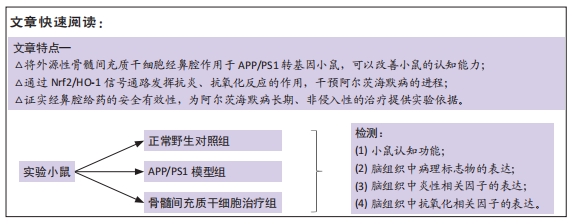
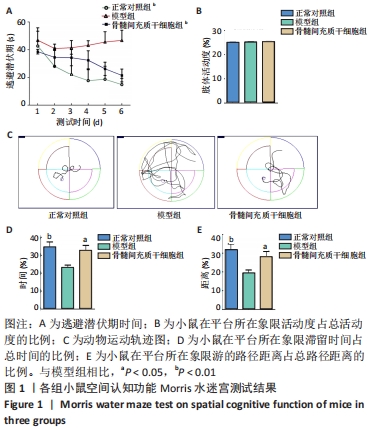
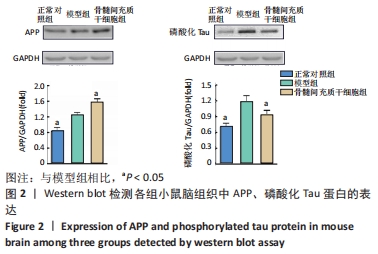
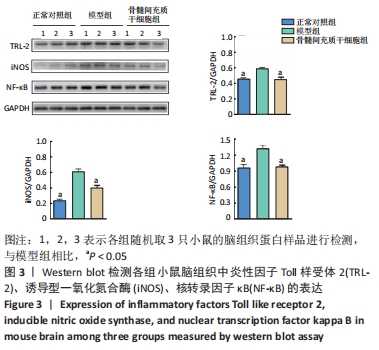
[1] PRINCE M, COMASHERRERA A, ADELINA K, et al. World Alzheimer Report 2016: Improving Healthcare for People Living with Dementia: Coverage, Quality and Costs Now and in the Future. London, UK: Alzheimer’s Disease International.2016.
[2] 谷青芳,尉杰忠,吴昊,等.FSD-C10调节阿尔茨海默病双转基因小鼠炎性微环境[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(10):1729-1737.
[3] GLASS CK, SAIJO K, WINNER B, et al. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell. 2010;140(6):918-934.
[4] NDISANG JF. Synergistic Interaction Between Heme Oxygenase (HO) and Nuclear-Factor E2- Related Factor-2 (Nrf2) against Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Related Diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(10): 1465-1470.
[5] JI H, XIAO F, LI S, et al. GRP78 effectively protect hypoxia/reperfusion-induced myocardial apoptosis via promotion of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(2):1228-1236.
[6] XU Y, YANG Y, HUANG Y, et al. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway by Dextran Sulfate suppresses angiogenesis of Gastric Cancer. J Cancer. 2021;12(4):1042-1060.
[7] LIN HY, YEH WL, HUANG BR, et al. Desipramine protects neuronal cell death and induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in Mes23.5 dopaminergic neurons. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50138.
[8] CHEN XQ, WU SH, ZHOU Y, et al. Lipoxin A4-induced heme oxygenase-1 protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury via p38 MAPK activation and Nrf2/ARE complex. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67120.
[9] WYSE RD, DUNBAR GL, ROSSIGNOL J. Use of genetically modified mesenchymal stem cells to treat neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(2):1719-1745.
[10] SALEM AM, AHMED HH, ATTA HM, et al. Potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in management of Alzheimer’s disease in female rats. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(12):1367-1383.
[11] 尉杰忠,闫玉清,谷青芳,等.法舒地尔通过促进APP/PS1双转基因小鼠神经再生改善认知功能[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(7): 1153-1161.
[12] YUE W, LI Y, ZHANG T, et al. ESC-Derived Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons Ameliorate the Cognitive Symptoms Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease in Mouse Models. Stem Cell Reports. 2015;5(5): 776-790.
[13] HUNSBERGER JG, RAO M, KURTZBERG J, et al. Accelerating stem cell trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15(2):219-230.
[14] SADATPOOR SO, SALEHI Z, RAHBAN D, et al. Manipulated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Applications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(1):24-45.
[15] YU J, YAN Y, GU Q, et al. Fasudil in Combination With Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (BMSCs) Attenuates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Changes Through the Regulation of the Peripheral Immune System. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:216.
[16] EFTEKHARZADEH M, NOBAKHT M, ALIZADEH A, et al. The effect of intrathecal delivery of bone marrow stromal cells on hippocampal neurons in rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(5):520-525.
[17] LI YH, FENG L, ZHANG GX, et al. Intranasal delivery of stem cells as therapy for central nervous system disease. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015; 98(2):145-151.
[18] YANG J, YAN Y, CIRIC B, et al. Evaluation of bone marrow- and brain-derived neural stem cells in therapy of central nervous system autoimmunity. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(4):1989-2001.
[19] LI YH, XIE C, ZHANG Y, et al. FSD-C10, a Fasudil derivative, promotes neuroregeneration through indirect and direct mechanisms. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41227.
[20] 宋国斌,席国萍,李艳花,等.Fasudil 联合骨髓源神经干细胞对 EAE小鼠的神经保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(12):2113-2120.
[21] YU JZ, LI YH, LIU CY, et al. Multitarget Therapeutic Effect of Fasudil in APP/PS1transgenic Mice. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(2): 199-209.
[22] FAN Y, LIU M, WU X, et al. Aquaporin-4 promotes memory consolidation in Morris water maze. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218(1):39-50.
[23] ROJAS-GUTIERREZ E, MUÑOZ-ARENAS G, TREVIÑO S, et al. Alzheimer’s disease and metabolic syndrome: A link from oxidative stress and inflammation to neurodegeneration. Synapse. 2017;71(10):e21990.
[24] ZHANG FQ, JIANG JL, ZHANG JT, et al. Current status and future prospects of stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(2):242-250.
[25] CIOFFI F, ADAM RHI, BROERSEN K. Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(4):981-1017.
[26] 谷青芳,尉杰忠,郭敏芳,等.新型Rho激酶抑制剂 FSD-C10对阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的神经保护作用[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2019,35(12):2227-2234.
[27] ZUO L, PRATHER ER, STETSKIV M, et al. Inflammaging and Oxidative Stress in Human Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Novel Treatments. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4472.
[28] VALKO M, LEIBFRITZ D, MONCOL J, et al. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(1):44-84.
[29] BO H, KANG W, JIANG N, et al. Exercise-induced neuroprotection of hippocampus in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via upregulation of mitochondrial 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:834502.
[30] ZHAO L, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. Effects of Curculigoside on Memory Impairment and Bone Loss via Anti-Oxidative Character in APP/PS1 Mutated Transgenic Mice. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133289.
[31] KIM DC, QUANG TH, OH H, et al. Steppogenin Isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata Shows Antineuroinflammatory Effects via NF-kappaB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV2 and Primary Rat Microglial Cells. Molecules. 2017;22(12):2130.
[32] MOLTENI M, ROSSETTI C. Neurodegenerative diseases: The immunological perspective. J Neuroimmunol. 2017;313:109-115.
[33] HONG Y, AN Z. Hesperidin attenuates learning and memory deficits in APP/PS1 mice through activation of Akt/Nrf2 signaling and inhibition of RAGE/NF-κB signaling. Arch Pharm Res. 2018;41(6):655-663.
[34] PRASAD KN. Simultaneous activation of Nrf2 and elevation of antioxidant compounds for reducing oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in human Alzheimer’s disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016; 153:41-47.
[35] JOSHI G, GAN KA, JOHNSON DA, et al. Increased Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in the APP/ PS1ΔE9 mouse model lacking Nrf2 through modulation of autophagy. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(2):664-679.
[36] CHIANG MC, NICOL CJ, CHENG YC, et al. Rosiglitazone activation of PPARγ-dependent pathways is neuroprotective in human neural stem cells against amyloid-beta-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;40:181-190.
[37] YANG H, YUE C, YANG H, et al. Intravenous Administration of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Cognitive Impairments and Reduces Amyloid-Beta Deposition in an AβPP/PS1 Transgenic Mouse Model. Neurochem Res. 2013:12(38):2474-2482.
|