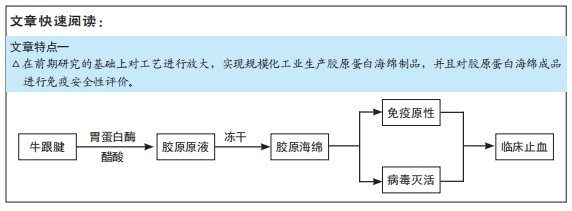
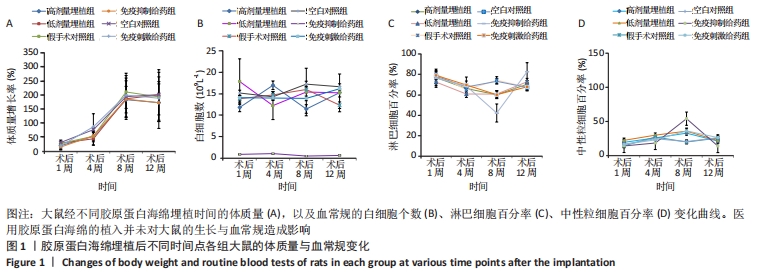
[1] BEHRENS AM, SIKORSKI MJ, KOFINAS P. Hemostatic strategies for traumatic and surgical bleeding. Journal of Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2014;102(11):4182-4194.
[2] SHEN W, ZHENG Z, RAN J, et al. Long-term effects of knitted silk-collagen sponge scaffold on anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and osteoarthritis prevention. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8154-8163.
[3] BARNARD J, MILLNER R. A review of topical hemostatic agents for use in cardiac surgery. Ann Surg. 2009;88(4):1377-1383.
[4] TOMPECK A, GAJDHAR AUR, DOWLING M, et al. A comprehensive review of topical hemostatic agents: the good, the bad, and the novel. J Trauma Acute Care. 2019;88(1):e1-e21.
[5] 孙国飞,刘建恒,张里程,等.院前创伤急救止血敷料:优势与问题及应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(22):3575-3582.
[6] SLEZAK P, MONFORTE X, FERGUSON J, et al. Properties of collagen-based hemostatic patch compared to oxidized cellulose-based patch. J Mater Sci Mater M. 2018;29(6):71.
[7] JIN J, JI Z, XU M, et al. Microspheres of carboxymethyl chitosan, sodium alginate, and collagen as a hemostatic agent in vivo. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(7):2541-2551.
[8] CHENG X, SHAO Z, LI C, et al. Isolation, Characterization and evaluation of collagen from jellyfish rhopilema esculentum kishinouye for use in hemostatic applications. Plos One. 2017;12(1):e0169731.
[9] 景沛.胶原蛋白质(Ⅰ-XⅫ型)[J].生命的化学,1995,15(6):30-31.
[10] FRIESS W. Collagen–biomaterial for drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 1998;45:113-136.
[11] ACHNECK HE, SILESHI B, JAMIOLKOWSKI RM, et al. A comprehensive review of topical hemostatic agents: efficacy and recommendations for use. Ann Surg. 2010;251(2):217-228.
[12] PALLASKE F, PALLASKE A, HERKLOTZ K, et al. The significance of collagen dressings in wound management: a review. J Wound Care. 2018;27(10):692-702.
[13] SILESHI B, ACHNECK HE, LAWSON JH. Management of surgical hemostasis: topical agents. Vascular. 2008;16 Suppl 1:S22-S28.
[14] MANON-JENSEN T, KJELD NG, KARSDAL MA. Collagen-mediated hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:438-448.
[15] FLECK CA, SIMMAN R. Modern collagen wound dressings: function and purpose. J Am Coll Cert Wound Spec. 2010;2(3):50-54.
[16] AN B, LIN Y, BRODSKY B. Collagen interactions: drug design and delivery. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2016;97:69-84.
[17] SHEEHY EJ, CUNNIFFE GM, O’BRIEN FJ. 5-Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue regeneration and repair. Peptides and Proteins as Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration and Repair. 2018:27-150.
[18] GELSE K, PÖSCHL E, AIGNER T. Collagens--structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(12):1531-1546.
[19] 陆美娇.动物源性修复材料的病毒灭活与免疫原的观察[D].烟台:烟台大学,2015.
[20] No. 97D-0411, Guidance for Industry: The sourcing and processing of gelatin to reduce the potential risk by bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in FDA-regulated products for human.1997.
[21] 史新立,谭芳奕,王召旭,等疯牛病病原体研究及动物源性医疗器械产品安全性思考[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(20):1138-1144.
[22] 国家食品药品监督管理局.血液制品去除/灭活病毒技术方法及验证指导原则[S].2002.
[23] LEBBINK RJ. Collagens are functional, high affinity ligands for the inhibitory immune receptor LAIR-1. J Exp Med. 2006;203(6):1419-1425.
[24] MEYAARD L, ADEMA G, CHANG C, et al. LAIR-1, a novel inhibitory receptor expressed on human mononuclear leukocytes. Immunity. 1997;7:283-290.
[25] POGGI A, TOMASELLO E, REVELLO V, et al. p40 molecule regulates NK cell activation mediated by NK receptors for HLA class I antigens and TCR-mediated triggering of T lymphocytes.Int Immunol. 1997;9:1271-1279.
[26] 付强.LAIRs和胶原分子调节人早孕蜕膜NK细胞功能的分子机制[D].上海:复旦大学,2014.
[27] 国家药品监督管理局.动物源性医疗器械注册技术审查指导原则(2017年版)[S]. 2017.
[28] NAGHSHINEH N, TAHVILDARI K, NOZARI M. Preparation of chitosan, sodium alginate, gelatin and collagen biodegradable sponge composites and their application in wound healing and curcumin delivery. J Polym Environ. 2019;27:2819-2830.
[29] FUKUSHIMA SI,YONETSU M, YASUI T. Polarization-resolved second-harmonic-generation imaging of dermal collagen fiber in prewrinkled and wrinkled skins of ultraviolet-B-exposed mouse. J Biomed Opt. 2018;24(3):1-8.
[30] ARAGONA F. Is bovine collagen safe? J Duro. 1991;97(6):279-281.
[31] LYNN AK, YANNAS IV, BONFIELD W. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of collagen. J Biomed Mater Res Part B. 2010;71B(2):343-354.
[32] BONDIOLI E, FINI M, VERONESI F, et al. Development and evaluation of a decellularized membrane from human dermis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2014;8(4):325-336.
[33] INABA S, NAGAHARA S, MAKITA N, et al. Atelocollagen-mediated systemic delivery prevents immunostimulatory adverse effects of siRNA in mammals. Mol Ther. 2012;20(2):356-366.
[34] ZHAO W, CHI C, ZHAO Y, et al. Preparation, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the swim bladders of miiuycroaker (miichthysmiiuy). Mar Drugs. 2018; 16(5):161.
[35] BAE JE, KIM CK, KIM S, et al. Virus inactivation during the manufacture of a collagen type I from bovine hides. Korean J Microbio. 2012;48(4): 314-318.
[36] LI L, ZHAO Y,HE Y, et al. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the scales of miiuycroaker (miichthysmiiuy). Mar Drugs. 2018;16(10): 394.
[37] BLANCO M, SOTELO CG, RICARDO I, et al. New strategy to cope with common fishery policy landing obligation: collagen extraction from skins and bones of undersized hake (merlucciusmerluccius). Polymers. 2019;11(9):1485.
[38] MONIRUZZAMAN SM, TAKAHASHI K, NESA NU, et al. Characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens extracted from scales of carp and lizardfish caught in Japan, Bangladesh and Vietnam with a focus on thermostability. Food Sci and Tech Res. 2019;25(2):331-340.
[39] CALIGIURI MA. Human natural killer cells. Blood. 2008;112(3):461-469.
[40] MELISSA, A, GELLER, JEFFREY J, et al. Use of allogeneic NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. 2011;3(12):1445-1459.
[41] SNYDER MR, WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The double life of NK receptors: stimulation or co-stimulation? Trends Immunol. 2004; 25(1):25-32.
[42] ALI RI, KUMAR S, ALI RA, et al. B and T cell epitope mapping and study the humoral and cell mediated immune response to B-T constructs of YscF antigen of Yersinia pestis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;36(4):365-378.
|