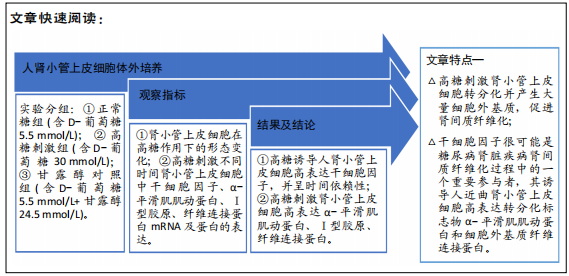
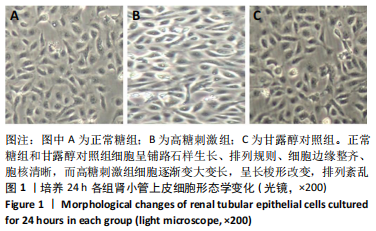
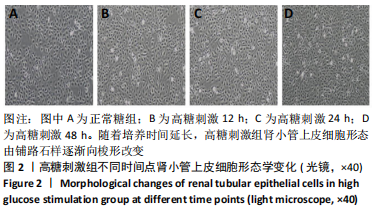
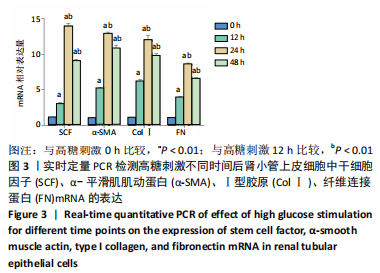
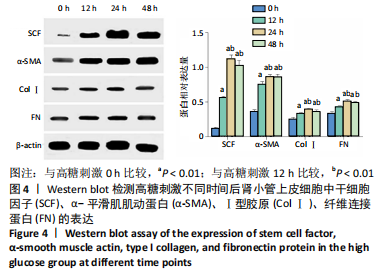
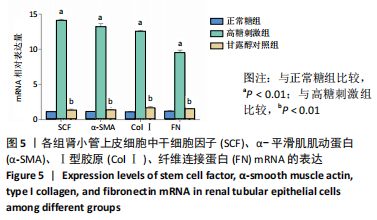
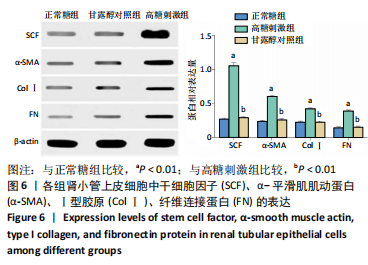
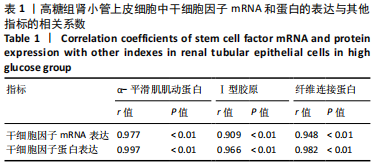
[1] LOEFFLER I, WOLF G. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Cells. 2015;4(4):631-652.
[2] YIN DD, LUO JH, ZHAO ZY, et al. Tranilast prevents renal interstitial fibrosis by blocking mast cell infiltration in a rat model of diabetic kidney disease. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):7356-7364.
[3] DING L, DOLGACHEV V, WU Z, et al. Essential role of stem cell factor-c-Kit signalling pathway in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Pathol. 2013;230(2):205-214.
[4] 刘雪梅,马瑞霞,周海燕,等.干细胞因子在狼疮肾炎患者肾组织中的表达及意义[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2009,13(6):376-380.
[5] 刘雪梅,张伟,王祥花,等.干细胞因子在尿酸性肾病大鼠模型肾组织中的表达及意义[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(3):179-184.
[6] AMERICAN DIABETES ASSOCIATION. Mierovascular Complications and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41(Suppl 1): S105-S118.
[7] WEI L, XIAO Y, LI L, et al. The Susceptibility Genes in Diabetic Nephropathy. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2018;4(4):226-237.
[8] SLYNE J, SLATTERY C, MCMORROW T, et al. New developments concerning the proximal tubule in diabetic nephropathy: in vitro models and mechanisms. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015;30 Suppl 4:iv60-iv67.
[9] MISE K, HOSHINO J, UENO T, et al. Prognostic Value of Tubulointerstitial Lesions, Urinary N-Acetyl-β-d-Glucosaminidase, and Urinary β2-Microglobulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Biopsy-Proven Diabetic Nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11(4):593-601.
[10] OLIVEIRA-SILVA GL, MORAIS IBM, FORTUNATO-SILVA J, et al. Testosterone and Mast Cell Interactions in the Development of Kidney Fibrosis after Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(8):1164-1169.
[11] CRUZ-SOLBES AS, YOUKER K. Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EndMT): Role and Implications in Kidney Fibrosis. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;60:345-372.
[12] BADAL SS, DANESH FR. New insights into molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;63(2 Suppl 2):S63-83.
[13] KITADA K, NAKANO D, OHSAKI H, et al. Hyperglycemia causes cellular senescence via a SGLT2- and p21-dependent pathway in proximal tubules in the early stage of diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2014; 28(5):604-611.
[14] GUO K, LU J, HUANG Y, et al. Protective role of PGC-1α in diabetic nephropathy is associated with the inhibition of ROS through mitochondrial dynamic remodeling. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0125176.
[15] PICKERING RJ, ROSADO CJ, SHARMA A, et al. Recent novel approaches to limit oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications. Clin Transl Immunology. 2018;7(4):e1016.
[16] AGHADAVOD E, KHODADADI S, BARADARAN A, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Factors in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2016; 10(6):337-343.
[17] ROCHETTE L, ZELLER M, COTTIN Y, et al. Diabetes, oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(9):2709-2729.
[18] MATSUDA M, SHIMOMURA I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity: implications for metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013;7(5):e330-e341.
[19] MARQUEZ-EXPOSITO L, LAVOZ C, RODRIGUES-DIEZ RR, et al. Gremlin Regulates Tubular Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition via VEGFR2: Potential Role in Renal Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1195.
[20] STRUTZ FM. EMT and proteinuria as progression factors. Kidney Int. 2009; 75(5):475-481.
[21] CHUNG Y, FU E, CHIN YT, et al. Role of Shh and TGF in cyclosporine-enhanced expression of collagen and α-SMA by gingival fibroblast. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42(1):29-36.
[22] ZHAO L, ZHAO J, WANG X, et al. Serum response factor induces endothelial-mesenchymal transition in glomerular endothelial cells to aggravate proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy. Physiol Genomics. 2016;48(10):711-718.
[23] ZSEBO KM, WILLIAMS DA, GEISSLER EN, et al. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990;63(1):213-224.
[24] WANG Y, MA H, TAO X, et al. SCF promotes the production of IL-13 via the MEK-ERK-CREB signaling pathway in mast cells. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(4): 2491-2496.
[25] MADJENE LC, PONS M, DANELLI L, et al. Mast cells in renal inflammation and fibrosis: lessons learnt from animal studies. Mol Immunol. 2015;63(1):86-93.
[26] OTSUBO S, NITTA K, UCHIDA K, et al. Mast cells and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in patients with ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2003;7(1):41-47.
[27] OKOŃ K, STACHURA J. Increased mast cell density in renal interstitium is correlated with relative interstitial volume, serum creatinine and urea especially in diabetic nephropathy but also in primary glomerulonephritis. Pol J Pathol. 2007;58(3):193-197.
[28] 李佳,郑洁,刘雪梅,等.干细胞因子对人肾小管上皮细胞表型变化及TGF-β1表达的影响[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2017,33 (2):140-142. |