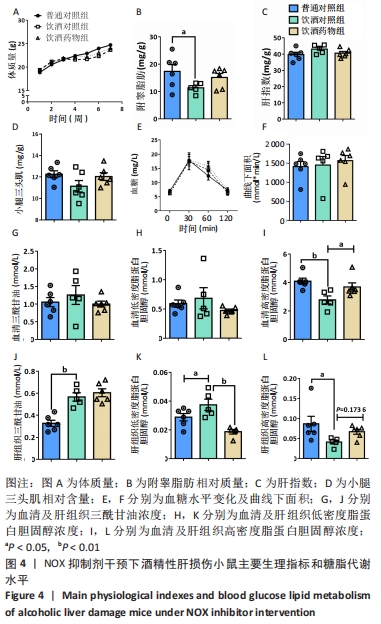
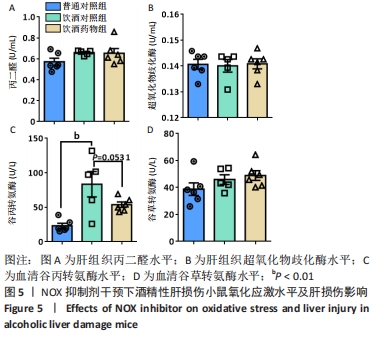
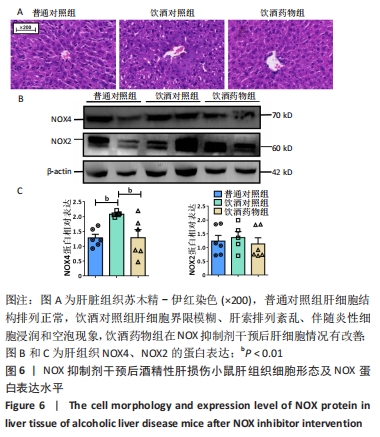
[1] LI S, HONG M, TAN HY, et al. Insights into the Role and Interdependence of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Liver Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:4234061.
[2] ZHOU T, ZHANG YJ, XU DP, et al. Protective Effects of Lemon Juice on Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7463571.
[3] LUSHUCHAK VI. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;224:164-175.
[4] SUMINMOTO H. Structure, regulation and evolution of Nox-family NADPH oxidases that produce reactive oxygen species. FEBS J. 2008;275(13):3249-3277.
[5] BRANDES RP, WEISSMANN N, SCHRODER K. Nox family NADPH oxidases: Molecular mechanisms of activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;76:208-226.
[6] SORCE S, KRAUSE KH, JAQUET V. Targeting NOX enzymes in the central nervous system: therapeutic opportunities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(14):2387-2407.
[7] MARTNER A, AYDIN E, HELLSTRAND K. NOX2 in autoimmunity, tumor growth and metastasis. J Pathol. 2019;247(2):151-154.
[8] SINGEL KL, SEGAL BH. NOX2-dependent regulation of inflammation. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016;130(7):479-490.
[9] CHAO Z, YONGJI X, LIZHI B, et al. Effects of Crocin on Nox2 Expression and ROS Level of Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced Injury of Cardiomyocytes. Medicinal Plant. 2020;11(5):71-75.
[10] TISEO G, CAVARRETTA E, FORNITI A, et al. Interplay between Nox2 Activity and Platelet Activation in Patients with Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Prospective Study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4165358.
[11] YANG Q, WU FR, WANG JN, et al. Nox4 in renal diseases: An update. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;124:466-472.
[12] CHEN C, LI L, ZHOU HJ, et al. The Role of NOX4 and TRX2 in Angiogenesis and Their Potential Cross-Talk. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017;6(2):42.
[13] IIATOVSKAYA DV, BLASS G, PALYGIN O, et al. A NOX4/TRPC6 Pathway in Podocyte Calcium Regulation and Renal Damage in Diabetic Kidney Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(7):1917-1927.
[14] RAJARAM RD, DISSARD R, FAIVRE A, et al. Tubular NOX4 expression decreases in chronic kidney disease but does not modify fibrosis evolution. Redox Biol. 2019; 26:101234.
[15] CHOUDHURY SR, BABES L, RAHN JJ, et al. Dipeptidase-1 Is an Adhesion Receptor for Neutrophil Recruitment in Lungs and Liver. Cell. 2019;178(5):1205-1221.
[16] KANURI BN, REBELLO SC, PATHAK P, et al. Glucose and lipid metabolism alterations in liver and adipose tissue pre-dispose p47(phox) knockout mice to systemic insulin resistance. Free Radic Res. 2018;52(5):568-582.
[17] TARAFDAR A, PULA G. The Role of NADPH Oxidases and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):3824.
[18] QIN YY, LI M, FENG X, et al. Corrigendum to “Combined NADPH and the NOX inhibitor apocynin provides greater anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of stroke” [Free Radic. Biol. Med. 104 (2017) 333-345].Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;115:498-499.
[19] BERTOLA A, MATHEWS S, KI SH, et al. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the NIAAA model). Nat Protoc. 2013,8(3):627-637.
[20] THOMPSON KJ, NAZARI SS, JACOBS WC, et al. Use of a crossed high alcohol preferring (cHAP) mouse model with the NIAAA-model of chronic-binge ethanol intake to study liver injury. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017;52(6):629-637.
[21] 崔玮,崔迪.白细胞介素-6在酒精性肝病中的作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2021,37(4):467-474.
[22] SEITZ HK, BATALLER R, CORTEZ-PINTO H, et al. Alcoholic liver disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):16.
[23] SZABO G. Gut-liver axis in alcoholic liver disease.Gastroenterology. 2015;148(1):30-36.
[24] TORRUELLAS C, FRENCH SW, MEDICI V. Diagnosis of alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(33):11684-11699.
[25] SASAKI Y, DEHNAD A, FISH S, et al. NOX4 Regulates CCR2 and CCL2 mRNA Stability in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46144.
[26] DE MINICIS S, BRENNER DA. NOX in liver fibrosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007; 462(2):266-272.
[27] SHI Q, LEE DY, FELIERS D, et al. Interplay between RNA-binding protein HuR and Nox4 as a novel therapeutic target in diabetic kidney disease. Mol Metab. 2020;36:100968.
[28] LI M, HE Y, ZHOU Z, et al. MicroRNA-223 ameliorates alcoholic liver injury by inhibiting the IL-6-p47(phox)-oxidative stress pathway in neutrophils. Gut. 2017; 66(4):705-715.
[29] WANG X, ZHAO S, SU M, et al. Geraniol improves endothelial function by inhibiting NOX-2 derived oxidative stress in high fat diet fed mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;474(1):182-187.
[30] CHENG S, GE J, ZHAO C, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise and diet on liver fat in pre-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease:A randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15952.
[31] VIEIRA AF, COSTA RR, MACEDO RC, et al. Effects of aerobic exercise performed in fasted v. fed state on fat and carbohydrate metabolism in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2016;116(7):1153-1164.
[32] MUSCELLA A, STEFANO E, LUNETTI P, et al. The Regulation of Fat Metabolism During Aerobic Exercise. Biomolecules. 2020;10(12):1699.
[33] 欧阳婷,崔玮,陈伟恺,等. NOX介导氧化应激与阿尔兹海默病研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(12):1338-1345.
[34] 刘姣,周刚,梅雨,等. 一次性力竭运动致大鼠骨骼肌氧化应激的机制[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2020,36(1):17-22.
[35] LIANG S, KISSELEVA T, BRENNER DA. The Role of NADPH Oxidases (NOXs) in Liver Fibrosis and the Activation of Myofibroblasts. Front Physiol. 2016;7:17.
[36] PAIK YH, KIM J, AOYAMA T, et al. Role of NADPH oxidases in liver fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20(17):2854-2872.
[37] SANCHO P, MAINEZ J, CROSAS-MOLIST E, et al. NADPH oxidase NOX4 mediates stellate cell activation and hepatocyte cell death during liver fibrosis development. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45285.
[38] GONCALVES I O, PASSOS E, ROCHA-RODRIGUES S, et al. Physical exercise antagonizes clinical and anatomical features characterizing Lieber-DeCarli diet-induced obesity and related metabolic disorders. Clin Nutr. 2015,34(2):241-247.
|