中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 2120-2126.doi: 10.12307/2022.343
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
巨噬细胞极化在骨组织工程免疫研究中的进展
赵月鑫,陈 滨
- 南方医科大学南方医院骨科-创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510515
-
收稿日期:2021-01-11修回日期:2021-01-12接受日期:2021-02-23出版日期:2022-05-08发布日期:2021-12-20 -
通讯作者:陈滨,博士,主任医师,南方医科大学南方医院骨科-创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510515 -
作者简介:赵月鑫,男,1996年生,河北省沧州市人,汉族,南方医科大学在读博士,主要从事骨组织工程及免疫相关研究。 -
基金资助:广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2020A1515011397),项目负责人:陈滨
Progress of macrophage polarization in immunology of bone tissue engineering
Zhao Yuexin, Chen Bin
- Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-11Revised:2021-01-12Accepted:2021-02-23Online:2022-05-08Published:2021-12-20 -
Contact:Chen Bin, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yuexin, Doctoral candidate, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2020A1515011397 (to CB)
摘要:
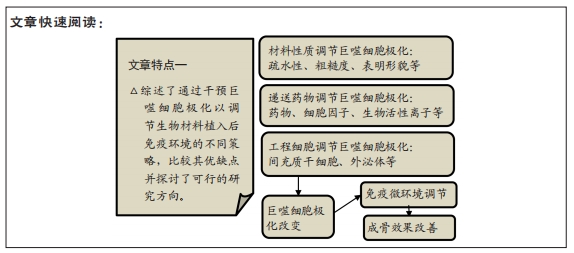
文题释义:
巨噬细胞极化:巨噬细胞会受到微环境中多种信号的调节与诱导,从而可以产生不同的极化状态。不同状态的巨噬细胞存在独特的表型及标志物并在体内行使不同的功能。根据刺激因素不同,巨噬细胞可以极化为M1表型或M2表型等,他们分别在炎症调节中行使促炎或抗炎的复杂功能。
药物递送系统:是指在空间、时间及剂量上全面调控药物在生物体内分布的技术体系。其目标是在恰当的时机将适量的药物递送到正确的位置,从而增加药物的利用效率,提高疗效,降低成本,减少毒副作用。药物递送系统是医学、工学(材料、机械、电子)及药学的融合学科,其研究对象既包括药物本身,也搭载药物的载体材料、装置,还包括对药物或载体等进行物理化学改性、修饰的相关技术。
背景:骨组织工程是一种有效的骨缺损修复方案,在组织工程材料植入后的免疫反应中,巨噬细胞有着极其重要的作用,干预其不同的极化状态成为调节局部免疫微环境的关键手段。
目的:对巨噬细胞在生物材料植入后免疫反应中的重要作用及调节巨噬细胞极化水平促进骨组织工程骨修复的最新研究进行了综述。
方法:利用PubMed、Web of Science和CNKI数据库检索2016-2020年发表的相关文献。检索文献类型为研究原著和综述。英文检索词设置为:macrophage polarization,M2,scaffold,tissue engineering,foreign body response,implant,surface,bone;中文检索词设置为:巨噬细胞极化,M2,组织工程,异物反应,移植物,表面,骨。对筛选出的该领域最新研究进展的文献进行归纳分析。
结果与结论:免疫反应对组织工程有显著影响,通过调节巨噬细胞极化比例来调节免疫微环境是促进骨组织工程成骨的关键手段。通过改变材料的理化特性(如疏水性、粗糙度、表面形貌等)的方法具有稳定性好持续时间长的特点,实现了显著的成骨改善;递送药物、细胞因子或微量元素也起到了很好的效果,但该策略面临因子易变性且持续释放时间短的问题;组织工程细胞与巨噬细胞的串扰进行免疫调节,其中间充质干细胞免疫调节能力强,可以较好地实现免疫调控及促进骨修复;研究强调了利用外泌体等实现对巨噬细胞极化及免疫环境的可控调节。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6004-0459(赵月鑫)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵月鑫, 陈 滨. 巨噬细胞极化在骨组织工程免疫研究中的进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(13): 2120-2126.
Zhao Yuexin, Chen Bin. Progress of macrophage polarization in immunology of bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2120-2126.
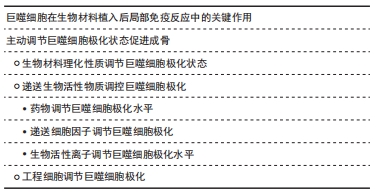
2.1 巨噬细胞在生物材料植入后局部免疫反应中的关键作用 巨噬细胞是人体免疫系统的重要组成部分,在炎症、宿主防御和组织修复中承担着重要功能。巨噬细胞具有多样性和可塑性,可以在不用的微环境中分化为不同的表型,从而发挥不同的作用,这个过程即为巨噬细胞极化。在体内,巨噬细胞的极化受到多种细胞及细胞因子的调控,巨噬细胞可以经过γ-干扰素、脂多糖介导的经典激活途径活化为M1型,也可在白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素13等因子作用下,经过替代途径活化为M2型。M1型巨噬细胞分泌高水平的促炎因子,促进炎症产生并杀灭微生物。M2型巨噬细胞以高表达清道夫受体为特征,发挥吞噬和免疫调节的功能,可对组织的修复产生促进作用。
不同极化状态的巨噬细胞在生物材料植入后的免疫反应中发挥重要作用。生物材料植入后,局部的蛋白、细胞、生物因子等迅速吸附到生物材料表面,并级联启动炎症反应及异物反应。最先到达损伤部位的是中性粒细胞,中性粒细胞数在早期炎症阶段迅速增加,起到一定抗感染和吞噬作用,并通过释放趋化因子,如白细胞介素6和趋化因子2,促进单核/巨噬细胞迁移到骨缺损部位[5]。此时巨噬细胞通过经典激活途径活化为M1型并分泌多种趋化因子和促炎性递质,例如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和趋化因子2,促进免疫细胞及间充质干细胞的募集,并释放活性氧和降解酶清除局部微生物及坏死组织。随着骨修复阶段进展,在辅助T细胞及间充质干细胞分泌的白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等因子作用下,巨噬细胞分化为M2型。M2型巨噬细胞分泌高水平的血管内皮生长因子和金属基质蛋白酶,二者对新血管形成和组织重塑至关重要[6]。M2型巨噬细胞与间充质干细胞均有较强的抗炎作用,两者共同作用结束炎症反应并进一步开启成骨修复。
如上所述,巨噬细胞极化状态的时序改变是骨组织工程顺利实现骨修复的关键。然而,由于生物材料为外来物质,且大部分为人工产物,具有较强的免疫原性。因此极易导致M1型巨噬细胞的持久激活,从而产生慢性炎症和纤维化,不利于生物材料负载的间充质干细胞的存活并极大地影响成骨效果[7]。同时随着异物反应持续时间延长,机体会在生物材料表面缓慢形成一层以纤维蛋白为主要结构的纤维囊,将工程材料包裹,导致生物材料无法继续发挥作用[3]。巨噬细胞两种极化状态对炎症有重要的调节作用,成为了免疫干预骨组织工程的关键位点。
2.2 主动调节巨噬细胞极化状态促进成骨 为了控制炎症反应并较早启动骨修复,许多学者采取了通过组织工程手段干预巨噬细胞极化状态的策略。骨组织工程主要包括生物材料支架、生物活性物质、工程细胞3个基本要素[8]。下面根据着眼的要素不同,分别对调控巨噬细胞极化状态以调节免疫微环境的不同策略进行讨论。
2.2.1 生物材料理化性质调节巨噬细胞极化状态 巨噬细胞对材料的理化特性十分敏感,通过调节和设计材料特性可以调节巨噬细胞极化状态,并创造更利于组织恢复的局部免疫微环境。材料表面化学和物理形貌的修饰被广泛研究,表1列出了对材料进行理化改性调控巨噬细胞极化状态并创造促进愈合的免疫微环境的最新研究。
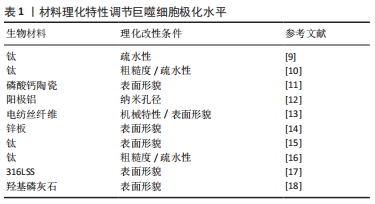
材料表面疏水性是一个重要的参数,影响了植入后宿主蛋白在其表面的吸附及相互作用情况,从而影响细胞行为。最近的一项研究对比了培养在钛表面和亲水性钛表面上的2型糖尿病小鼠的巨噬细胞,在体外观察到亲水钛表面上的巨噬细胞向M2型分化,减少了促炎因子的表达并刺激了共培养成骨细胞的促成骨基因表达。在体内,亲水钛表面通过减弱炎症反应并激活M2巨噬细胞,成功恢复了2型糖尿病中受损M2型巨噬细胞的功能,并形成了有利于增强骨愈合的组织环境[9]。以上结果提示表面亲水性强的材料可以促进抗炎性微环境的产生并改善骨再生。HOTCHKISS等[10]的研究探讨了材料表面特性如何影响巨噬细胞来调节免疫反应,他们将具有不同表面疏水性的钛植入物植入雄性C57BL/6小鼠的股骨中,手术3 d后,高亲水性组中抗炎因子白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10的表达及Th2和Treg细胞的浸润较高。为了进一步评估巨噬细胞的影响,研究人员应用了巨噬细胞消融模型并检测到了较低的白细胞介素10及Th2/Treg水平。结果表明巨噬细胞可以通过释放多种细胞因子对不同粗糙度和疏水性的植入物表面进行反应,从而调节间充质干细胞的募集和辅助T细胞的表型以产生促进伤口愈合的免疫微环境。
材料表面形貌对巨噬细胞及免疫环境同样起到了重要的调节作用。LI等[11]比较了两种表面形貌不同的磷酸钙陶瓷的成骨能力,亚微米表面形貌引起了骨形成,而微米表面形貌则未观察到骨形成。进一步的研究表明亚微米表面形貌可以招募更多的巨噬细胞,并通过PI3K/AKT途径指导巨噬细胞极化,极化后的抗炎性巨噬细胞促进了间充质干细胞的成骨分化。耗竭巨噬细胞阻止了这种骨形成,证实了巨噬细胞在其中的关键性作用。材料表面地形特征可以通过改变细胞黏附和细胞形状影响巨噬细胞行为,考虑到物理形貌具有可控性高和稳定性强的特点,改变物理形貌干预免疫反应有较好的应用前景。
生物材料的其他特性也受到关注。一项研究中探讨了纳米孔径对巨噬细胞的调节作用,实验结果表明纳米孔径的大小影响了巨噬细胞的黏附行为,改变了其扩散和细胞形态,从而调节了其极化水平及生物行为[12]。SCHAUB等[13]生产了5种具有不同表面形貌和机械性能的电纺丝纤维支架,理化表征表明不同的纤维具有相同的纤维直径和相似的弹性模量,但具有不同的刚度值。其中不同机械特性的纤维可以改变巨噬细胞对细胞因子的分泌情况,并引发独特的细胞和组织反应,从而影响局部的免疫环境。以上材料理化特性的相关研究为生物材料的设计和合成提供了一定的指导意义。
2.2.2 递送生物活性物质调控巨噬细胞极化
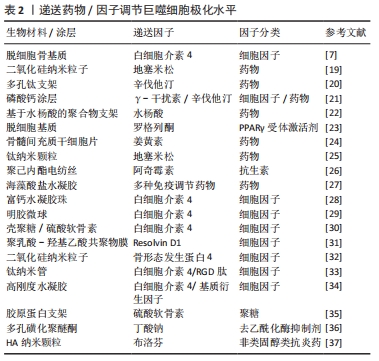
(1)药物调节巨噬细胞极化水平:临床上多种免疫调节药物在组织工程领域得到了应用。通过设计支架可以实现药物在局部的控制释放。地塞米松是临床上常用的激素类药物,具有广泛而持久的抑炎作用。QIU等[19]构建了负载有地塞米松的二氧化硅纳米粒子的组织工程复合支架,实现了地塞米松早期的快速释放和后期缓慢而持久的释放,体外实验表明在此支架上培养的骨髓间充质干细胞有更高的成骨能力,可以形成更多的矿化基质并高表达骨钙素。在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中该复合支架比未负载地塞米松的支架表现出更好的颅骨缺损修复效果。辛伐他汀作为传统的降脂药物,近年来其抗炎效果及促成骨作用逐渐受到关注。LIU等[20]设计了可以3D打印的多孔钛支架,并将负载辛伐他汀的温敏水凝胶填充其内。植入兔胫骨缺损模型后,该支架处的血管形成和骨生成显著优于未搭载辛伐他汀的多孔钛支架,进一步的研究表明新骨的体积与新血管的形成显著相关。
为了达到更好的成骨效果,联合递送是一种可行的策略。ALHAMDI等[21]利用仿生磷酸钙涂层实现了γ-干扰素与辛伐他汀的顺序递送,早期释放γ-干扰素诱导促炎巨噬细胞,后期转为释放辛伐他汀,将促炎型巨噬细胞转变为再生型巨噬细胞,实现了巨噬细胞由M1至M2的顺序激活,从而调节局部免疫环境以治疗老年骨骼损伤。交替激活同时关注了早期M1的促炎趋化作用及中晚期M2的促愈合效果,更贴近生理性的骨缺损愈合过程。这也提示需要更加关注免疫反应的时序性,何时进行调控可以达到最佳的效果尤为重要,通过设计不同的调控时间点来观察局部免疫环境变化可以加深对时序性的认识。虽然联合递送展现出一定的效果,但是可能更要关注不同因子之间的串扰,从而尽可能实现预期的疗效。
除了上述药物外,其他多种免疫抑制类药物也被开发用于递送。YU等[22]开发了基于水杨酸的聚合物形成的微球,可以对抗炎药水杨酸进行持续递送,从而通过长期缓解局部炎症来显著增强糖尿病条件下的骨再生。HAN等[23]在异种脱细胞基质表面上携带了免疫调节剂罗格列酮,一种过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma,PPARγ)的合成高选择性激动剂。实验结果表明该材料有效降低了白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,同时增加了白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达,激活了M2型巨噬细胞,从而创造了良好的免疫微环境,并促进了PPARγ介导的骨再生。最早从生姜中提取的色素姜黄素有多种生物活性作用,其中抗癌及抗炎作用日益受到关注。YANG等[24]的研究证明姜黄素可以通过促进基质细胞衍生因子1的产生,促进白细胞的大量迁移和M2型巨噬细胞极化,从而调节免疫微环境,体内实验结果表明术后第7天γ-干扰素及肿瘤坏死因子α表达明显下降,巨噬细胞向M2极化,证明炎症快速转为有利愈合的抗炎环境。
虽然利用支架进行药物递送实现了控制释放和免疫调节,但是仍然面临药物失脱、持续作用时间短等问题。多种新型的递送系统为解决问题提供了策略和方向,为后续开发更有效的递送策略提供了坚实基础。ALOTAIBI等[25]开发了可加载在钛纳米颗粒表面的地塞米松涂层。药物涂层实现了长达数月的持续释放,释放出的地塞米松调节巨噬细胞为M2型,减少了肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的产生,抑制了局部的免疫反应,并促进了成骨细胞和成纤维细胞的生长。MATHEW等[26]通过溶剂蒸发技术将阿奇霉素固定在聚己内酯电纺丝制成的膜上,实现了药物在14 d内的持续释放。体外实验表明,材料具有抗菌和免疫调节特性,可有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌生长。在啮齿动物颅骨缺损中植入后1周,观察到其诱导巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,并在术后8周显著增加了骨再生。一项最新的研究中使用了无溶剂晶体结构,分别在啮齿动物和非人类灵长类动物中抑制异物反应至少1.3年和6个月[27]。
(2)递送细胞因子调节巨噬细胞极化:另一类常用于递送的为细胞因子,主要包括白细胞介素家族等。其中,白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10由于强大的免疫抑制效果并且可以直接激活巨噬细胞替代途径的极化[4, 6],而在组织工程修复中占有重要地位。ZHENG等[7]在大鼠颅骨缺损模型材料植入后的第3天,将不同剂量的白细胞介素4递送到缺损部位,均观察到新骨和血管形成增加,其中10 ng组的M1/M2巨噬细胞极化比例最优,降低了材料周围组织的细胞凋亡水平,并增强间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨分化。借助生物材料,可以实现细胞因子在植入部位的控制释放。ZHANG等[28]合成了负载白细胞介素4的水凝胶珠,可以促进M2巨噬细胞极化并增加转化生长因子β的表达,从而激活骨髓间充质干细胞中的TGFβ/Smad信号通路并促进成骨分化,同时该水凝珠减少了细胞凋亡,在体内实现了优异的骨缺损修复效果。
由于细胞因子本质多为小分子蛋白质,他们更容易在与材料结合时出现变性、脱失等问题,从而影响递送效果。白细胞介素4具有与肝素结合的结构域,白细胞介素4与肝素的结合可稳定该细胞因子,使其免受变性和降解。HU等[29]利用这一特性,将白细胞介素4掺入肝素修饰的明胶微球中,实现了白细胞介素4的延长释放。加载白细胞介素4的明胶微球将促炎性M1型巨噬细胞转变为促愈合的M2表型,有效地减轻了炎症,并最终增强了成骨细胞的分化和骨再生。此外,HACHIM等[30]开发了可以释放白细胞介素4的纳米涂层,可以对释放数量和时间进行调节。体内外研究均表明植入物界面处的M2型巨噬细胞百分比增加,并且观察到了植入物周围纤维囊形成的减少和组织整合的改善。
随着白细胞介素家族的研究和应用日益深入的同时,也有越来越多的因子开发用于组织工程。多不饱和脂肪酸衍生的Resolvins因其在抑制嗜中性粒细胞侵入发炎组织,促进巨噬细胞吞噬中的重要作用而受到关注。在SOK等[31]的研究中,将阿司匹林引发的Resolvin D1封装到可降解的生物材料中,损伤后1 d和3 d的流式细胞仪和成像分析表明,局部Resolvin D1递送能够显著增加抗炎单核细胞和M2型巨噬细胞的积累,同时限制中性粒细胞的浸润。SUN等[32]设计了可持续释放骨形态发生蛋白4的含二氧化硅纳米粒子的生物支架,释放的骨形态发生蛋白4将巨噬细胞极化为M2型,降低了局部炎症水平。同时,骨形态发生蛋白4和M2型巨噬细胞分泌骨形态发生蛋白2共同刺激了支架中骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。在糖尿病大鼠的颅骨缺损模型中也观察到了M2型巨噬细胞的极化,改善了炎症环境并显著促进了骨再生。
许多学者对细胞因子的联合递送进行了尝试和探索。LI等[33]将抗炎因子白细胞介素4和促成骨的RGD肽逐层组装在钛纳米管上,并在其表面用羟甲基壳聚糖水凝胶层对两者进行固定和控制释放。在细胞共培养模型中研究了其对巨噬细胞极化和成骨效果的影响,结果表明搭载两种因子既可以驱动巨噬细胞向抗炎的M2表型转化并产生修复性细胞因子,另一方面增强了骨形态发生蛋白2介导的成骨分化。HE等[34]发现高刚度水凝胶刺激了巨噬细胞向M1极化,不利于成骨。通过向基质中添加白细胞介素4可以调节巨噬细胞向M2极化,同时促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。添加基质细胞衍生因子则可以显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移,募集更多的细胞。通过将两种因子联合递送到体内,相较于单一因子的策略,接受两种因子的实验动物有最多的新骨形成。细胞因子递送取得了优异的成果,进一步开发出优秀的递送系统并实现时序递送有望成为更佳的策略。表2中总结了多项递送细胞因子和药物的相关研究。

材料表面疏水性是一个重要的参数,影响了植入后宿主蛋白在其表面的吸附及相互作用情况,从而影响细胞行为。最近的一项研究对比了培养在钛表面和亲水性钛表面上的2型糖尿病小鼠的巨噬细胞,在体外观察到亲水钛表面上的巨噬细胞向M2型分化,减少了促炎因子的表达并刺激了共培养成骨细胞的促成骨基因表达。在体内,亲水钛表面通过减弱炎症反应并激活M2巨噬细胞,成功恢复了2型糖尿病中受损M2型巨噬细胞的功能,并形成了有利于增强骨愈合的组织环境[9]。以上结果提示表面亲水性强的材料可以促进抗炎性微环境的产生并改善骨再生。HOTCHKISS等[10]的研究探讨了材料表面特性如何影响巨噬细胞来调节免疫反应,他们将具有不同表面疏水性的钛植入物植入雄性C57BL/6小鼠的股骨中,手术3 d后,高亲水性组中抗炎因子白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10的表达及Th2和Treg细胞的浸润较高。为了进一步评估巨噬细胞的影响,研究人员应用了巨噬细胞消融模型并检测到了较低的白细胞介素10及Th2/Treg水平。结果表明巨噬细胞可以通过释放多种细胞因子对不同粗糙度和疏水性的植入物表面进行反应,从而调节间充质干细胞的募集和辅助T细胞的表型以产生促进伤口愈合的免疫微环境。
材料表面形貌对巨噬细胞及免疫环境同样起到了重要的调节作用。LI等[11]比较了两种表面形貌不同的磷酸钙陶瓷的成骨能力,亚微米表面形貌引起了骨形成,而微米表面形貌则未观察到骨形成。进一步的研究表明亚微米表面形貌可以招募更多的巨噬细胞,并通过PI3K/AKT途径指导巨噬细胞极化,极化后的抗炎性巨噬细胞促进了间充质干细胞的成骨分化。耗竭巨噬细胞阻止了这种骨形成,证实了巨噬细胞在其中的关键性作用。材料表面地形特征可以通过改变细胞黏附和细胞形状影响巨噬细胞行为,考虑到物理形貌具有可控性高和稳定性强的特点,改变物理形貌干预免疫反应有较好的应用前景。
生物材料的其他特性也受到关注。一项研究中探讨了纳米孔径对巨噬细胞的调节作用,实验结果表明纳米孔径的大小影响了巨噬细胞的黏附行为,改变了其扩散和细胞形态,从而调节了其极化水平及生物行为[12]。SCHAUB等[13]生产了5种具有不同表面形貌和机械性能的电纺丝纤维支架,理化表征表明不同的纤维具有相同的纤维直径和相似的弹性模量,但具有不同的刚度值。其中不同机械特性的纤维可以改变巨噬细胞对细胞因子的分泌情况,并引发独特的细胞和组织反应,从而影响局部的免疫环境。以上材料理化特性的相关研究为生物材料的设计和合成提供了一定的指导意义。
2.2.2 递送生物活性物质调控巨噬细胞极化
(1)药物调节巨噬细胞极化水平:临床上多种免疫调节药物在组织工程领域得到了应用。通过设计支架可以实现药物在局部的控制释放。地塞米松是临床上常用的激素类药物,具有广泛而持久的抑炎作用。QIU等[19]构建了负载有地塞米松的二氧化硅纳米粒子的组织工程复合支架,实现了地塞米松早期的快速释放和后期缓慢而持久的释放,体外实验表明在此支架上培养的骨髓间充质干细胞有更高的成骨能力,可以形成更多的矿化基质并高表达骨钙素。在大鼠颅骨缺损模型中该复合支架比未负载地塞米松的支架表现出更好的颅骨缺损修复效果。辛伐他汀作为传统的降脂药物,近年来其抗炎效果及促成骨作用逐渐受到关注。LIU等[20]设计了可以3D打印的多孔钛支架,并将负载辛伐他汀的温敏水凝胶填充其内。植入兔胫骨缺损模型后,该支架处的血管形成和骨生成显著优于未搭载辛伐他汀的多孔钛支架,进一步的研究表明新骨的体积与新血管的形成显著相关。
为了达到更好的成骨效果,联合递送是一种可行的策略。ALHAMDI等[21]利用仿生磷酸钙涂层实现了γ-干扰素与辛伐他汀的顺序递送,早期释放γ-干扰素诱导促炎巨噬细胞,后期转为释放辛伐他汀,将促炎型巨噬细胞转变为再生型巨噬细胞,实现了巨噬细胞由M1至M2的顺序激活,从而调节局部免疫环境以治疗老年骨骼损伤。交替激活同时关注了早期M1的促炎趋化作用及中晚期M2的促愈合效果,更贴近生理性的骨缺损愈合过程。这也提示需要更加关注免疫反应的时序性,何时进行调控可以达到最佳的效果尤为重要,通过设计不同的调控时间点来观察局部免疫环境变化可以加深对时序性的认识。虽然联合递送展现出一定的效果,但是可能更要关注不同因子之间的串扰,从而尽可能实现预期的疗效。
除了上述药物外,其他多种免疫抑制类药物也被开发用于递送。YU等[22]开发了基于水杨酸的聚合物形成的微球,可以对抗炎药水杨酸进行持续递送,从而通过长期缓解局部炎症来显著增强糖尿病条件下的骨再生。HAN等[23]在异种脱细胞基质表面上携带了免疫调节剂罗格列酮,一种过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma,PPARγ)的合成高选择性激动剂。实验结果表明该材料有效降低了白细胞介素1和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,同时增加了白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达,激活了M2型巨噬细胞,从而创造了良好的免疫微环境,并促进了PPARγ介导的骨再生。最早从生姜中提取的色素姜黄素有多种生物活性作用,其中抗癌及抗炎作用日益受到关注。YANG等[24]的研究证明姜黄素可以通过促进基质细胞衍生因子1的产生,促进白细胞的大量迁移和M2型巨噬细胞极化,从而调节免疫微环境,体内实验结果表明术后第7天γ-干扰素及肿瘤坏死因子α表达明显下降,巨噬细胞向M2极化,证明炎症快速转为有利愈合的抗炎环境。
虽然利用支架进行药物递送实现了控制释放和免疫调节,但是仍然面临药物失脱、持续作用时间短等问题。多种新型的递送系统为解决问题提供了策略和方向,为后续开发更有效的递送策略提供了坚实基础。ALOTAIBI等[25]开发了可加载在钛纳米颗粒表面的地塞米松涂层。药物涂层实现了长达数月的持续释放,释放出的地塞米松调节巨噬细胞为M2型,减少了肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的产生,抑制了局部的免疫反应,并促进了成骨细胞和成纤维细胞的生长。MATHEW等[26]通过溶剂蒸发技术将阿奇霉素固定在聚己内酯电纺丝制成的膜上,实现了药物在14 d内的持续释放。体外实验表明,材料具有抗菌和免疫调节特性,可有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌生长。在啮齿动物颅骨缺损中植入后1周,观察到其诱导巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,并在术后8周显著增加了骨再生。一项最新的研究中使用了无溶剂晶体结构,分别在啮齿动物和非人类灵长类动物中抑制异物反应至少1.3年和6个月[27]。
(2)递送细胞因子调节巨噬细胞极化:另一类常用于递送的为细胞因子,主要包括白细胞介素家族等。其中,白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10由于强大的免疫抑制效果并且可以直接激活巨噬细胞替代途径的极化[4, 6],而在组织工程修复中占有重要地位。ZHENG等[7]在大鼠颅骨缺损模型材料植入后的第3天,将不同剂量的白细胞介素4递送到缺损部位,均观察到新骨和血管形成增加,其中10 ng组的M1/M2巨噬细胞极化比例最优,降低了材料周围组织的细胞凋亡水平,并增强间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨分化。借助生物材料,可以实现细胞因子在植入部位的控制释放。ZHANG等[28]合成了负载白细胞介素4的水凝胶珠,可以促进M2巨噬细胞极化并增加转化生长因子β的表达,从而激活骨髓间充质干细胞中的TGFβ/Smad信号通路并促进成骨分化,同时该水凝珠减少了细胞凋亡,在体内实现了优异的骨缺损修复效果。
由于细胞因子本质多为小分子蛋白质,他们更容易在与材料结合时出现变性、脱失等问题,从而影响递送效果。白细胞介素4具有与肝素结合的结构域,白细胞介素4与肝素的结合可稳定该细胞因子,使其免受变性和降解。HU等[29]利用这一特性,将白细胞介素4掺入肝素修饰的明胶微球中,实现了白细胞介素4的延长释放。加载白细胞介素4的明胶微球将促炎性M1型巨噬细胞转变为促愈合的M2表型,有效地减轻了炎症,并最终增强了成骨细胞的分化和骨再生。此外,HACHIM等[30]开发了可以释放白细胞介素4的纳米涂层,可以对释放数量和时间进行调节。体内外研究均表明植入物界面处的M2型巨噬细胞百分比增加,并且观察到了植入物周围纤维囊形成的减少和组织整合的改善。
随着白细胞介素家族的研究和应用日益深入的同时,也有越来越多的因子开发用于组织工程。多不饱和脂肪酸衍生的Resolvins因其在抑制嗜中性粒细胞侵入发炎组织,促进巨噬细胞吞噬中的重要作用而受到关注。在SOK等[31]的研究中,将阿司匹林引发的Resolvin D1封装到可降解的生物材料中,损伤后1 d和3 d的流式细胞仪和成像分析表明,局部Resolvin D1递送能够显著增加抗炎单核细胞和M2型巨噬细胞的积累,同时限制中性粒细胞的浸润。SUN等[32]设计了可持续释放骨形态发生蛋白4的含二氧化硅纳米粒子的生物支架,释放的骨形态发生蛋白4将巨噬细胞极化为M2型,降低了局部炎症水平。同时,骨形态发生蛋白4和M2型巨噬细胞分泌骨形态发生蛋白2共同刺激了支架中骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。在糖尿病大鼠的颅骨缺损模型中也观察到了M2型巨噬细胞的极化,改善了炎症环境并显著促进了骨再生。
许多学者对细胞因子的联合递送进行了尝试和探索。LI等[33]将抗炎因子白细胞介素4和促成骨的RGD肽逐层组装在钛纳米管上,并在其表面用羟甲基壳聚糖水凝胶层对两者进行固定和控制释放。在细胞共培养模型中研究了其对巨噬细胞极化和成骨效果的影响,结果表明搭载两种因子既可以驱动巨噬细胞向抗炎的M2表型转化并产生修复性细胞因子,另一方面增强了骨形态发生蛋白2介导的成骨分化。HE等[34]发现高刚度水凝胶刺激了巨噬细胞向M1极化,不利于成骨。通过向基质中添加白细胞介素4可以调节巨噬细胞向M2极化,同时促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。添加基质细胞衍生因子则可以显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移,募集更多的细胞。通过将两种因子联合递送到体内,相较于单一因子的策略,接受两种因子的实验动物有最多的新骨形成。细胞因子递送取得了优异的成果,进一步开发出优秀的递送系统并实现时序递送有望成为更佳的策略。表2中总结了多项递送细胞因子和药物的相关研究。
(3)生物活性离子调节巨噬细胞极化水平:在生物材料中掺杂微量元素或进行离子递送是一项备受重视的策略,得益于微量元素本身的化学性质,其不易发生变性和降解,因而释放和递送策略更为灵活。表3中总结通过不同生物活性离子调节巨噬细胞极化状态以调控免疫微环境的多项研究。
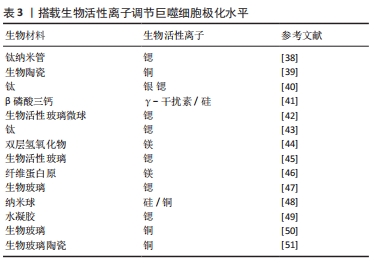
GUO等[38]制造了负载锶的钛纳米棒组成的持续释放系统,通过调节M1巨噬细胞转化为M2巨噬细胞并高表达血小板衍生生长因子,促进了人脐静脉内皮细胞迁移并分化为血管。体内研究观察到了血管生成和骨形成的改善。另一方面,递送离子也可以通过极化炎性巨噬细胞,增加材料表面的抗菌能力,从而减轻感染的风险。HUANG等[39]观察到直接向培养基中添加铜离子或从含铜的生物陶瓷表面释放铜离子可将巨噬细胞极化为M1表型,而生物材料则依靠自身特性通过调节整联蛋白表现出一定程度的抗炎作用。在体外,含铜生物陶瓷增强了巨噬细胞的吞噬和杀菌的能力。大鼠模型中,在植入周围检测到M1标志物以及成骨细胞中骨钙素和RunX-2表达的增加,这表明含铜表面促进了生物材料/骨组织界面处的骨整合增强。虽然M2型巨噬细胞介导的免疫微环境对组织修复有关键作用,但植入早期M1型巨噬细胞功能也对成骨有促进效果。为了进一步提高成骨效果,充分利用M1及M2型巨噬细胞的功能是十分重要的,因此有必要进一步研究最佳的M1/M2表型比例及对应的局部免疫环境。
多个研究团队也开发了联合递送或顺序递送的策略。LI等[40]构建了涂在钛表面的双重递送系统,可以释放银和锶以清除病原体并将巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,从而促进了成骨细胞分化,体内实验表明该系统显著增强了兔股骨干缺损模型的成骨潜力。LI等[41]采用了顺序递送的策略,植入皮下的支架早期释放γ-干扰素促使巨噬细胞向M1极化,中后期则释放硅诱导巨噬细胞M2极化,交替激活的方式极大的促进了巨噬细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子、血小板衍生生长因子等细胞因子,实现了更多新血管生成。
由于生物离子良好的理化性质,其可以和多种生物材料相结合,极大的增加了其研究和应用价值。
2.2.3 工程细胞调节巨噬细胞极化 通过生物材料直接携带细胞进入骨缺损部位,依靠细胞自身生物学特性可实现免疫调节和成骨促进。由于组织工程系统为外来物质,植入体内后的炎症反应会对工程细胞产生有害影响,因此工程细胞和机体之间的相互作用尤为关键。通过工程细胞与巨噬细胞的串扰调节巨噬细胞极化状态的研究,见表4。
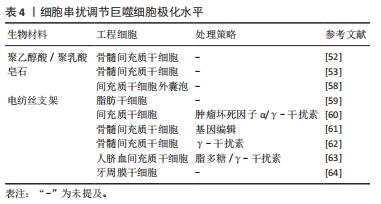
间充质干细胞自身有强大的免疫抑制能力,植入后可分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、IDO等因子,促使巨噬细胞向M2型转化,减弱异物反应,结束炎症反应并开启成骨修复,因此在骨组织工程中占有重要地位。DING等[52]的研究显示基于骨髓间充质干细胞的工程软骨比单独或联合使用软骨细胞的工程软骨支架有更好的组织存活率。进一步验证发现负载有骨髓间充质干细胞的工程支架可促进巨噬细胞向抗炎表型M2极化,包括CD206的上调、白细胞介素10合成的增加、白细胞介素1β分泌的减少以及标志从M1到M2过渡的基因表达的改变,从而改善了支架植入后诱导的炎性反应,促进了软骨组织再生。体外的共培养模型表明骨髓间充质干细胞可以诱导巨噬细胞向M2型极化,从而改变细胞因子的分泌。最近LI等[53]分析了单独的皂石以及将骨髓间充质干细胞引入皂石后的局部免疫情况,发现骨髓间充质干细胞将皂石诱导的鼠源巨噬细胞RAW 264.7细胞从M1转为M2,并实现了成骨促进。体内研究证实,与单独使用皂石相比,联合使用骨髓间充质干细胞引发较轻的免疫反应,并且对骨骼有更好的再生效果。以上结果表明间充质干细胞的存在可以一定程度上改变炎症反应同时自身也可以释放成骨成血管相关物质促进成骨。考虑到间充质干细胞来源的多样性,骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪干细胞、诱导多能干细胞、胚胎干细胞和脐带来源的间充质干细胞都实现了在骨组织工程中的应用,且各有优劣[54]。
新的研究发现间充质干细胞对巨噬细胞表型的调节作用并非通过两个细胞之间的直接接触,而是由间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体所包含的信息引起的[55-57]。HENAO AGUDELO等[58]研究了间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡对巨噬细胞的影响。利用囊泡可以调节M1型巨噬细胞,使其炎症分子水平降低同时抗炎标志物表达升高。体内实验中,囊泡处理减少了巨噬细胞浸润并诱导了M2型的产生。调节间充质干细胞的旁分泌因子水平成为可行的干预策略。其中材料对间充质干细胞的旁分泌水平有较大影响,特别是材料的本体特性。SU等[59]设计了3种不同排列(随机/平行/网状)的电纺丝支架,电纺丝支架相比于常规孔板显著促进了脂肪干细胞促血管生成因子和免疫调节细胞因子的分泌,且不同的支架形貌显示出不同的调节能力。在动物模型中,在电纺丝支架上收集的脂肪干细胞条件培养基促进了巨噬细胞的募集,并增强了巨噬细胞向愈合表型转化。这提示可以通过改变材料的理化特性影响间充质干细胞的分泌功能,实现可控调节。
此外可以通过预处理和基因治疗等方式增加间充质干细胞的抗炎特性。LIN等[60]开发了脂多糖联合肿瘤坏死因子α的新型预处理策略,在体外共培养模型中,新策略预处理的间充质干细胞增强了抗炎M2巨噬细胞标志物的表达(精氨酸酶1和CD206),并降低了炎性M1巨噬细胞标志物(肿瘤坏死因子α/ 白细胞介素1Ra)的表达;与γ-干扰素+肿瘤坏死因子α预处理组或单一因素预处理组相比,间充质干细胞对巨噬细胞的免疫调节能力显著增强;机制研究表明,这与前列腺素E2的产生增加和精氨酸酶1表达上调相关,并且可被环氧化酶2的选择性抑制剂塞来昔布所阻断。
基因调节的策略则更为灵活,LIN等[61]开发了核因子κB反应性的白细胞介素4慢病毒载体并转至骨髓间充质干细胞中,基因编辑后的细胞可以通过感受脂多糖来显著诱导白细胞介素4的分泌,含有白细胞介素4的上清液抑制原代鼠巨噬细胞M1标记(诱导型一氧化氮合成酶和肿瘤坏死因子α)的表达,并增强M2标记(精氨酸酶1,CD206和IL1Ra)的表达。此外,干细胞的年龄对其作用也存在影响,YIN等[62]比较了幼年和老年小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞对巨噬细胞的影响以及两者的成骨能力,研究表明两者都可将巨噬细胞诱导为M2表型,并促进抗炎细胞因子的分泌;但与老骨髓间充质干细胞相比,幼骨髓间充质干细胞有更强的成骨分化能力和免疫调节作用;两者的免疫调节作用均可在γ-干扰素预处理下得到增强。在充分考虑宿主免疫反应的前提下,设计可控的间充质干细胞旁分泌系统并增强其免疫调节能力是未来可行的研究方向。另一方面,无细胞递送系统的设计也成为可能,利用外泌体等实现对巨噬细胞极化及免疫环境的可控调节。

| [1] MISHRA R, BISHOP T, VALERIO IL, et al. The potential impact of bone tissue engineering in the clinic. Regen Med. 2016;11(6):571-587. [2] JULIER Z, PARK AJ, BRIQUEZ PS, et al. Promoting tissue regeneration by modulating the immune system. Acta Biomater. 2017;53:13-28. [3] MARIANI E, LISIGNOLI G, BORZI RM, et al. Biomaterials: Foreign Bodies or Tuners for the Immune Response? . Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):636. [4] SCHLUNDT C, EL KHASSAWNA T, SERRA A, et al. Macrophages in bone fracture healing: Their essential role in endochondral ossification. Bone. 2018;106:78-89. [5] KOVTUN A, BERGDOLT S, WIEGNER R, et al. The crucial role of neutrophil granulocytes in bone fracture healing. Eur Cell Mater. 2016; 32:152-162. [6] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [7] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, WU DY, et al. Development of an Accurate and Proactive Immunomodulatory Strategy to Improve Bone Substitute Material-Mediated Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018; 8(19):5482-5500. [8] TOOSI S, BEHRAVAN N, BEHRAVAN J. Nonunion fractures, mesenchymal stem cells and bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106(9):2552-2562. [9] LEE RSB, HAMLET SM, MOON HJ, et al. Re-establishment of macrophage homeostasis by titanium surface modification in type II diabetes promotes osseous healing. Biomaterials. 2020;267:120464. [10] HOTCHKISS KM, CLARK NM, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R. Macrophage response to hydrophilic biomaterials regulates MSC recruitment and T-helper cell populations. Biomaterials. 2018;182:202-215. [11] LI M, GUO X, QI W, et al. Macrophage polarization plays roles in bone formation instructed by calcium phosphate ceramics. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(9):1863-1877. [12] CHEN Z, NI S, HAN S, et al. Nanoporous microstructures mediate osteogenesis by modulating the osteo-immune response of macrophages. Nanoscale. 2017;9(2):706-718. [13] SCHAUB NJ, D’AMATO AR, MASON A, et al. The effect of engineered nanotopography of electrospun microfibers on fiber rigidity and macrophage cytokine production. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2017; 28(13):1303-1323. [14] COCKERILL I, SU Y, LEE JH, et al. Micro-/Nanotopography on Bioresorbable Zinc Dictates Cytocompatibility, Bone Cell Differentiation, and Macrophage Polarization. Nano Lett. 2020;20(6):4594-4602. [15] 雒静. 微纳米形貌调控小鼠巨噬细胞M2极化促进种植体表面成骨分化的机制及应用研究[D]. 西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学, 2019. [16] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434. [17] NI S, ZHAI D, HUAN Z, et al. Nanosized concave pit/convex dot microarray for immunomodulatory osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Nanoscale. 2020;12(31):16474-16488. [18] YANG C, ZHAO C, WANG X, et al. Stimulation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis by micro/nano hierarchical hydroxyapatite via macrophage immunomodulation. Nanoscale. 2019;11(38):17699-17708. [19] QIU K, CHEN B, NIE W, et al. Electrophoretic Deposition of Dexamethasone-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles onto Poly(L-Lactic Acid)/Poly(epsilon-Caprolactone) Composite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(6):4137-4148. [20] LIU H, LI W, LIU C, et al. Incorporating simvastatin/poloxamer 407 hydrogel into 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds for the promotion of angiogenesis, osseointegration and bone ingrowth. Biofabrication. 2016;8(4):045012. [21] ALHAMDI J R, PENG T, AL-NAGGAR IM, et al. Controlled M1-to-M2 transition of aged macrophages by calcium phosphate coatings. Biomaterials. 2019;196:90-99. [22] YU W, BAJOREK J, JAYADE S, et al. Salicylic acid (SA)-eluting bone regeneration scaffolds with interconnected porosity and local and sustained SA release. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(1):311-318. [23] HAN X, LIAO L, ZHU T, et al. Xenogeneic native decellularized matrix carrying PPARgamma activator RSG regulating macrophage polarization to promote ligament-to-bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;116:111224. [24] YANG Z, HE C, HE J, et al. Curcumin-mediated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets create a favorable immune microenvironment for adult full-thickness cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):21. [25] ALOTAIBI HF, PERNI S, PROKOPOVICH P. Nanoparticle-based model of anti-inflammatory drug releasing LbL coatings for uncemented prosthesis aseptic loosening prevention. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14: 7309-7322. [26] MATHEW A, VAQUETTE C, HASHIMI S, et al. Antimicrobial and Immunomodulatory Surface-Functionalized Electrospun Membranes for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(10). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201601345. [27] FARAH S, DOLOFF J C, MULLER P, et al. Long-term implant fibrosis prevention in rodents and non-human primates using crystallized drug formulations. Nat Mater. 2019;18(8):892-904. [28] ZHANG J, SHI H, ZHANG N, et al. Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-beta1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect . Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12907. [29] HU Z, MA C, RONG X, et al. Immunomodulatory ECM-like Microspheres for Accelerated Bone Regeneration in Diabetes Mellitus. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(3):2377-2390. [30] HACHIM D, LOPRESTI ST, YATES CC, et al. Shifts in macrophage phenotype at the biomaterial interface via IL-4 eluting coatings are associated with improved implant integration. Biomaterials. 2017;112: 95-107. [31] SOK MCP, TRIA MC, OLINGY CE, et al. Aspirin-Triggered Resolvin D1-modified materials promote the accumulation of pro-regenerative immune cell subsets and enhance vascular remodeling. Acta Biomater. 2017;53:109-122. [32] SUN X, MA Z, ZHAO X, et al. Three-dimensional bioprinting of multicell-laden scaffolds containing bone morphogenic protein-4 for promoting M2 macrophage polarization and accelerating bone defect repair in diabetes mellitus. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(3):757-769. [33] LI M, WEI F, YIN X, et al. Synergistic regulation of osteoimmune microenvironment by IL-4 and RGD to accelerate osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110508. [34] HE X T, LI X, XIA Y, et al. Building capacity for macrophage modulation and stem cell recruitment in high-stiffness hydrogels for complex periodontal regeneration: Experimental studies in vitro and in rats. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:162-180. [35] TARABALLI F, CORRADETTI B, MINARDI S, et al. Biomimetic collagenous scaffold to tune inflammation by targeting macrophages. J Tissue Eng. 2016;7:2041731415624667. [36] YANG C, OUYANG L, WANG W, et al. Sodium butyrate-modified sulfonated polyetheretherketone modulates macrophage behavior and shows enhanced antibacterial and osteogenic functions during implant-associated infections. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(36):5541-5553. [37] SAFI S, KARIMZADEH F, LABBAF S. Mesoporous and hollow hydroxyapatite nanostructured particles as a drug delivery vehicle for the local release of ibuprofen. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 92:712-719. [38] GUO S, YU D, XIAO X, et al. A vessel subtype beneficial for osteogenesis enhanced by strontium-doped sodium titanate nanorods by modulating macrophage polarization. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(28):6048-6058. [39] HUANG Q, OUYANG Z, TAN Y, et al. Activating macrophages for enhanced osteogenic and bactericidal performance by Cu ion release from micro/nano-topographical coating on a titanium substrate. Acta Biomater. 2019;100:415-426. [40] LI D, LI Y, SHRESTHA A, et al. Effects of Programmed Local Delivery from a Micro/Nano-Hierarchical Surface on Titanium Implant on Infection Clearance and Osteogenic Induction in an Infected Bone Defect. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(11):e1900002. [41] LI T, PENG M, YANG Z, et al. 3D-printed IFN-gamma-loading calcium silicate-beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold sequentially activates M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages to promote vascularization of tissue engineering bone. Acta Biomater. 2018;71:96-107. [42] ZHAO F, LEI B, LI X, et al. Promoting in vivo early angiogenesis with sub-micrometer strontium-contained bioactive microspheres through modulating macrophage phenotypes. Biomaterials. 2018;178:36-47. [43] 徐安恬. 纯钛种植体掺锶微纳米表面调节巨噬细胞极化影响骨整合的研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020. [44] CHENG S, ZHANG D, LI M, et al. Osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immune response of Mg-Al layered double hydroxide coating on pure Mg. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):91-105. [45] 张文, 黄德球, 郭周义, 等. 掺锶生物活性玻璃通过调控巨噬细胞极化促进成骨[J]. 激光生物学报,2018,27(3):232-239. [46] BESSA-GONCALVES M, SILVA AM, BRAS JP, et al. Fibrinogen and magnesium combination biomaterials modulate macrophage phenotype, NF-kB signaling and crosstalk with mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:471-484. [47] ZHANG W, ZHAO F, HUANG D, et al. Strontium-Substituted Submicrometer Bioactive Glasses Modulate Macrophage Responses for Improved Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(45): 30747-30758. [48] SHI M, CHEN Z, FARNAGHI S, et al. Copper-doped mesoporous silica nanospheres, a promising immunomodulatory agent for inducing osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:334-344. [49] LOURENCO AH, TORRES AL, VASCONCELOS DP, et al. Osteogenic, anti-osteoclastogenic and immunomodulatory properties of a strontium-releasing hybrid scaffold for bone repair. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;99:1289-1303. [50] ZHOU Y, HAN S, XIAO L, et al. Accelerated host angiogenesis and immune responses by ion release from mesoporous bioactive glass. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(20):3274-3284. [51] 林荣才. 含铜生物玻璃陶瓷对骨软骨界面的修复和诱导巨噬细胞极化的研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2019. [52] DING J, CHEN B, LV T, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Engineered Cartilage Ameliorates Polyglycolic Acid/Polylactic Acid Scaffold-Induced Inflammation Through M2 Polarization of Macrophages in a Pig Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(8):1079-1089. [53] LI T, LIU Z L, XIAO M, et al. Impact of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation on the osteogenic effects of laponite. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):100. [54] YOUSEFI AM, JAMES PF, AKBARZADEH R, et al. Prospect of Stem Cells in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6180487. [55] FURUTA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Fracture Healing in a Mouse Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620-1630. [56] HE X, DONG Z, CAO Y, et al. MSC-Derived Exosome Promotes M2 Polarization and Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:7132708. [57] TOH WS, LAI RC, HUI JHP, et al. MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:56-64. [58] HENAO AGUDELO JS, BRAGA TT, AMANO MT, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Microvesicles Regulate an Internal Pro-Inflammatory Program in Activated Macrophages. Front Immunol. 2017;8:881. [59] SU N, GAO PL, WANG K, et al. Fibrous scaffolds potentiate the paracrine function of mesenchymal stem cells: A new dimension in cell-material interaction. Biomaterials. 2017;141:74-85. [60] LIN T, PAJARINEN J, NABESHIMA A, et al. Preconditioning of murine mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced immunomodulation and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):277. [61] Lin T, Pajarinen J, Nabeshima A, et al. Establishment of NF-kappaB sensing and interleukin-4 secreting mesenchymal stromal cells as an “on-demand” drug delivery system to modulate inflammation. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(9):1025-1034. [62] Yin Y, Wu RX, He XT, et al. Influences of age-related changes in mesenchymal stem cells on macrophages during in-vitro culture. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):153. [63] 陈柄全, 彭漪, 肖轶, 等. 人脐血间充质干细胞对小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞M2亚型的转化作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(25):3987-3992. [64] Liu J, Chen B, Bao J, et al. Macrophage polarization in periodontal ligament stem cells enhanced periodontal regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):320. |
| [1] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | 薛亚东, 周新社, 裴立家, 孟繁宇, 李 键, 王金子. 自体髂骨块联合钛板重建Paprosky Ⅲ型髋臼骨缺损为假体提供坚强的初始固定#br#[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [3] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [4] | 肖 豪, 刘 静, 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [5] | 田 川, 朱向情, 杨再玲, 鄢东海, 李 晔, 王严影, 杨育坤, 何 洁, 吕冠柯, 蔡学敏, 舒丽萍, 何志旭, 潘兴华. 骨髓间充质干细胞调控猕猴卵巢的衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [6] | 吴玮玥, 郭晓东, 包崇云. 工程化外泌体在骨修复再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [7] | 胡 伟, 谢兴奇, 屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [8] | 侯婧瑛, 郭天柱, 于萌蕾, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理通过激活MALAT1靶向抑制miR-195促进骨髓间充质干细胞的生存和血管形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [9] | 梁学振, 杨 曦, 李嘉程, 骆 帝, 许 波, 李 刚. 补肾活血胶囊介导Hedgehog信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨成脂分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [10] | 闻丹丹, 李 强, 沈才齐, 纪 哲, 金培生. 外用红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架提高脂肪间充质干细胞活性修复糖尿病创面[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | 朱兵兵, 邓江华, 陈晶晶, 慕晓玲. 白细胞介素8受体可提高脐带间充质干细胞迁移和向损伤内皮的黏附[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [12] | 罗小玲, 张 丽, 杨茂桦, 徐 洁, 徐晓梅. 柚皮素干预人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [13] | 房晓磊, 冷 军, 张 晨, 刘会敏, 郭 文. 间充质干细胞不同移植途径治疗缺血性脑卒中疗效差异的系统评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [14] | 郭 嘉, 丁琼桦, 刘 泽, 吕思懿, 周泉程, 高玉花, 白春雨. 间充质干细胞来源外泌体的生物学特性及免疫调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [15] | 康坤龙, 王新涛. 生物支架材料促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究热点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
骨组织工程介导的骨修复在现今临床及研究中起到越来越重要的作用,但是仍未达到满意的效果[1]。随着骨免疫学的发展,免疫反应对骨再生的重要影响逐渐被阐释。在骨组织工程修复的早期阶段,多种免疫细胞,如巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞等介导炎症反应及异物反应,有利于抗感染和坏死物质的清除[2]。然而,过度的炎症反应会损伤工程细胞并促使巨噬细胞及成纤维细胞等在生物材料表面形成纤维囊[3],纤维囊将生物材料与组织分隔,导致工程材料植入失败。随着对早期炎症反应认识的不断深入,研究人员发现巨噬细胞的极化状态对炎症反应的进程有着关键性的影响。巨噬细胞通过经典激活途径激活为M1型,主要表现为促炎作用,促进早期炎症反应的激活;亦会通过替代途径激活为M2型,主要表现为抗炎特性,促进炎症反应的消除并有利于成骨成血管[4]。通过干预巨噬细胞极化状态,调节局部免疫微环境是减轻异物反应、早期开展骨修复的重要手段。
该综述首先介绍了巨噬细胞在生物材料植入体内后面临的炎症反应过程中的重要作用,之后重点讨论调节巨噬细胞极化状态干预免疫微环境以促进成骨的相关研究进展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.2 入选标准 纳入标准:与研究主题相关的文献;排除标准:观点陈旧,研究内容重复的文献。
1.3 质量评估 文献内容及观点有创新性,论证科学严谨,体现该领域最新研究进展的文献为重点纳入的文献,与研究内容和目的无关及质量低的不纳入综述。
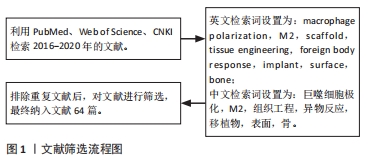
1.4 数据提取 在数据库对文献进行初步检索,排除重复文献后,根据入选标准筛选文献并对文献进行质量评估,最终得到文献64篇。文献筛选流程图见图1。
目前已有多种材料开发用于组织工程,并进行了不同材料的表面化学和物理形貌对巨噬细胞及免疫反应的影响性的评估。研究了不同药物、生物因子及微量元素递送对巨噬细胞和免疫环境的调节作用,实现了多因子的共递送,设计出多种递送系统,一定程度上解决了药物/因子失活的问题,并延长了其在体内的作用时间。在外源性细胞植入的策略中,最新的研究提出工程细胞对巨噬细胞极化的调节作用主要通过旁分泌作用实现,为调节免疫开辟了新思路。除了通过巨噬细胞极化的策略,还有其他调节局部免疫环境的方法,在此文中并未进行讨论,但也在骨组织工程免疫研究中占有重要地位。
综上所述,调节巨噬细胞极化以调控免疫反应在骨组织工程中有巨大的应用价值,但仍需要进一步探索:①由于免疫反应进程存在时序性,因此何时进行免疫调节能达到最佳的干预效果有待研究;②虽然M2型巨噬细胞对组织修复有重要意义,但骨再生是连续的过程,M1型巨噬细胞的作用也必不可少,因此关注和干预炎症过程中M1/M2型巨噬细胞对修复和成骨的最佳表型比例具有深入研究的价值;③如何进一步延长药物/因子在体内的释放和作用时间以达到长久的治疗作用;④无细胞递送的新型策略有待开发。
文章总结了目前通过巨噬细胞调节免疫微环境以促进成骨的骨组织工程研究,希望为研究者加深对该领域的认识提供途径,同时展望了有潜力的研究方向,以期为之后的研究提供启发,期待未来有更加优异的骨组织工程方案以改善临床骨缺损的治疗。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
巨噬细胞极化:巨噬细胞会受到微环境中多种信号的调节与诱导,从而可以产生不同的极化状态。不同状态的巨噬细胞存在独特的表型及标志物并在体内行使不同的功能。根据刺激因素不同,巨噬细胞可以极化为M1表型或M2表型等,他们分别在炎症调节中行使促炎或抗炎的复杂功能。
药物递送系统:是指在空间、时间及剂量上全面调控药物在生物体内分布的技术体系。其目标是在恰当的时机将适量的药物递送到正确的位置,从而增加药物的利用效率,提高疗效,降低成本,减少毒副作用。药物递送系统是医学、工学(材料、机械、电子)及药学的融合学科,其研究对象既包括药物本身,也搭载药物的载体材料、装置,还包括对药物或载体等进行物理化学改性、修饰的相关技术。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
骨组织工程是指利用生物活性支架搭载成骨相关细胞及因子并植入骨缺损内部,通过诱导及支撑的方式促进成骨的骨修复策略。由于生物材料植入后需面临体内的异物及炎症反应,其成骨效果受到限制。近年的研究强调了调节局部免疫微环境,尤其是巨噬细胞极化水平,对生物材料顺利整合和发挥成骨促进作用的重要意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||