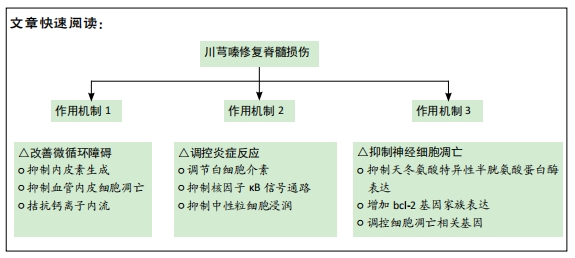
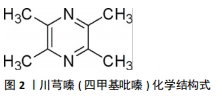
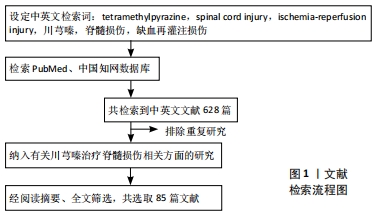
[1] ASHAMMAKHI N, KIM HJ, EHSANIPOUR A, et al. Regenerative Therapies for Spinal Cord Injury. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2019;25(6):471-491.
[2] COWAN H, LAKRA C, DESAI M. Autonomic dysreflexia in spinal cord injury. BMJ. 2020;371:m3596.
[3] Karsy M, Hawryluk G. Modern Medical Management of Spinal Cord Injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019;19(9):65.
[4] OYINBO CA. Secondary injury mechanisms in traumatic spinal cord injury: a nugget of this multiply cascade. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2011;71(2):281-299.
[5] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[6] ANWAR MA, AL SHEHABI TS, EID AH. Inflammogenesis of Secondary Spinal Cord Injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016;10:98.
[7] SHIMIZU EN, SEIFERT JL, JOHNSON KJ, et al. Prophylactic Riluzole Attenuates Oxidative Stress Damage in Spinal Cord Distraction. J Neurotrauma. 2018;35(12):1319-1328.
[8] DYCK S, KATARIA H, ALIZADEH A, et al. Perturbing chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan signaling through LAR and PTPσ receptors promotes a beneficial inflammatory response following spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):90.
[9] SODERBLOM C, LUO X, BLUMENTHAL E, et al. Perivascular fibroblasts form the fibrotic scar after contusive spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2013;33(34):13882-13887.
[10] SANDEAN D. Management of acute spinal cord injury: A summary of the evidence pertaining to the acute management, operative and non-operative management. World J Orthop. 2020;11(12):573-583.
[11] LI J, LIU G, ZHENG Y, et al. The epidemiological survey of acute traumatic spinal cord injury (ATSCI) of 2002 in Beijing municipality. Spinal Cord. 2011;49(7):777-782.
[12] YANG R, GUO L, HUANG L, et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury in Guangdong, China. Spine. 2017; 42(9):E555-E561.
[13] ZHENG Y, QI S, WU F, et al. Chinese Herbal Medicine in Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(7):1593-1616.
[14] LU Y, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110136.
[15] 韩炜.川芎的化学成分与药理作用研究进展[J].中国现代中药, 2017,19(9):1341-1349.
[16] KOUSHKI D, LATIFI S, NOROUZI JAVIDAN A, et al. Efficacy of some non-conventional herbal medications (sulforaphane, tanshinone IIA, and tetramethylpyrazine) in inducing neuroprotection in comparison with interleukin-10 after spinal cord injury: A meta-analysis. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015;38(1):13-22.
[17] HU JZ, WANG XK, CAO Y, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Facilitates Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting MMP2, MMP9, and Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017;14(2):110-116.
[18] 姜宇懋,王丹巧.川芎嗪药理作用研究进展[J].中国现代中药, 2016,18(10):1364-1370.
[19] ZHAO Y, LIU Y, CHEN K. Mechanisms and Clinical Application of Tetramethylpyrazine (an Interesting Natural Compound Isolated from Ligusticum Wallichii): Current Status and Perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:2124638.
[20] DING Y, DU J, CUI F, et al. The protective effect of ligustrazine on rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2019;38(10):1168-1177.
[21] ZHANG H, DING S, XIA L. Ligustrazine inhibits the proliferation and migration of ovarian cancer cells via regulating miR-211. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1):BSR20200199.
[22] JIANG G, XIN R, YUAN W, et al. Ligustrazine ameliorates acute kidney injury through downregulation of NOD2 mediated inflammation. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(3):731-742.
[23] REN Z, MA J, ZHANG P, et al. The effect of ligustrazine on L-type calcium current, calcium transient and contractility in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;144(3):555-561.
[24] YU L, SHE T, LI M, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and tumor necrosis factor-α secretion through an NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Int J Mol Med. 2013;32(3):717-722.
[25] QIAN W, XIONG X, FANG Z, et al. Protective effect of tetramethylpyrazine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:107501.
[26] CAI X, CHEN Z, PAN X, et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis, fibrosis and thrombosis by tetramethylpyrazine: mechanisms contributing to the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88176.
[27] TIAN Y, LIU Y, CHEN X, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine promotes proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells from rat brain in hypoxic condition via mitogen-activated protein kinases pathway in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 2010;474(1):26-31.
[28] 吴贤良,王小勇,黄建军.川芎嗪对急性脊髓损伤患者术后神经功能恢复的影响[J].山东医药,2019,59(29):67-69.
[29] 黎启福,赵金平,王宏新,等.丹参川芎嗪注射液联合甲基泼尼松龙治疗胸腰段急性脊髓损伤[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2012,33(4): 450-451.
[30] 俞勇,陈明,彭爱明,等.丹参川芎嗪注射液联合高压氧对急性脊髓损伤早期并发症的预防作用[J].中国药房,2018,29(2):244-247.
[31] 侯建雄,马海燕,李莉.手术配合丹参川芎嗪、甲基泼尼松龙治疗颈椎骨折伴脊髓损伤的临床观察[J].河北医药,2013,35(14):2110-2112.
[32] 都芳涛,方继峰,李兴晶,等.不同剂量川芎嗪治疗脊髓损伤的临床效果比较[J].中国医药,2019,14(10):1511-1514.
[33] TRAN AP, WARREN PM, SILVER J. The Biology of Regeneration Failure and Success After Spinal Cord Injury. Physiol Rev. 2018;98(2):881-917.
[34] FAN B, WEI Z, YAO X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866.
[35] GUO J, LI Y, HE Z, et al. Targeting endothelin receptors A and B attenuates the inflammatory response and improves locomotor function following spinal cord injury in mice. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(1):74-82.
[36] A JC, LI ZY, LONG QF, et al. MiR-379-5p improved locomotor function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats by reducing endothelin 1 and inhibiting astrocytes expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019; 23(22):9738-9745.
[37] PETERS CM , ROGERS SD , POMONIS JD, et al. Endothelin receptor expression in the normal and injured spinal cord: potential involvement in injury-induced ischemia and gliosis.Exp Neurol. 2003;180(1):1-13.
[38] 李洋. 川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓急性损伤段微循环影响的实验性研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2007.
[39] BARTANUSZ V, JEZOVA D, ALAJAJIAN B, et al. The blood-spinal cord barrier: morphology and clinical implications. Ann Neurol. 2011;70(2): 194-206.
[40] JIN LY, LI J, WANG KF, et al. The blood-spinal cord barrier in spinal cord injury: a review. J Neurotrauma. 2021 Feb 16. doi: 10.1089/neu. 2020.7413.
[41] 魏正军,朱涛,江荣才,等.脊髓损伤大鼠内皮祖细胞与脊髓血管新生[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(36):6774-6778.
[42] 李东哲.川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后微血管及胶原成分的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2014.
[43] HU J, CAO Y, WU T, et al. Micro-CT as a Tool to Investigate the Efficacy of Tetramethylpyrazine in a Rat Spinal Cord Injury Model. Spine. 2016; 41(16):1272-1278.
[44] REMPE RG, HARTZ AMS, BAUER B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood-brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(9):1481-1507.
[45] HU JZ, WANG XK, CAO Y, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Facilitates Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury by Inhibiting MMP2, MMP9, and Vascular Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2017;14(2):110-116.
[46] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264.
[47] 吴天定. 川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后血管再生的作用及相关机制的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2012.
[48] ZHANG M, GAO F, TENG F, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine promotes the proliferation and migration of brain endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10(1):29-32.
[49] LIANG X, ZHOU H, DING Y, et al. TMP prevents retinal neovascularization and imparts neuroprotection in an oxygen-induced retinopathy model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(4):2157-2169.
[50] YANG G, QIAN C, WANG N, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation-Induced Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Injury via Rho/Rho-kinase Signaling Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2017;37(4):619-633.
[51] 刘如春. 电针对急性脊髓损伤大鼠差异表达基因及钙离子作用的实验研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2007.
[52] 蔡卫华,叶晓健,谭炳毅,等.急性脊髓损伤后内皮素-1与Ca~ (2+)含量的变化关系的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(20):1568-1570.
[53] LU D, SHAO HT, GE WP, et al. Ginsenoside-Rb1 and tetramethylpyrazine phosphate act synergistically to prevent dilated cardiomyopathy in cTnTR141W transgenic mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2012;59(5):426-433.
[54] 孙海燕,贾连顺,陈宣维,等.川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤段电解质、水含量改变的保护作用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2005,13(2):4-6.
[55] MIRON VE, FRANKLIN RJ. Macrophages and CNS remyelination. J Neurochem. 2014;130(2):165-171.
[56] 王涛丽,顾兵,李华南,等.急性脊髓损伤后的炎症反应及其抗炎治疗[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(4):452-457.
[57] DONNELLY DJ, POPOVICH PG. Inflammation and its role in neuroprotection, axonal regeneration and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2008;209(2):378-388.
[58] 王明,陈铁戈,杨新乐,等.脊髓损伤炎症反应的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2018,39(8):723-726.
[59] JONES TB, MCDANIEL EE, POPOVICH PG. Inflammatory-mediated injury and repair in the traumatically injured spinal cord. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(10):1223-1236.
[60] ULNDREAJ A, CHIO JC, AHUJA CS, et al. Modulating the immune response in spinal cord injury. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;16(10): 1127-1129.
[61] 李晓明. 川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤模型IL-10、IL-18表达的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2008.
[62] WANG C, WANG P, ZENG W, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine improves the recovery of spinal cord injury via Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26(4):1287-1291.
[63] SU X, YE J, HSUEH EC, et al. Tumor microenvironments direct the recruitment and expansion of human Th17 cells. J Immunol. 2010; 184(3):1630-1641.
[64] 张男,赵茗,孙亚澎.川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复的影响及机制[J].中国医科大学学报,2015,44(1):60-63.
[65] SHIN JW, MOON JY, SEONG JW, et al. Effects of tetramethylpyrazine on microglia activation in spinal cord compression injury of mice. Am J Chin Med. 2013;41(6):1361-1376.
[66] HAN X, LU M, WANG S, et al. Targeting IKK/NF-κB pathway reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2012;511(1):28-32.
[67] 周小珏,赵小华,张安仁.脊髓损伤炎症中的NF-кB信号通路[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2020,36(10):1159-1164.
[68] HU JZ, HUANG JH, XIAO ZM, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine accelerates the function recovery of traumatic spinal cord in rat model by attenuating inflammation. J Neurol Sci. 2013;324(1-2):94-99.
[69] ZHANG L, LU X, GONG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Integrity by Modulating Microglia Polarization Through Activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and Inhibition of NF-кB Signaling Pathways in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;10.1007/s10571-020-00878-3.
[70] NEIRINCKX V, COSTE C, FRANZEN R, et al. Neutrophil contribution to spinal cord injury and repair. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:150.
[71] FAN L, WANG K, SHI Z, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine protects spinal cord and reduces inflammation in a rat model of spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(1):192-200.
[72] 黎俊豪. 川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤模型P-选择素、中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶表达的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.
[73] 刘建敏,王福川,周亚净,等.电针刺激对脊髓挫伤模型大鼠神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(5):616-621.
[74] 孙正义,赵斌,洪光祥,等.大鼠脊髓慢性压迫及减压后神经细胞凋亡及其相关基因的表达[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2003,13(3):33-36+63.
[75] Wu B, Liang J. Pectolinarigenin promotes functional recovery and inhibits apoptosis in rats following spinal cord injuries. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(5):3877-3882.
[76] 沈正祥,吕红斌,李小明,等.川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤模型caspase-3和NF表达的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2008, 33(8):693-699.
[77] 王圣轩. 川芎嗪对大鼠急性脊髓损伤模型中FADD表达及Caspase-8活性的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2009.
[78] 王健,贾玉柱,郑纯威,等.川芎嗪对急性脊髓损伤大鼠神经细胞早期凋亡和Caspase-3mRNA表达的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2011,29(12):2662-2668.
[79] ZHU N, RUAN J, YANG X, et al. Triptolide improves spinal cord injury by promoting autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis. Cell Biol Int. 2020; 44(3):785-794.
[80] 孙海燕. 川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓继发性损伤神经保护作用及机制的研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2004.
[81] FAN LH, WANG KZ, CHENG B, et al. Anti-apoptotic and neuroprotective effects of Tetramethylpyrazine following spinal cord ischemia in rabbits. BMC Neurosci. 2006;7:48.
[82] Fan Y, Wu Y. Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates neural apoptosis in injured spinal cord via the downregulation of miR-214-3p. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;94:827-833.
[83] Bhattacharyya S, Dinda A, Vishnubhatla S, et al. A combinatorial approach to modulate microenvironment toward regeneration and repair after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2021;741:135500.
[84] 周赟,胡建中,吕红斌,等.川芎嗪对脊髓急性损伤大鼠神经营养因子表达的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2010,19(9):1058-1060.
[85] 黄江湖. MicroRNA-21在急性脊髓损伤中的作用及川芎嗪的抗凋亡作用机制研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.
|