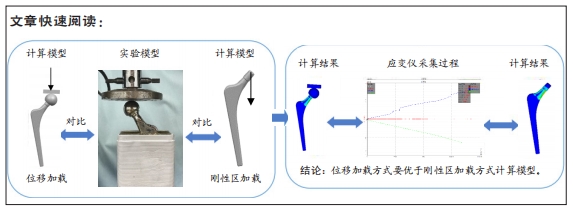
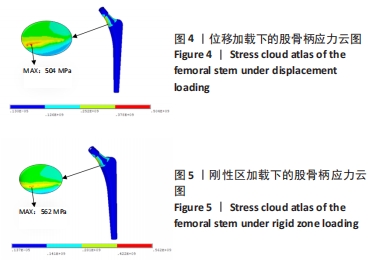
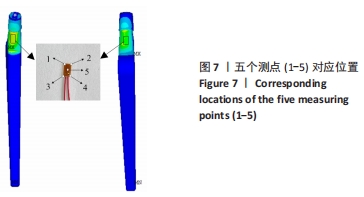
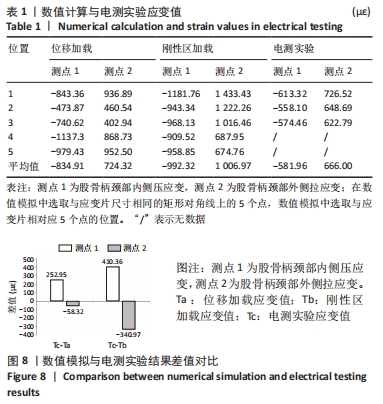
[1] 刘乐乐,戴宁,丁龙伟,等.髋关节假体多孔结构优化设计研究[J].机械设计与制造工程,2020,49(6):12-16.
[2] 李翰祥.有骨小梁结构的人工髋关节置换的数值模拟与实验研究[D].天津:天津理工大学,2019.
[3] 杨洋洋,杨磊,王跃,等.髋关节中不同假体柄长对股骨的力学分析[J].机械,2018,45(6):20-26+51.
[4] LERCH M,WINDHAGEN H,KURTZ AE,et al.‘Pre-launch’ finite element analysis of a short-stem total hip arthroplasty system consisting of two implant types. Clin Biomech.2019;61:31-37.
[5] BEHRENS BA,NOLTE I,WEFSTAEDT P,et al.Numerical investigations on the strain-adaptive bone remodelling in the periprosthetic femur: Influence of the boundary conditions. BioMed Eng OnLine.2009;8(1):7.
[6] BURCHARD R,BRAAS S,SOOST C,et al.Bone preserving level of osteotomy in short-stem total hip arthroplasty does not influence stress shielding dimensions-A comparing finite elements analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):343.
[7] 何荣新,罗银森,严世贵,等.Elite全髋置换前后股骨应力变化的三维有限元分析[J].中华医学杂志,2004,84(18):1549-1553.
[8] 严世贵,何荣新,陈维善,等.全髋关节置换前后股骨应力变化的有限元分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(9):561-565.
[9] SPEIRS AD, HELLER MO, TAYLOR WR, et al. Influence of changes in stem positioning on femoral loading after THR using a short-stemmed hip implant. Clin Biomech. 2007;22(4):430-439.
[10] TRAINA F, FINE MD, BIONDI F,et al. The influence of the centre of rotation on implant survival using a modular stem hip prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1513-1518.
[11] KLEEMANN RU, HELLER MO, STOECKLE U, et al. THA loading arising from increased femoral anteversion and offset may lead to critical cement stresses. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(5):767-774.
[12] DELP SL, KOMATTU AV, WIXSON RL. Superior displacement of the hip in total joint replacement: Effects of prosthetic neck length, neck-stem angle, and anteversion angle on the moment-generating capacity of the muscles. J Orthop Res. 1994;12(6):860-870.
[13] HIRATA Y, INABA Y, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Comparison of Mechanical Stress and Change in Bone Mineral Density Between Two Types of Femoral Implant Using Finite Element Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(10):1731-1735.
[14] FAIZAN A, WUESTEMANN T, NEVELOS J, et al. Development and Verification of a Cementless Novel Tapered Wedge Stem for Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(2):235-240.
[15] ARABNEJAD S, JOHNSTON B, TANZER M, et al. Fully porous 3D printed titanium femoral stem to reduce stress-shielding following total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(8):1774-1783.
[16] 白波,罗林聪,彭鳒侨.有限元法在髋关节运动力学研究中的应用进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(1):24-27.
[17] 王韶进,刘胜厚,刘文广,等. 骨水泥型长短柄假体置换治疗高龄粉碎性转子间骨折的三维有限元对比分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2010, 30(11):1144-1150.
[18] 骆园,曹晓东,顾建伟,等. 短柄股骨假体全髋关节置换术后股骨近端骨改建及有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(8): 823-825.
[19] 郑晓雯,封小建,张延宾.人工股骨柄形状和表面处理对置换术后假体和人体股骨应力分布影响的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学, 2006,21(4):322-327.
[20] Trieb K, Huber D, Sonntag R, et al. Finite Element Analysis and Biomechanical Testing of the New MiniMIS Short Stem. Z Orthop Unfall. 2019;157(2):188-193.
[21] HE S, ZHU J, ZHAO J. Finite element analysis on the hollow porous design at the proximal end of cementless femoral prosthesis stem. Niger J Clin Pract. 2019;22(9):1276-1280.
[22] Takai H, Nakayama D, Murayama M, et al. Analysis of a Cementless Femoral Stem Neck Fracture Using Scanning Electron Microscopy and the Finite Element Method. Case Rep Orthop. 2019;2019:7204598.
[23] Nandi S, Shah A, Joukar A, et al. Short single-wedge stems have higher risk of periprosthetic fracture than other cementless stem designs in Dorr type A femurs: a finite element analysis. Hip Int. 2020: 1120700020949185.
[24] 刘文广,刘胜厚,殷庆丰,等. 水泥型人工髋关节置换治疗老年Evans Ⅰ-Ⅲ型粗隆间骨折股骨假体的生物力学特性[J]. 中国医学科学院学报,2013,35(1):108-111.
[25] 展影,雷新玮,屈瑾,等. 髋关节表面置换术假体柄的不同安放角度与其术后骨折风险相关性的有限元分析[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志,2011,34(4):307-311.
[26] 王少林,谭祖键,周明全. 基于偏髓分型应用骨水泥型长短柄假体置换治疗高龄偏髓Ⅰ型粗隆间骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(18):1848-1857.
[27] 蔡春元,李永奖,张美超,等. 股骨柄假体与骨固定界面三维有限元模型的构建及其生物力学意义[J]. 医学研究杂志,2013,42(3): 65-69.
[28] LEE EW, KIM HT. Early fatigue failures of cemented,forged,cobalt-chromium femoral stems at the neck–shoulder junction. J Arthroplasty. 2001;16(2):236-238.
[29] REITO A,ESKELINEN A, PAJAMÄKI J, et al. Neck fracture of the Exeter stem in 3 patients: a cause for concern? Acta Orthop. 2016;87(2):93-196.
[30] HAMLIN K, MACEACHERN C. Fracture of an exeter stem: a case report. JBJS Case Connect. 2014;4(3):e66-e73.
[31] Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Annual Report 2020. Adelaide: Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry, 2020.
[32] 冯辰栋,夏宇,李祥,等.3D打印多孔钛支架微观孔隙结构和力学性能[J].医用生物力学,2017,32(3):256-260.
[33] 魏崇斌,马骏,王彩梅,等.电子束熔融法制备的医用Ti6Al4V在人工模拟体液中的耐腐蚀行为[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2017, 14(4):6-10+82.
[34] AL-JASSIR FF, FOUAD H, ALOTHMAN OY. In vitro assessment of Function Graded (FG) artificial Hip joint stem in terms of bone/cement stresses: 3D Finite Element (FE) study. Biomed Eng Online. 2013;12:5.
[35] 王志坚,李彦旭,韩青,等.髋关节置换术中2种不同髋关节假体的有限元分析:应力集中和位移变化比较[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2019,45(2):347-352.
[36] 曹照华.人工髋关节置换的数值模拟与实验研究[D].天津:天津理工大学,2018.
|