DCFH探针检测三羟乙基芦丁对TBHP诱导细胞中活性氧产生的影响,采用Western blot方法检测三羟乙基芦丁和STAT3抑制剂对TBHP刺激后的PC12细胞及颈脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中氧化应激水平的影响,免疫荧光染色检测三羟乙基芦丁对颈脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中STAT3和锰超氧化物歧化酶表达的影响。
1.4.2 细胞实验
(1)细胞培养:大鼠肾上腺PC12细胞购于美国模式菌种收集中心(ATCC)细胞库。将大鼠肾上腺PC12细胞胰酶消化、离心、悬浮后均匀接种于细胞培养皿中,每皿中加入6-8 mL DMEM完全培养基(包含体积分数5%灭活胎牛血清以及10%马血清,青霉素/链霉素双抗生素液100 U/mL),置于37 ℃、体积分数5%CO2细胞孵育箱中培养。
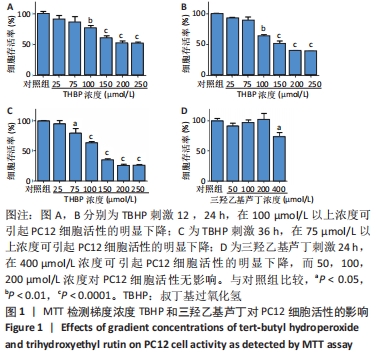
(2) MTT法检测梯度浓度TBHP对PC12细胞活性的影响:将PC12细胞重悬后均匀接种于96孔板中,采用细胞计数板计数,每孔接种细胞浓度为1×104 L-1,每组均设置6个复孔,置于细胞培养箱中孵育24 h后,分别加入含有0,25,75,100,150,200,250 μmol/L等不同浓度的TBHP培养基,置于细胞培养箱中继续孵育,分别于TBHP刺激12,24,36 h后进行MTT比色法检测,置于多功能酶标仪测定吸光度值(A值),波长设定为490 nm,统计不同TBHP刺激浓度及不同刺激时间段细胞的存活率。
(3) MTT法检测梯度浓度三羟乙基芦丁对PC12细胞活性的影响:将PC12细胞重悬后均匀接种于96孔板中,采用细胞计数板计数,每孔接种细胞浓度为1×104 L-1,每组均设置6个复孔,置于细胞培养箱中孵育24 h后,分别加入含有0,50,100,200,400 μmol/L等不同浓度的三羟乙基芦丁培养基,置于细胞培养箱中继续孵育,于培养24 h后进行MTT比色法检测。
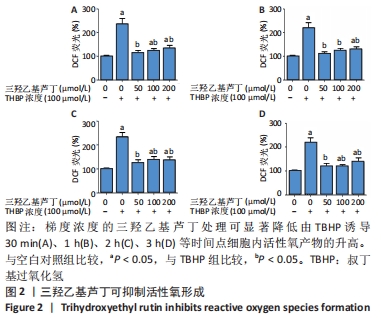
(4)DCFH探针检测三羟乙基芦丁对TBHP诱导PC12细胞中活性氧产生的影响:将PC12细胞重悬后均匀接种于96孔板中,采用细胞计数板计数,每孔接种细胞浓度为1×104 L-1,每组均设置6个复孔,置于细胞培养箱中孵育24 h。根据MTT实验结果,选取三羟乙基芦丁的浓度为0,50,100,200 μmol/L等浓度梯度的溶液,加入96孔板中于细胞培养箱中预孵细胞12 h,将96孔板中的细胞培养基吸除,避光下加入浓度为10 μmol/L DCFH-DA荧光探针培养基,置于细胞培养箱中反应30 min。选取的TBHP刺激浓度为100 μmol/L,置于细胞培养箱中持续刺激30 min及1,2,3 h;取出96孔板避光下移至多功能酶标仪检测室,调节多功能酶标仪,设定激发光波长为488 nm,发生光波长为525 nm,轻微振荡后检测各个孔中的荧光强度。
1.4.3 动物实验
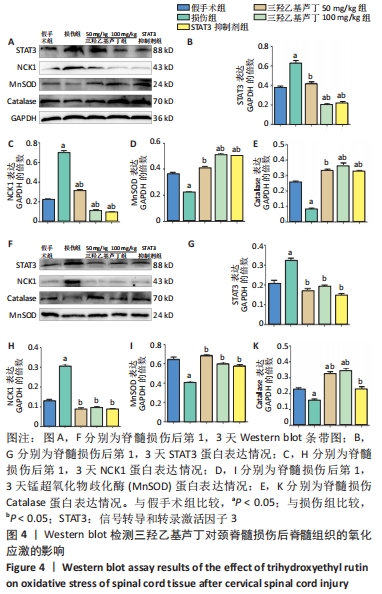
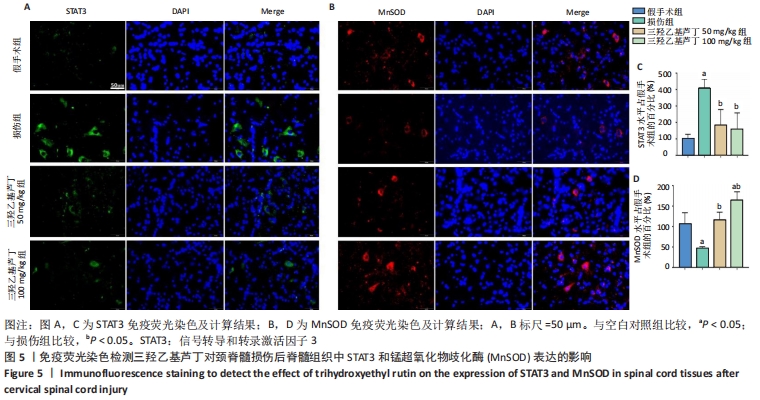
(1)动物分组:60只大鼠随机分为6组:假手术组(n=12);损伤组(n=12),三羟乙基芦丁50 mg/kg 组(n=12),三羟乙基芦丁100 mg/kg组(n=12),STAT3抑制剂组(n=12)。
(2)颈脊髓损伤模型的建立:大鼠颈脊髓半侧挫伤模型制作参考既往研究[9]。操作过程:以C5节段为中心行一长2.0-3.0 cm纵行手术切口,逐层分离,显露C5节段椎板骨性结构,咬骨钳咬除C5左侧椎板,显露出脊髓后中央动脉,大鼠固定后置于Instron E1000电磁伺服材料试验机试验平台装置上,设定参数为打击速度500 mm/s,打击深度为2.0 mm。三羟乙基芦丁50 mg/kg组和100 mg/kg组大鼠根据体质量在损伤造模后分别立即予以腹腔注射三羟乙基芦丁50 mg/kg和100 mg/kg,1次/d,连续注射3 d;抑制剂组在损伤造模后立即给予STAT3抑制剂2 000 µg/kg,1次/d,连续注射3 d;假手术组的动物进行了椎板切除术,但未施行挫伤打击操作。假手术组和损伤组大鼠予以腹腔注射生理盐水,1次/d,连续注射3 d。

1.4.4 Western blot检测相关蛋白表达水平
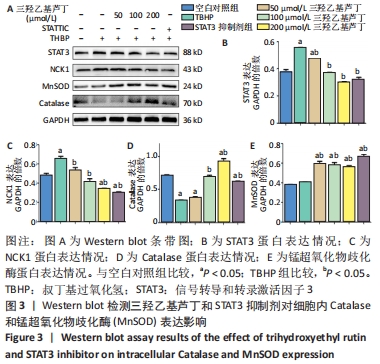
(1)细胞蛋白样品的制备:将细胞分为空白对照组,TBHP 100 μmol/L刺激组,三羟乙基芦丁 50,100,200 μmol/L组,STAT3抑制剂 2 μmol/L组共计6组,除对照组外,其余各培养皿细胞培养12 h后分别加入TBHP进行刺激,刺激浓度为100 μmol/L。培养皿中加入细胞蛋白裂解液,冰上裂解充分反应,细胞刮刀刮取细胞,置于冰上预冷的EP离心管,用超声波进一步充分裂解细胞(冰上进行,以防温度过高降解蛋白),超声30 s,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心30 min,将蛋白上清液转入新的离心管中,-80℃冰箱冻存备用中;BCA法蛋白定量,在562 nm波长下比色,根据待测蛋白样品的吸光值,计算相应样品的蛋白浓度;蛋白质预变性,将蛋白样品与含有溴酚蓝SDS的上样缓冲液(Loading Buffer)按照4∶1的比例混合均匀后,置于100 ℃温度沸水中5-7 min使蛋白充分变性,EP管分装后,置于-80 ℃冰箱保存。
(2)脊髓组织蛋白样品的制备:在大鼠颈脊髓损伤后第1,3天用3 g/L戊巴比妥钠过量麻醉进行颈脊髓组织取材,每个时间点6只,以C5损伤节段为中心冰上切取1 cm长的颈脊髓组织标本,在每1 mL预冷Lysis Buffer中加入1 µL蛋白酶抑制剂、5 µL磷酸酶抑制剂和5 µL 100 mmol/L的 PMSF,混合均匀后置于冰上备用。按照100 mg组织∶1 000 µL裂解液的比例冰上操作,用超声波更充分地裂解组织(冰上进行,以防温度过高降解蛋白),超声30 s,4 ℃下12 000 r/min离心30 min,将蛋白上清液转入新的离心管中,-80 ℃冰箱冻存备用。蛋白定量和预变性方法同上述(1)部分。
(3)电泳、转膜、免疫杂交:根据不同蛋白分子量大小配置不同浓度的胶,电泳缓冲液清洗上样孔,将准备好的样品上样。①电泳:浓缩胶设定参数为恒压80 V,30 min,使蛋白样品在上层的浓缩胶中发生线性浓缩;当样品蛋白进入分离胶时,蛋白Marker的条带发生分离,分离胶设定参数为恒压120 V,60 min;待溴酚蓝跑至凝胶下方停止电泳;②转膜:设定参数为恒流200 mA,转移时间90 min,将转膜槽置于冰水中,防止转膜温度过高影响转膜效果,直至相应的蛋白Marker转移至PVDF膜上;③免疫杂交:将目的蛋白抗体和内参抗体使用一抗稀释液稀释,稀释浓度为兔抗大鼠锰超氧化物歧化酶抗体1∶1 000,兔抗大鼠GAPDH抗体1∶2 000,兔抗大鼠NCK1抗体1∶1 000,兔抗大鼠Catalase抗体1∶1 000,兔抗大鼠STAT3抗体1∶1 000,将PVDF膜置于相应抗体液中,置于4 ℃摇床上慢摇孵育过夜,加入PBST于快速摇床上洗膜3次,每次10 min;二抗用封闭液稀释各蛋白一抗对应的二抗 (1∶5 000)室温下孵育1 h,PBST洗膜3次,每次10 min;④显影:加入化学发光试剂孵育,发光显影,拍照记录,对获得的条带使用Image J软件进行分析,计算各目标蛋白与对应的内参蛋白条带的灰度百分比,即为该目标蛋白的相对表达量。
1.4.5 免疫荧光检测三羟乙基芦丁对颈脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中STAT3和锰超氧化物歧化酶表达 组织切片室温下复温30 min,置于丙酮溶液中固定10-15 min,将脊髓组织切片置于PBS中3次,每次5 min;加入0.5%TritonX-100进行细胞打孔,于37 ℃打孔5 min,吸除多余的TritonX-100液,置于PBS中3次,每次5 min,加入3%BSA溶液进行抗原封闭,37 ℃温度下封闭1 h;加入一抗兔抗大鼠STAT3抗体1∶200和兔抗大鼠锰超氧化物歧化酶抗体1∶200,置于4 ℃孵育过夜;置于PBS中3次,每次5 min;加入荧光二抗室温避光孵育2 h,置于PBS中3次,每次5 min;加入DAPI(1∶1 000稀释) 室温下避光染核5 min,PBS漂洗3次,于激光共聚焦显微镜下观察和拍照。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①梯度浓度TBHP和三羟乙基芦丁对PC12细胞活性的影响;②三羟乙基芦丁对TBHP诱导细胞内活性氧产生的影响;③三羟乙基芦丁和STAT3抑制剂对TBHP刺激后的PC12细胞及颈脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中氧化应激水平的影响;④三羟乙基芦丁对颈脊髓损伤后脊髓组织中STAT3和锰超氧化物歧化酶表达的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 20.0统计软件(SPSS Inc.,IL,美国)进行数据统计分析,所有计量资料数据以x±s表示,多组数据比较使用单因素方差分析进行统计,组内两两比较使用最小显著性差异法(LSD)进行统计。所有实验均重复3次或3次以上, P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。