[1] VANSANT L, CADENAS DS LLANO-PERUL M, VERDONCK A, et al. Expression of biological mediators during orthodontic tooth movement: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;95:170-186.
[2] SIRISOONTORN I, HOTOKEZAKA H, HASHIMOTO M, et al. Tooth movement and root resorption; The effect of ovariectomy on orthodontic force application in rats. Angle Orthod. 2011;81(4):570-577.
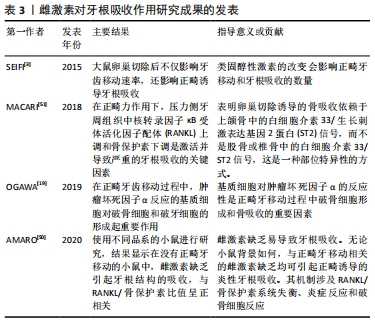
[3] SEIFI M, EZZATI B, SAEDI S, et al. The effect of ovariectomy and orchiectomy on orthodontic tooth movement and root resorption in wistar rats. J Dent (Shiraz). 2015;16(4):302-309.
[4] 周翊飞,郑茜,毛杰,等.口服避孕药对大鼠正畸牙牙周组织改建的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(4):542-547.
[5] 王斌,杨曦,周建萍,等.青少年女性月经周期不同阶段加力对正畸牙移动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(15):2332-2337.
[6] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by cytokine networks. Immune Netw. 2018;18(1):e8.
[7] ROSS FP, Teitelbaum SL. αvβ3 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor: partners in osteoclast biology. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:88-105.
[8] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26.
[9] YANG CY, JEON HH, ALSHABAB A, et al. RANKL deletionc in periodontal ligament and bone lining cells blocks orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Oral Sci. 2018;10(1):3.
[10] DANKS L, KOMATSU N, GUERRINI MM, et al. RANKL expressed on synovial fibroblasts is primarily responsible for bone erosions during joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1187-1195.
[11] TSUKASAKI M, KOMATSU N, NAGASHIMA K, et al. Host defense against oral microbiota by bone-damaging T cells. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1-11.
[12] TSUKASAKI M, ASANO T, MURO R, et al. OPG production matters where it happened. Cell Rep. 2020;32(10):108124.
[13] CAWLEY KM, BUSTANANTE-GOMEZ NC, GUHA AG, et al. Local production of osteoprotegerin by osteoblasts suppresses bone resorption. Cell Rep. 2020; 32(10):108052.
[14] TONG X, GU J, SONG R, et al. Osteoprotegerin inhibit osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption by enhancing autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 120(2):1630-1642.
[15] OHNUMA K, KASAGI S, UTO K, et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits TNF-α and IL-6 induced osteoclastogenesis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(4):689-695.
[16] KIM JH, JIN HM, KIM K, et al. The mechanism of osteoclast differentiation induced by IL-1. J Immunol. 2009;183:1862-1870.
[17] MARALEH A, KITAURA H, OHORI F, et al. TNF-α directly enhances osteocyte RANKL expression and promotes osteoclast formation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1-12.
[18] WU L, GUO Q, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes osteoclast formation Via PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated blimp1 expressio upregulation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6):1308-1315.
[19] OGAWA S, KITAURA H, KISHIKAWA A, et al. TNF-α is responsible for the contribution of stromal cells to osteoclast and odontoclast formation during orthodontic tooth movement. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e223989.
[20] MCGREGOR NE, MURAT M, ELANGO J, et al. IL-6 exhibits both cis- and trans-signaling in osteocytes and osteoblasts, but only trans-signaling promotes bone formation and osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(19):7850-7863.
[21] WU Q, ZHOU X, HUANG D, et al. IL-6 Enhances osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis by promoting JAK2 and RANKL activity in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1360-1369.
[22] GAVALI S, GUPTA MK, DASWANI B, et al. LYN, a key mediator in estrogen-dependent suppression of osteoclast differentiation, survival, and function. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(3):547-557.
[23] RYOO G, MOON YJ, ChOI S, et al. Tussilagone promotes osteoclast apoptosis and prevents estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):508-514.
[24] CHUANG S, CHEN C, CHOU Y, et al. G Protein-coupled estrogen receptor mediates cell proliferation through the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6490.
[25] YUR J, LOREZ JM. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2346.
[26] THOUVEREY C, CAVERZASIO J. Ablation of p38α MAPK signaling in osteoblast lineage cells protects mice from bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. Endocrinology. 2015;156(12):4377-4387.
[27] LIU G, Lu Y, MAIZ, et al. Suppressing MicroRNA-30b by estrogen promotes osteogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019; 2019:1-13.
[28] PIAO H, CHU X, LV W, et al. Involvement of receptor interacting protein 140in estrogen-mediated osteoclasts differentiation, apoptosis, and bone resorption. J Physiol Sci. 2017;67(1):141-150.
[29] KIM H, PONTEF, NOOKAEW I, et al. Estrogens decrease osteoclast number by attenuating mitochondria oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production in early osteoclast precursors. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):11933.
[30] CRUZOE-SOUZA M, SASSO-CERRI E, CERRI PS. Immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor β in alveolar bone cells of estradiol-treated female rats: possible direct action of estrogen on osteoclast life span. J Anat. 2009;215(6):673-681.
[31] SHI C, WU J, YAN Q, et al. Bone marrow ablation demonstrates that estrogen plays an important role in osteogenesis and bone turnover via an antioxidative mechanism. Bone. 2015;79:94-104.
[32] GAVALI S, GUPTA MK, DASWANI B, et al. Estrogen enhances human osteoblast survival and function via promotion of autophag. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019;1866(9):1498-1507.
[33] 孙晓琪.雌二醇通过G蛋白偶联雌激素受体30(GPR30)/ERK1/2信号通路调节MC3T3-E1细胞线粒体自噬的分子机制研究[A]//中国营养学会、亚太临床营养学会、江苏省科学技术协会、中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所、农业农村部食物与营养发展研究所、中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所.营养研究与临床实践——第十四届全国营养科学大会暨第十一届亚太临床营养大会、第二届全球华人营养科学家大会论文摘要汇编[C].中国营养学会、亚太临床营养学会、江苏省科学技术协会、中国疾病预防控制中心营养与健康所、农业农村部食物与营养发展研究所、中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所:中国营养学会,2019:2.
[34] Uder C, Brückner S, Winkler S, et al. Mammalian MSC from selected species: features and applications. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1): 32-49.
[35] 王洁,张鹏,代庆刚,等.雌激素对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):654-660.
[36] WANG Q, YU J, ZHAI H, et al. Temporal expression of estrogen receptor alpha in rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;347(1):117-123.
[37] GAO B, HUANG Q, JIE Q, et al. Dose-response estrogen promotes osteogenic differentiation via GPR40 (FFAR1) in murine BMMSCs. Biochimie. 2015;110:36-44.
[38] ZHANG M, CHEN F, WANG A, et al. Estrogen and its receptor enhance mechanobiological effects in compressed bone mesenchymal stem cells. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;195(5):400-413.
[39] WU G, XU R, ZHANG P, et al. Estrogen regulates stemness and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells to prevent osteoporosis via ERβ-SATB2 pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(5):4194-4204.
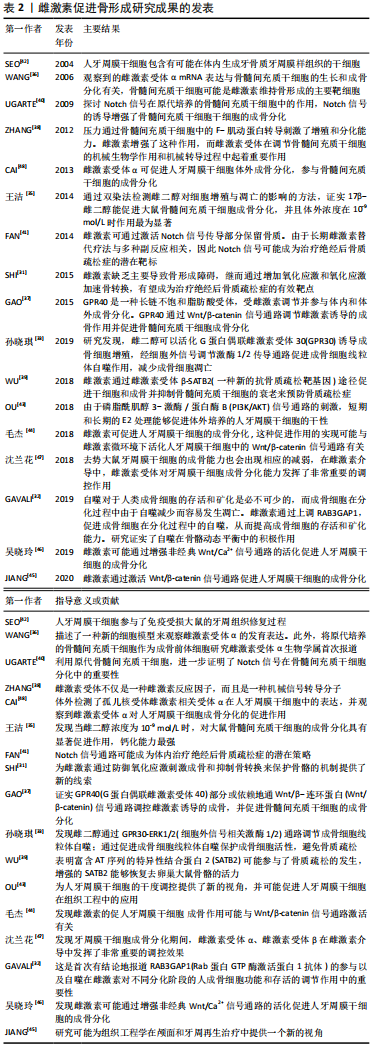
[40] UGARTE F, RYSER M, THIEME S, et al. Notch signaling enhances osteogenic differentiation while inhibiting adipogenesis in primary human bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 2009;37(7):867-875.
[41] FAN J, YANG L, MENG G, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93.
[42] Seo B, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155.
[43] OU Q, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Oestrogen retains human periodontal ligament stem cells stemness in long-term culture. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(2): e12396.
[44] 毛杰,周翊飞,吴晓玲,等. 雌激素介导下Wnt/β-catenin传导通路调控人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研,2018,22(13):2087-2092.
[45] JIANG B, XU J, ZHOU Y, et al. Estrogen enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(2):583-587.
[46] 吴晓玲,郑茜,吕佳岭,等.雌激素微环境下非经典Wnt/Ca2+传导通路调控人牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2019,35(1):33-37.
[47] 沈兰花,张瑞,孟玲娜.雌激素受体对去势大鼠牙周膜干细胞成骨分化能力的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2018,34(4):448-451.
[48] CAI C, YUAN G, HUANG YE, et al. Estrogen-related receptor α is involved in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human periodontal ligaments. Int J Mol Med. 2013;31(5):1195-1201.
[49] LI T, ZHOU Z, WANG H, et al. Effects of estrogen on root repair after orthodontically induced root resorption in ovariectomized rats. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020;158(2):247-263.
[50] AMARO ERS, ORTIZ FR, DORNELES LS, et al. Estrogen protects dental roots from orthodontic-induced inflammatory resorption. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;117:104820.
[51] MACARI S, MADEIRA MFM, LIMA ILA, et al. ST2 regulates bone loss in a site dependent and estrogen‐dependent manner. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(10): 8511-8521.
[52] 朱倩,蔡萍.雌激素对正畸骨改建相关细胞因子的影响[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2014,41(6):694-698.
[53] 姜欢,胡敏.正畸牙移动相关牙根吸收研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2011, 27(2):168-169.
|