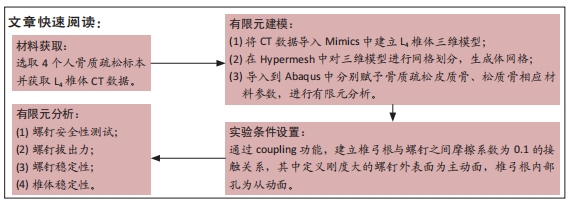
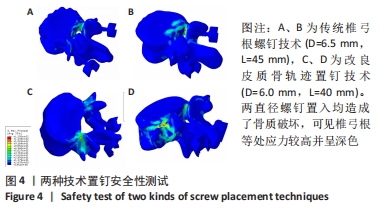
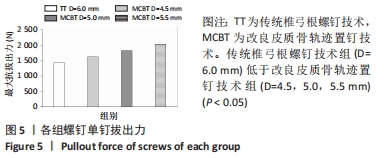
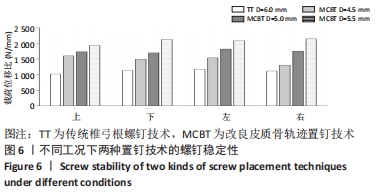
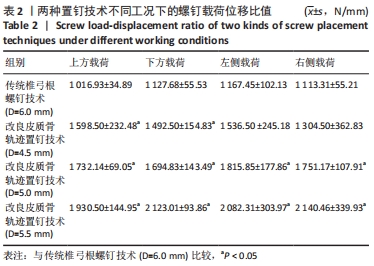
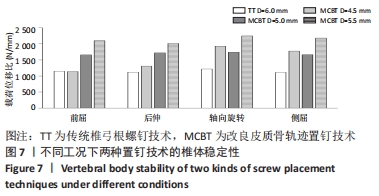
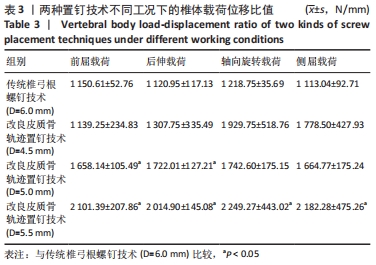
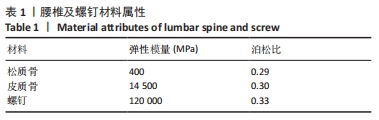
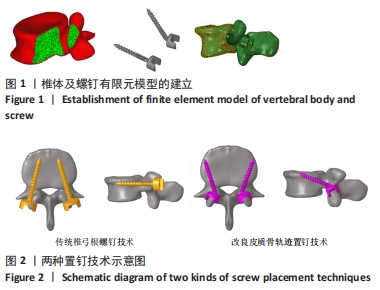
[1] ROY-CAMILLE R, SAILLANT G, MAZEL C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop. 1986;203(203):7-17.
[2] HAJEK PD, UPKA J, HARTLINE P, et al. Biomechanical study of CI-C2 posterior arthrodesistechniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(2):173-177.
[3] OKUYAMA K, ABE E, SUZUKI T, et al. Influence of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation: A study of pedicle screw fixation augmenting posterior lumbar interbody fusion in elderly patients. Spine J. 2001;1(6):402-407.
[4] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine J. 2009;9:366-373.
[5] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, KATO T, et al. In vivo analysis of insertionaltorque during pedicle screwing using cortical bone trajectory technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(4):E240-245.
[6] WITTENBERG RH, SHEA M, SWARTZ DE, et al. Importance of bone mineral density in instrumented spine fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(6):647-652.
[7] REXITI P, ABUDUREXITI T, ABUDUWALI N, et al. Measurement of lumbar isthmus parameters for novel starting points for cortical bone trajectory screws using computed radiography. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(8):2413-2423.
[8] REXITI P, AIERKEN G, WANG S, et al. Anatomical research on strength of screw track fixation in novel cortical bone trajectory for osteoporosis lumbar spine. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(11):6850-6859.
[9] REXITI P, AIERKEN A, SADEER A, et al. Anatomy and Imaging Studies on Cortical Bone Screw Freehand Placement Applying Anatomical Targeting Technology. ORTHOP SURG. 2020;12(6):1954-1962.
[10] SHI W, AIERKEN G, WANG S, et al. Application study of three-dimensional printed navigation template between traditional and novel cortical bone trajectory on osteoporosis lumbar spine. J Clin Neurosci. 2021;85:41-48.
[11] REXITI P, ABULIZI Y, MUHEREMU A, et al. Anatomical and radiologic characteristics of isthmus parameters in guiding pedicle screw placement. J Int Med Res. 2018; 46(6):2386-2397.
[12] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, IMABAYASHI H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the fixation strength of lumbar pedicle screws using cortical bone trajectory: a finite element study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;23:471-478.
[13] 邵明昊,吕飞舟,马晓生,等.腰椎皮质骨钉道螺钉在骨质疏松症患者中应用的三维有限元分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(2):1-6.
[14] 吴晓宇,王哲,甘浩然,等.皮质骨轨迹螺钉技术应用于骨质疏松患者腰椎固定的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(12):1126-1131.
[15] HADDAS R, XU M, LIEBERMAN I, et al. Finite Element Based-Analysis for Pre and Post Lumbar Fusion of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis Patients. Spine Deform. 2019;7(4):543-552.
[16] CAMPBELL GM, GLÜER CC. Skeletal assessment with finite element analysis: relevance, pitfalls and interpretation. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(4):402-409.
[17] JAUMARD NV, WELCH WC, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury and degenerative conditions. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(7):071010.
[18] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y, NEMOTO O, et al. Morphometric Measurement of Cortical Bone Trajectory for Lumbar Pedicle Screw Insertion Using Computed Tomography. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26:248-253.
[19] ZHANG QH, TAN SH, CHOU SM. Effects of bone materials on the screw pull-out strength in human spine. Med Eng Phys. 2006;28(8):795-801.
[20] 敖俊,方国芳,冯伟,等.以三维有限元模型分析短节段腰椎椎弓根螺钉系统固定后螺钉应力的分布[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(39): 7601-7604.
[21] 王宇,靳安民,方国芳,等.腰椎椎弓根螺钉系统断裂的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(48):9439-9442.
[22] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y. Biomechanical evaluation of fixation strength among different sizes of pedicle screws using the cortical bone trajectory: what is the ideal screw size for optimal fixation? Acta Neurochir. 2016;158:465-471.
[23] HOINESS P, STROMSOE K. Tricortical versus quadricortical syndesmosis fixation in ankle fractures: a prospective, randomized study comparing two methods of syndesmosis fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(6):331-337.
[24] THOMPSON MC, GESINK DS. Biomechancial comparison of syndesmosis fixation with 3 .5-and 4.5-millimeter stainless steel screws. Foot Ankle Int. 2000;2l:736-741.
[25] TORTOLANI PJ, STROH DA. Cortical Bone Trajectory Technique for Posterior Spinal Instrumentation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(11):755.
[26] TOSHIKA O, KOICHI I, YU-ICHIRO O, et al. Isthmus-guided Cortical Bone Trajectory Reduces Postoperative Increases in Serum Creatinine Phosphokinase Concentrations. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(3):232-238.
[27] MCLACHLIN SD, BEATON BJ, SABO MT, et al. Comparing the fixation of a novel hollow screw versus a conventional solid screw in human sacra under cyclic loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(17):1870-1875.
[28] 宗治国,刘肃,马朋朋,等.植入不同直径椎弓根螺钉后腰椎体与椎弓根结合部位骨折力学的稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(18):2794-2798.
[29] LIU CW, WANG LL, XU YK, et al. Traditional and cortical trajectory screws of static and dynamic lumbar fixation- a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):463.
[30] POLLY DW JR, ORCHOWSKI JR, ELLENBOGEN RG. Revision pedicle screws. Bigger, longer shims--what is best? Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(12):1374-1379.
[31] 黄飞,欧阳柳,吴强,等.经皮椎体成形术治疗腰椎骨折中骨水泥用量与恢复状态和并发症的相关性分析[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2020,12(11): 82-85.
[32] 郭瑞,文豪,杨利学,等.椎体强化术后骨水泥渗漏并发症与危险因素的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2019(1):50-56.
|