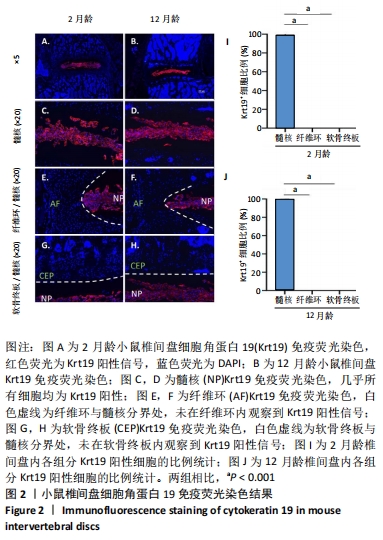
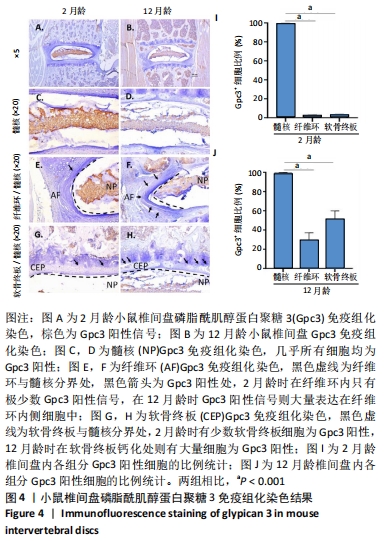
[1] GBD 2019 DISEASES AND INJURIES COLLABORATORS. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (London, England). 2020;396(10258):1204-1222.
[2] KIM HJ, GREEN DW. Adolescent back pain. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2008;20(1): 37-45.
[3] LAVELLE WF, BIANCO A, MASON R, et al. Pediatric disk herniation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(11):649-656.
[4] SÄÄKSJÄRVI S, KERTTULA L, LUOMA K, et al. Disc Degeneration of Young Low Back Pain Patients: A Prospective 30-year Follow-up MRI Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2020;45(19):1341-1347.
[5] MAHER C, UNDERWOOD M, BUCHBINDER R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet (London, England). 2017; 389(10070):736-747.
[6] LONGO UG, LOPPINI M, DENARO L, et al. Rating scales for low back pain. Br Med Bull. 2010;94:81-144.
[7] CIEZA A, CAUSEY K, KAMENOV K, et al. Global estimates of the need for rehabilitation based on the Global Burden of Disease study 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet (London, England). 2021;396(10267):2006-2017.
[8] DIELEMAN JL, CAO J, CHAPIN A, et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996-2016. JAMA. 2020;323(9):863-884.
[9] WUERTZ K, HAGLUND L. Inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disk degeneration and discogenic pain. Global Spine J. 2013;3(3):175-184.
[10] LYU FJ, CUI H, PAN H, et al. Painful intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation: from laboratory evidence to clinical interventions. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):7.
[11] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组. 腰椎间盘突出症诊疗指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020,40(8):477-487.
[12] ZHAO L, MANCHIKANTI L, KAYE AD, et al. Treatment of Discogenic Low Back Pain: Current Treatment Strategies and Future Options-a Literature Review. Curr Pain Head Rep. 2019;23(11):86.
[13] KREINER DS, MATZ P, BONO CM, et al. Guideline summary review: an evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain. Spine J. 2020;20(7):998-1024.
[14] Hanley EN Jr, Herkowitz HN, Kirkpatrick JS, et al. Debating the value of spine surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(5):1293-1304.
[15] ADAMS MA, DOLAN P, MCNALLY DS. The internal mechanical functioning of intervertebral discs and articular cartilage, and its relevance to matrix biology. Matrix Biol. 2009;28(7):384-389.
[16] DALY C, GHOSH P, JENKIN G. A Review of Animal Models of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Pathophysiology, Regeneration, and Translation to the Clinic. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5952165.
[17] LI Z, CHEN X, XU D, et al. Circular RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12704.
[18] ZHANG Y, YANG B, WANG J, et al. Cell Senescence: A Nonnegligible Cell State under Survival Stress in Pathology of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9503562.
[19] CHOI H, JOHNSON ZI, RISBUD MV. Understanding nucleus pulposus cell phenotype: a prerequisite for stem cell based therapies to treat intervertebral disc degeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(4):307-316.
[20] SUN B, LIAN M, HAN Y, et al. A 3D-Bioprinted dual growth factor-releasing intervertebral disc scaffold induces nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(1):179-190.
[21] WEN T, WANG H, LI Y, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promote the repair of intervertebral disc degeneration by transferring microRNA-199a. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex). 2021:1-15.
[22] SINKEMANI A, WANG F, XIE Z, et al. Nucleus Pulposus Cell Conditioned Medium Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation into Nucleus Pulposus-Like Cells under Hypoxic Conditions. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8882549.
[23] SAKAI D, NAKAI T, MOCHIDA J, et al. Differential phenotype of intervertebral disc cells: microarray and immunohistochemical analysis of canine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Spine. 2009;34(14):1448-1456.
[24] LEE C, SAKAI D, NAKAI T, et al. A phenotypic comparison of intervertebral disc and articular cartilage cells in the rat. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2174-2185.
[25] RICHARDSON S M, KNOWLES R, TYLER J, et al. Expression of glucose transporters GLUT-1, GLUT-3, GLUT-9 and HIF-1alpha in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;129(4):503-511.
[26] ALINI M, EISENSTEIN SM, ITO K, et al. Are animal models useful for studying human disc disorders/degeneration? Eur Spine J. 2008;17(1):2-19.
[27] MELROSE J, TESSIER S, RISBUD MV. Genetic murine models of spinal development and degeneration provide valuable insights into intervertebral disc pathobiology. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;41:52-72.
[28] XU X, WANG D, ZHENG C, et al. Progerin accumulation in nucleus pulposus cells impairs mitochondrial function and induces intervertebral disc degeneration and therapeutic effects of sulforaphane. Theranostics. 2019;9(8):2252-2267.
[29] BIAN Q, MA L, JAIN A, et al. Mechanosignaling activation of TGFβ maintains intervertebral disc homeostasis. Bone Res. 2017;5:17008.
[30] NAKAMICHI R, ITO Y, INUI M, et al. Mohawk promotes the maintenance and regeneration of the outer annulus fibrosus of intervertebral discs. 2016;7:12503.
[31] KATZ JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(suppl_2): 21-24.
[32] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina). 2019;73(6):421-424.
[33] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015; 23(7):1057-1070.
[34] NI L, ZHENG Y, GONG T, et al. Proinflammatory macrophages promote degenerative phenotypes in rat nucleus pulpous cells partly through ERK and JNK signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5362-5371.
[35] TAVANA S, MASOUROS S, BAXAN N, et al. The Effect of Degeneration on Internal Strains and the Mechanism of Failure in Human Intervertebral Discs Analyzed Using Digital Volume Correlation (DVC) and Ultra-High Field MRI. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:610907.
[36] DUDEK M, YANG N, RUCKSHANTHI JP, et al. The intervertebral disc contains intrinsic circadian clocks that are regulated by age and cytokines and linked to degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(3):576-584.
[37] SAKAI D, NAKAMURA Y, NAKAI T, et al. Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1264.
[38] JI ML, JIANG H, ZHANG XJ, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):5051.
[39] SAKAI D, NAKAI T, MOCHIDA J, et al. Differential phenotype of intervertebral disc cells: microarray and immunohistochemical analysis of canine nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(14):1448-1456.
[40] FUJITA N, MIYAMOTO T, IMAI J, et al. CD24 is expressed specifically in the nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005; 338(4):1890-1896.
[41] RUTGES J, CREEMERS LB, DHERT W, et al. Variations in gene and protein expression in human nucleus pulposus in comparison with annulus fibrosus and cartilage cells: potential associations with aging and degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):416-423.
[42] MACIVER N, JACOBS S, WIEMAN H, et al. Glucose metabolism in lymphocytes is a regulated process with significant effects on immune cell function and survival. J Leukocyte Biol. 2008;84(4):949-957.
[43] XIAO L, DING B, GAO J, et al. Curcumin prevents tension-induced endplate cartilage degeneration by enhancing autophagy. Life Sci. 2020;258:118213.
[44] HAN Y, LI X, YAN M, et al. Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;516(3):1026-1032.
[45] TESSIER S, MADHU V, JOHNSON Z, et al. NFAT5/TonEBP controls early acquisition of notochord phenotypic markers, collagen composition, and sonic hedgehog signaling during mouse intervertebral disc embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 2019;455(2):369-381.
[46] YAO G, YIN J, WANG Q, et al. Glypican-3 Enhances Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolism in Liver Cancer Cells. Biomed Res Int. 2019; 2019:2560650.
[47] ZHENG Y, FU X, LIU Q, et al. Characterization of Cre recombinase mouse lines enabling cell type-specific targeting of postnatal intervertebral discs. J Cell Physiol. 2019;10.1002/jcp.28166.
[48] MOHANTY S, PINELLI R, PRICOP P, et al. Chondrocyte-like nested cells in the aged intervertebral disc are late-stage nucleus pulposus cells. Aging Cell. 2019; 18(5):e13006.
[49] MEANS AL, XU Y, ZHAO A, et al. A CK19(CreERT) knockin mouse line allows for conditional DNA recombination in epithelial cells in multiple endodermal organs. Genesis (New York, NY: 2000). 2008;46(6):318-323.
|