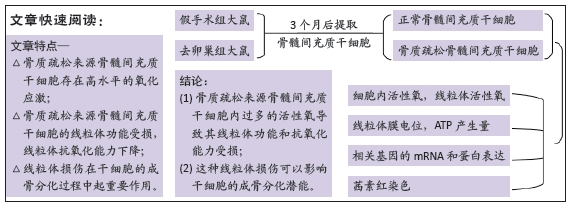
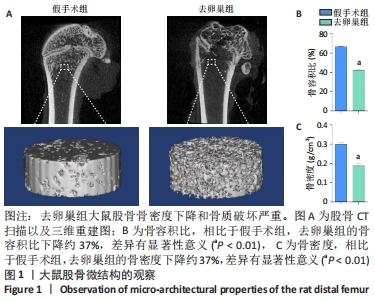
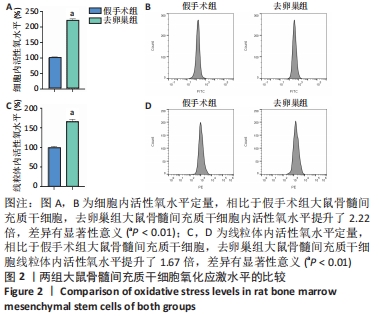
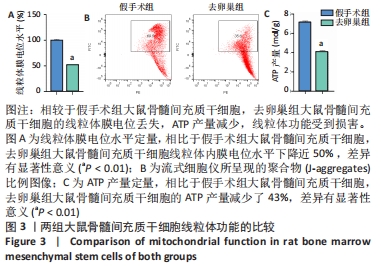
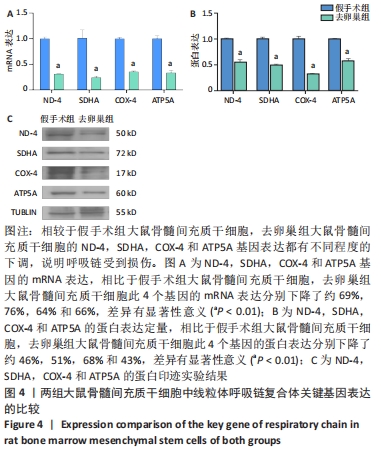
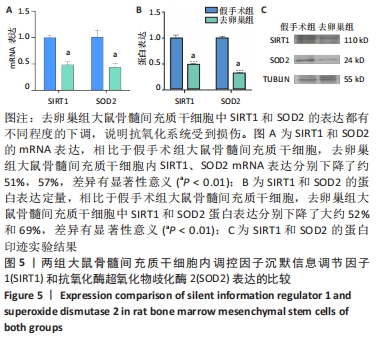
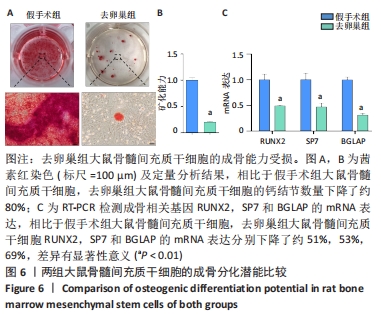
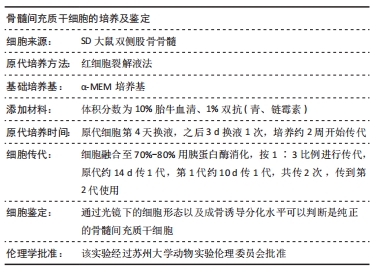
[1] LANGDAHL BL. Overview of treatment approaches to osteoporosis. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(9):1891-1906.
[2] ANAM AK, INSOGNA K. Update on Osteoporosis Screening and Management. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105(6):1117-1134.
[3] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287.
[4] SALARI N, GHASEMI H, MOHAMMADI L, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):609.
[5] CHENG X, ZHAO K, ZHA X, et al. Opportunistic Screening Using Low-Dose CT and the Prevalence of Osteoporosis in China: A Nationwide, Multicenter Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(3):427-435.
[6] LEE NK, CHOI YG, BAIK JY, et al. A crucial role for reactive oxygen species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Blood. 2005; 106(3):852-859.
[7] HO PJ, YEN ML, TANG BC, et al. H2O2 accumulation mediates differentiation capacity alteration, but not proliferative decline, in senescent human fetal mesenchymal stem cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;18(15):1895-1905.
[8] ZHANG YB, ZHONG ZM, HOU G, et al. Involvement of oxidative stress in age-related bone loss. J Surg Res. 2011;169(1):e37-42.
[9] KALYANARAMAN B. Teaching the basics of repurposing mitochondria-targeted drugs: From Parkinson’s disease to cancer and back to Parkinson’s disease. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101665.
[10] MENDIVIL-PEREZ M, SOTO-MERCADO V, GUERRA-LIBRERO A, et al. Melatonin enhances neural stem cell differentiation and engraftment by increasing mitochondrial function. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(2). doi: 10.1111/jpi.12415.
[11] KUNG HC, LIN KJ, KUNG CT, et al. Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Neuroprotection of Polyphenols with Respect to Resveratrol in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomedicines. 2021;9(8):918.
[12] SHARES BH, BUSCH M, WHITE N, et al. Active mitochondria support osteogenic differentiation by stimulating β-catenin acetylation. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(41):16019-16027.
[13] GRAYSON WL, ZHAO F, BUNNELL B, et al. Hypoxia enhances proliferation and tissue formation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;358(3):948-953.
[14] WANG C, MENG H, WANG X, et al. Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Osteoblasts and Adipocytes and its Role in Treatment of Osteoporosis. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:226-233.
[15] KOMAROVA SV, ATAULLAKHANOV FI, GLOBUS RK. Bioenergetics and mitochondrial transmembrane potential during differentiation of cultured osteoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;279(4):C1220-1229.
[16] CHA Y, HAN MJ, CHA HJ, et al. Metabolic control of primed human pluripotent stem cell fate and function by the miR-200c-SIRT2 axis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(5):445-456.
[17] DI MEO S, REED TT, VENDITTI P, et al. Role of ROS and RNS Sources in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:1245049.
[18] WANG FS, WU RW, CHEN YS, et al. Biophysical Modulation of the Mitochondrial Metabolism and Redox in Bone Homeostasis and Osteoporosis: How Biophysics Converts into Bioenergetics. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(9):1394.
[19] YANG S, FESKANICH D, WILLETT WC, et al. Association between global biomarkers of oxidative stress and hip fracture in postmenopausal women: a prospective study. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(12):2577-2583.
[20] LANGDAHL JH, FREDERIKSEN AL, HANSEN SJ, et al. Mitochondrial Point Mutation m.3243A>G Associates With Lower Bone Mineral Density, Thinner Cortices, and Reduced Bone Strength: A Case-Control Study. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(10):2041-2048.
[21] OZGOCMEN S, KAYA H, FADILLIOGLU E, et al. Role of antioxidant systems, lipid peroxidation, and nitric oxide in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;295(1-2):45-52.
[22] ZINNUROGLU M, DINCEL AS, KOSOVA F, et al. Prospective evaluation of free radicals and antioxidant activity following 6-month risedronate treatment in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(4):875-880.
[23] TANG X, MA S, LI Y, et al. Evaluating the Activity of Sodium Butyrate to Prevent Osteoporosis in Rats by Promoting Osteal GSK-3β/Nrf2 Signaling and Mitochondrial Function. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(24): 6588-6603.
[24] KOBAYASHI K, NOJIRI H, SAITA Y, et al. Mitochondrial superoxide in osteocytes perturbs canalicular networks in the setting of age-related osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9148.
[25] CHEN CT, SHIH YR, KUO TK, et al. Coordinated changes of mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant enzymes during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(4):960-968.
[26] DICKIE LJ, AZIZ AM, SAVIC S, et al. Involvement of X-box binding protein 1 and reactive oxygen species pathways in the pathogenesis of tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(12):2035-2043.
[27] ANDRÉ L, GOUZI F, THIREAU J, et al. Carbon monoxide exposure enhances arrhythmia after cardiac stress: involvement of oxidative stress. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6):1235-1246.
[28] SATO T, SAITO T, SAEGUSA N, et al. Mitochondrial Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cardiac myocytes: a mechanism of the cardioprotective effect and modulation by protein kinase A. Circulation. 2005;111(2): 198-203.
[29] ZHANG F, CUI J, LIU X, et al. Correction to: Roles of microRNA-34a targeting SIRT1 in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):331.
[30] LI HJ, SUN XM, LI ZK, et al. LncRNA UCA1 Promotes Mitochondrial Function of Bladder Cancer via the MiR-195/ARL2 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(6):2548-2561.
[31] ZHOU J, ZHANG F, MENG H, et al. Introducing extra NADPH consumption ability significantly increases the photosynthetic efficiency and biomass production of cyanobacteria. Metab Eng. 2016;38:217-227.
[32] LV YJ, YANG Y, SUI BD, et al. Resveratrol counteracts bone loss via mitofilin-mediated osteogenic improvement of mesenchymal stem cells in senescence-accelerated mice. Theranostics. 2018;8(9):2387-2406.
[33] EBERT R, ULMER M, ZECK S, et al. Selenium supplementation restores the antioxidative capacity and prevents cell damage in bone marrow stromal cells in vitro. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1226-1235.
[34] NDI M, MARIN-BUERA L, SALVATORI R, et al. Biogenesis of the bc(1) Complex of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain. J Mol Biol. 2018; 430(21):3892-3905.
[35] GELDON S, FERNÁNDEZ-VIZARRA E, TOKATLIDIS K. Redox-Mediated Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Dynamics, and Respiratory Chain Assembly in Yeast and Human Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 720656.
[36] HE J, LIU X, SU C, et al. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage Improves Reendothelialization Capacity of Endothelial Progenitor Cells via SIRT3 (Sirtuin 3)-Enhanced SOD2 (Superoxide Dismutase 2) Deacetylation in Hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019; 39(8):1682-1698.
[37] TSAI YT, YEH HY, CHAO CT, et al. Superoxide Dismutase 2 (SOD2) in Vascular Calcification: A Focus on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, Calcification Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Strategies. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6675548.
[38] CHEN W, CHEN X, CHEN AC, et al. Melatonin restores the osteoporosis-impaired osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by preserving SIRT1-mediated intracellular antioxidant properties. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;146:92-106.
[39] GAO J, FENG Z, WANG X, et al. SIRT3/SOD2 maintains osteoblast differentiation and bone formation by regulating mitochondrial stress. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(2):229-240.
|