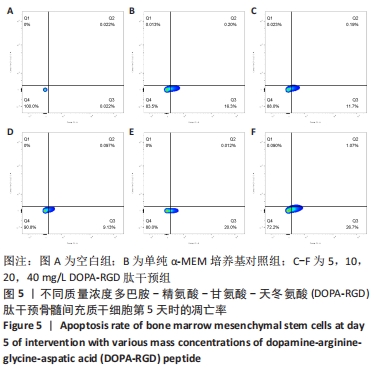
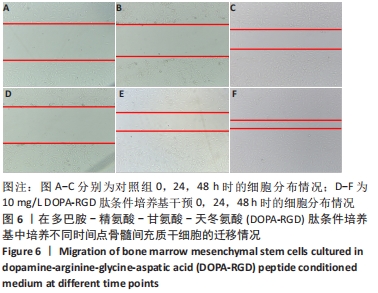
[1] GIANNOUDIS PV, CALORI GM, BÉGUÉ T, et al. Tissue loss and bone repair: Time to develop an international strategy? Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 8:S1-2.
[2] PAPAKOSTIDIS C, BHANDARI M, GIANNOUDIS PV. Distraction osteogenesis in the treatment of long bone defects of the lower limbs: effectiveness, complications and clinical results; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(12):1673-1680.
[3] VERLINDEN CR, VAN DE VIJFEIJKEN SE, TUINZING DB, et al. Complications of mandibular distraction osteogenesis for developmental deformities: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44(1):44-49.
[4] 张进,张永红,王钞琦,等.髓内延长钉技术的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(5):642-647.
[5] PALEY D. Problems, obstacles, and complications of limb lengthening by the Ilizarov technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(250):81-104.
[6] YANAGISAWA Y, ITO A, HARA Y, et al. Initial clinical trial of pins coated with fibroblast growth factor-2-apatite composite layer in external fixation of distal radius fractures. J Orthop. 2018;16(1):69-73.
[7] GATHEN M, PLOEGER MM, JAENISCH M, et al. Outcome evaluation of new calcium titanate schanz-screws for external fixators. First clinical results and cadaver studies. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(11):124.
[8] BAKHSH K, ZIMRI FK, ATIQ-UR-REHMAN, et al. Outcome of complex non-unions of femoral fractures managed with Ilizarov method of distraction osteogenesis. Pak J Med Sci. 2019;35(4):1055-1059.
[9] GUICHET JM, DEROMEDIS B, DONNAN LT, et al. Gradual femoral lengthening with the Albizzia intramedullary nail. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(5):838-848.
[10] GARCÍA-CIMBRELO E, CURTO DE LA MANO A, GARCÍA-REY E, et al. The intramedullary elongation nail for femoral lengthening. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84(7):971-977.
[11] LEE DH, RYU KJ, SONG HR, et al. Complications of the Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor (ISKD) in distraction osteogenesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(12):3852-3859.
[12] KRIEG AH, LENZE U, SPETH BM, et al. Intramedullary leg lengthening with a motorized nail. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(3):344-350.
[13] COLE JD, JUSTIN D, KASPARIS T, et al. The intramedullary skeletal kinetic distractor (ISKD): first clinical results of a new intramedullary nail for lengthening of the femur and tibia. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 4:SD129-139.
[14] WANG K, EDWARDS E. Intramedullary skeletal kinetic distractor in the treatment of leg length discrepancy--a review of 16 cases and analysis of complications. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26(9):e138-144.
[15] GUICHET JM, SPIVAK JM, TROUILLOUD P, et al. Lower limb-length discrepancy. An epidemiologic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(272):235-241.
[16] QI MC, ZOU SJ, HAN LC, et al. Expression of bone-related genes in bone marrow MSCs after cyclic mechanical strain: implications for distraction osteogenesis. Int J Oral Sci. 2009;1(3):143-150.
[17] QI MC, HU J, ZOU SJ, et al. Mechanical strain induces osteogenic differentiation: Cbfa1 and Ets-1 expression in stretched rat mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37(5):453-458.
[18] 姜涛,吴硕,李志强,等.血小板衍生生长因子BB促进SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):1976-1981.
[19] PEREZ JR, KOUROUPIS D, LI DJ, et al. Tissue Engineering and Cell-Based Therapies for Fractures and Bone Defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6: 105.
[20] DUCHAMP DE LAGENESTE O, JULIEN A, Abou-Khalil R, et al. Periosteum contains skeletal stem cells with high bone regenerative potential controlled by Periostin. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):773.
[21] GUO X, LIU Y, BAI J, et al. Efficient Inhibition of Wear-Debris-Induced Osteolysis by Surface Biomimetic Engineering of Titanium Implant with a Mussel-Derived Integrin-Targeting Peptide. Adv Biosyst. 2019;3(2):e1800253.
[22] PAN G, SUN S, ZHANG W, et al. Biomimetic Design of Mussel-Derived Bioactive Peptides for Dual-Functionalization of Titanium-Based Biomaterials. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138(45):15078-15086.
[23] VERSTAPPEN JFM, JIN J, KOÇER G, et al. RGD-functionalized supported lipid bilayers modulate pre-osteoblast adherence and promote osteogenic differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(4):923-937.
[24] HORI N, UENO T, MINAMIKAWA H, et al. Electrostatic control of protein adsorption on UV-photofunctionalized titanium. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(10): 4175-4180.
[25] AITA H, HORI N, TAKEUCHI M, et al. The effect of ultraviolet functionalization of titanium on integration with bone. Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):1015-1025.
[26] GUTIÉRREZ-SÁNCHEZ M, ESCOBAR-BARRIOS VA, POZOS-GUILLÉN A, et al. RGD-functionalization of PLA/starch scaffolds obtained by electrospinning and evaluated in vitro for potential bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;96:798-806.
[27] LUO F, HONG G, MATSUI H, et al. Initial osteoblast adhesion and subsequent differentiation on zirconia surfaces are regulated by integrins and heparin-sensitive molecule. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:7657-7667.
[28] CHEN X, SEVILLA P, APARICIO C. Surface biofunctionalization by covalent co-immobilization of oligopeptides. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;107: 189-197.
[29] KANTLEHNER M, SCHAFFNER P, FINSINGER D, et al. Surface coating with cyclic RGD peptides stimulates osteoblast adhesion and proliferation as well as bone formation. Chembiochem. 2000;1(2):107-114.
[30] MAS-MORUNO C, FRAIOLI R, ALBERICIO F, et al. Novel peptide-based platform for the dual presentation of biologically active peptide motifs on biomaterials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(9):6525-6536.
[31] WAITE JH. The DOPA Ephemera: A Recurrent Motif in Invertebrates. Biol Bull. 1992;183(1):178-184.
[32] WAITE JH. The phylogeny and chemical diversity of quinone-tanned glues and varnishes. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1990;97(1):19-29.
[33] 李娜,章非敏.多巴胺与Ⅰ型胶原对MC3T3-E1细胞初期粘附形态的影响[J].口腔生物医学,2018,9(4):187-190.
[34] HUANG YZ, WANG JJ, HUANG YC, et al. Organic composite-mediated surface coating of human acellular bone matrix with strontium. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;84:12-20.
[35] HUANG S, LIANG N, HU Y, et al. Polydopamine-Assisted Surface Modification for Bone Biosubstitutes. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2389895.
[36] DE JONGE LT, LEEUWENBURGH SC, WOLKE JG, et al. Organic-inorganic surface modifications for titanium implant surfaces. Pharm Res. 2008; 25(10):2357-2369.
[37] BRUBAKER CE, MESSERSMITH PB. Enzymatically degradable mussel-inspired adhesive hydrogel. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(12):4326-4334.
[38] SECCHI AG, GRIGORIOU V, SHAPIRO IM, et al. RGDS peptides immobilized on titanium alloy stimulate bone cell attachment, differentiation and confer resistance to apoptosis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007;83(3):577-584.
[39] ELMENGAARD B, BECHTOLD JE, SØBALLE K. In vivo study of the effect of RGD treatment on bone ongrowth on press-fit titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3521-3526.
[40] KROESE-DEUTMAN HC, VAN DEN DOLDER J, SPAUWEN PH, et al. Influence of RGD-loaded titanium implants on bone formation in vivo. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(11-12):1867-1875.
|