1.1 设计 体外细胞观察性实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2018年10月至2019年12月在广西中医药大学第一附属医院分子生物学实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 SPF级Wistar雌性大鼠32只,6-8周龄,体质量160-200 g,购于北京维通利华实验动物有限公司,合格证号:SCXK(京)2017-0006,于SPF条件下饲养于广西中医药大学科学实验中心,许可证号:SYXK(桂)2019-0001。该实验经过广西中医药大学动物伦理委员会批准(动物伦理审查号:2019010)。
1.3.2 实验细胞 人肝癌HepG2细胞购自赛百慷(上海)生物技术股份有限公司,货号:iCell-h092。
1.3.3 实验试剂及药物 PBS、青链霉素混合液(100×)、胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、RIPA裂解液(北京索莱宝科技有限公司,批号分别为sv300160.03、P1400、T1300、PH0326、P0013B);B27、N2、乳铁蛋白、DMEM(美国Gibco公司,批号分别为17504-004、17502048、
yb-E12455、MD202);成纤维细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子(美国PEPROTECH公司,批号分别为Rs-6706R、HZ-4567R);DMEM/F12(中国武汉BOSTER公司,批号:11330032);MACS Buffer、CD133microbead kit(德国美天旎生物技术公司,批号分别为130-091-221、130-097-049);PE MOUSE
ANTI-HUMAN CD133(北京BD Biosciences公司,批号:
12-1331-82);山羊抗兔IgG、山羊抗鼠IgG、二甲基亚砜(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司,批号分别为ab97051、1010-04、D8371);脱脂奶粉(中国光明牌,批号:080922 DN7);
SDS-PAGE上样缓冲液、SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒、ECL发光液、干细胞消化液(碧云天上海生物技术有限公司,批号分别为YT050-CWN、P1200、PH0353、MX2001);SOX2、OCT4、NANOG、β-catenin(CST中国公司,批号分别为14-9811、ab18976、ab21624、AC106);引物(中国武汉金开瑞公司,批号:D3118);CCK-8试剂盒(中国上海东仁化学科技有限公司,批号:ab228554);Scientific TRIzolTM Reagent (Thermo中国公司,批号:15596026);NSuperReal PreMix Plus、FastKing
RT Kit(TIANGE,批号分别为FP205、KR116-02);Nuclease-Free
Water(莫纳生物科技有限公司,批号:AM9932)。
1.3.4 实验药物 敷和备化方经过广西中医药大学第一附属医院药剂科主任杨政滕鉴定符合2015年版《中国药典》的规定和标准,为正品药物。敷和备化方由西洋参10 g,柴胡12 g,制香附12 g,茵陈蒿30 g,制半夏12 g,白花蛇舌草30 g,杭白芍12 g,鳖甲24 g,生姜10 g,白术15 g,茯苓15 g,枳实10 g,莪术12 g,当归12 g,三七10 g,牛膝30 g,
甘草6 g组成,所用药物均为江阴天江药业有限公司生产的免煎颗粒。由广西中医药大学第一附属医院制剂室统一用120目网筛过滤药液,浓缩至1 g/mL的含药液,封装,灭菌,4 ℃保存待用。
1.3.5 实验仪器 BBS-H1500型超净工作台(中国山东博科生物产业有限公司);DMi1型倒置生物显微镜(德国Leica公
司);MCO175M型CO2细胞培养箱(日本Sanyo公司);高压蒸汽灭菌锅(中国上海三申医疗器械厂);全波长酶标仪、磁力搅拌器、电泳仪、CL10型离心机、Multiskan FC型酶标仪(美国Thermo公司);GE多功能成像仪、PCR循环仪(美国通用);制冰机(美国Bio-Rad公司);170-4158型转膜仪(美国Bio-rad公司);水平摇床(北京市六一仪器厂);CytoFLEX流式细胞仪(美国贝克曼公司)。
1.4 实验方法
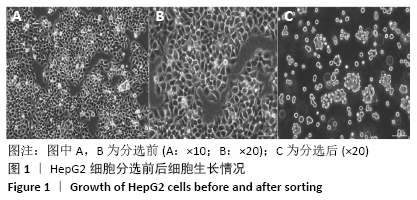
1.4.1 HepG2细胞培养 将人HepG2肝癌细胞株从-80 ℃冰箱迅速取出,梯度升温溶解,生物安全柜内将细胞从冻存管移至培养瓶,置于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中,用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM完全培养液培养,隔天换液。显微镜下观察细胞贴壁80%-90%时,用0.25%胰酶-0.02% EDTA消化,计数,以1∶3的比例传代,每两三天传代1次,取对数生长期的细胞用于后续实验。该细胞实验经过广西中医药大学第一附属医院伦理委员会批准。
1.4.2 CD133+HepG2肝癌干细胞的分离、纯化
(1)干细胞诱导:预先配置干细胞培养液:DMEM/F12+表皮生长因子(20 μg/L)+成纤维细胞生长因子(20 μg/L)+人白血病抑制因子(10 μg/L)+B27(1×)+N2(1×)。取对数生长期HepG2细胞,弃旧培养液,PBS洗涤,加入1 mL干细胞消化液消化细胞,待细胞变圆盾、立体,加入适量DMEM终止消化,
4 ℃、1 000 r/min低温离心5 min,弃上清,加入1 mL干细胞培养液,充分抽吸混匀,使用细胞计数板测定细胞总数,将细胞悬液接种于低粘连6孔板中(2×104个/孔),加入2 mL
干细胞培养液继续培养,至细胞数达到108个,进行磁珠分选。
(2)磁珠分选:用干细胞消化液消化细胞,300×g离心
10 min,弃上清,收集细胞沉淀,加入300 μL buffer缓冲液充分混匀,重悬细胞,计数,将细胞悬液调整到100个细胞/
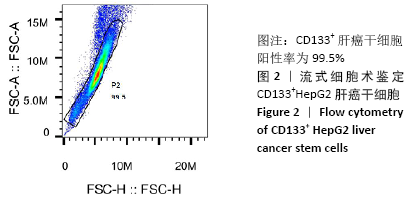
组。每100个细胞加入100 μL FCR Blocking Reagent,再加入100 μL CD133 Micro Beads,混匀后4 ℃避光孵育30 min;将LS柱置于MACS磁选机,buffer冲洗LS柱3次,将细胞悬液置于柱中,使其缓慢滴落,再用1.0-2.0 mL buffer冲洗LS柱,将滴落的细胞悬液收集至离心管中,离心,PBS清洗1次后计数铺板,继续培养于装有不含酚红的DMEM/F12培养基的悬浮细胞孔培养皿中,5 d后离心收集干细胞球,加入1 mL胰酶进行重悬,静置5 min;用移液器反复吹打直至细胞球变成单个细胞,PBS清洗后再次离心;去除上清,将细胞重悬于干细胞培养基中,按 1∶2比例传代于新的6孔悬浮细胞培养板中;每日观察细胞状态,防止污染;CD133阳性细胞培养3代后(每代5-7 d)用流式细胞术鉴定细胞纯度。
(3)鉴定:从培养箱取出低粘板,4 ℃,1 000 r/min离心5 min,加入1 mL PBS重悬细胞。准备计数板,往计数板A孔中加入10 μL细胞悬液,插入计数器中,细胞总数超过106可进行下一步实验。将获得细胞分为实验组、空白对照组、同型对照组。EP管分别加入100 μL细胞悬液,实验组加入10 μL PE CD133抗体,空白对照组为染色对照,同型对照组加入10 μL CD133同型对照抗体,充分抽吸混匀,4 ℃避光反应30 min,离心后弃上清,PBS清洗2次,重复离心,加入500 μL PBS重悬细胞,上机测定CD133比例。
1.4.3 敷和备化方含药血清制备 严格按照中药复方血清药理学研究方法制备敷和备化方含药血清[13]。将32只Wistar大鼠随机分为空白组(16只)和中药组(16只),分笼饲养,喂食,连续灌胃7 d(1次/d),以成人(60 kg)临床计量,大鼠按体质量100 g灌胃1 mL的药量,空白组灌胃等量生理盐水,末次给药后2 h进行腹主动脉取血,收集血液,避免污染,室温静置4 h,300 r/min离心15 min,收集上层亮黄色血清,56 ℃水浴锅灭活30 min,在生物安全柜内用注射滤器(0.22 μm微孔滤膜)过滤除菌,得到正常大鼠血清和敷和备化方含药血清,用15 mL离心管分装,保存于-20 ℃冰箱以备后续实验用。
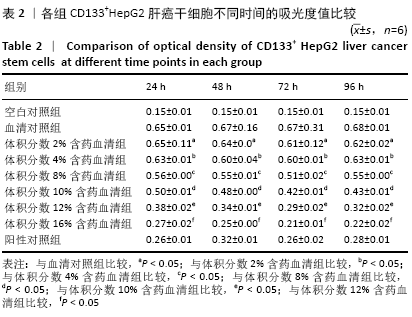
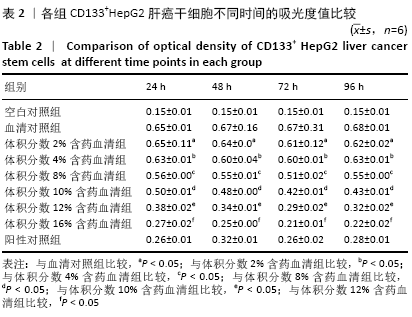
1.4.4 CCK-8法测定最佳体积分数含药血清 预先配置2%,4%,8%,10%,12%,16% 6个不同体积分数实验组以及对照组含药血清备用,取对数生长期CD133+HepG2细胞测定细胞总数,按105/孔稀释浓度,在96孔板中均匀加入1 mL细胞悬液,每组6个复孔,放入培养箱培养,镜下观察细胞生长情况,细胞结构正常,基本铺满孔底,且无大量堆积现象,即可加入2%,4%,8%,10%,12%,16%不同体积分数大鼠含药血清,1 mL/孔。对照组加入体积分数10%大鼠正常血清,1 mL/孔。阳性对照组加入1 mL 0.05%二甲基亚砜溶液,放入培养箱培养24,48,72,96 h,测定吸光度值。从培养箱取出96孔板,观察各组培养液颜色异同,镜下观察各组细胞状态,于生物安全柜中操作,吸去旧培养液,PBS充分洗涤2次后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,放入培养箱培养1-4 h
后用酶标仪在450 nm处测定吸光度值,筛选出最佳体积分数含药血清。
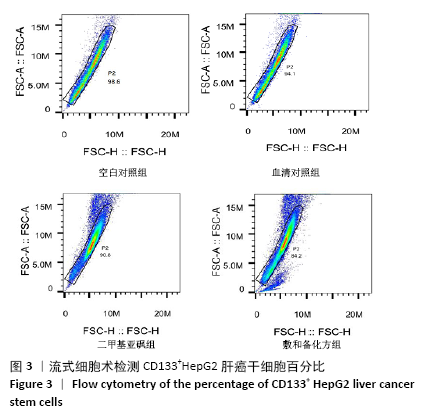
1.4.5 流式细胞术检测敷和备化方含药血清干预后CD133+HepG2细胞百分比 将CD133+HepG2细胞分为空白对照组、血清对照组、二甲基亚砜组和敷和备化方组。敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数16%敷和备化方含药血清的培养基,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数16%正常大鼠血清的培养基,二甲基亚砜组加入含2 mL 0.05%二甲基亚砜的培养基,空白对照组加入无血清培养基,继续培养6 d,第6天进行流式鉴定。从培养箱取出低粘板,镜下观察细胞生长情况,计数,记细胞总数超过106可进行下一步实验。从每组细胞中吸取100 μL细胞悬液至无菌EP管中,加入10 μL PE MOUSE ANTI-HUMAN CD133,4 ℃避光反应30 min,4 ℃,1 200 r/min离心5 min,弃上清,500 μL PBS重悬,上机测定结果。
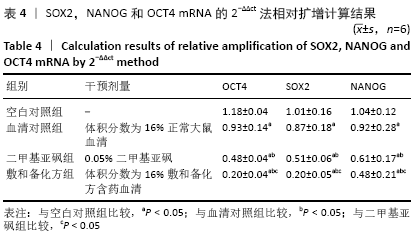
1.4.6 RT-PCR检测干性转录因子SOX2、NANOG和OCT4 的mRNA水平 将CD133+HepG2细胞分为空白对照组、血清对照组、二甲基亚砜组和敷和备化方组。敷和备化方组加入2 mL
含体积分数16%敷和备化方含药血清的培养基,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数16%正常大鼠血清的培养基,二甲基亚砜组加入含2 mL 0.05%二甲基亚砜的培养基,空白对照组加入无血清培养基,继续培养6 d,第6天进行RT-PCR检测。
(1)Triol法提取RNA:从培养箱取出待用细胞,弃旧培养液,PBS充分清洗后,加入1 mL Triol/孔(标本量不超过Triol体积的10%),充分混匀,转移至1.5 mL EP管中,室温放置5 min,彻底分离核蛋白复合体;加入0.2 mL氯仿,剧烈摇晃EP管15 s,室温放置3 min,4 ℃ 12 000×g离心
15 min,可见EP管中呈现3层, RNA存在于水相层,移液枪转移上层水相至新的EP管,加入0.5 mL异丙醇,室温静置10 min,4 ℃ 12 000×g离心10 min,EP管底部或侧壁可见白色絮状RNA沉淀,弃上清,加入1 mL体积分数为75%乙醇洗涤,振荡器混匀,4 ℃ 7 500×g离心5 min,弃上清,置于空气中干燥,用无酶水重悬,静置10 min,于-20 ℃长期保存。测定浓度:取2 μL储存液加入新EP管,再加入
98 μL无酶水,短暂离心,混匀,以无酶水作为空白对照,测定A260/A280值。
(2)反转录:使用miRcute Puls miRNA First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit试剂盒,严格按照说明书进行反转录操作,将提取的RNA反转录为cDNA,冰上配制反应体系,将配置好的反应体系混匀,适当离心,放置于PCR循环仪,42 ℃反应2 min;反转录反应:将配置好的反应体系混匀,适当离心,放置于PCR循环仪,37 ℃反应15 min,85 ℃反应5 s,4 ℃停止反转录反应,得到反转录产物备用。
(3)RT-PCR:将FastKing RT Kit(with gDNase)试剂盒从
20 ℃取出,置于冰上,待融为液体之后振荡,适当离心,配制反应体系于PCR仪器上进行扩增反应,将八联管适当离心,确保反应液全部沉到八联管底部,95 ℃反应15 s预变性,94 ℃反应30 s变性,55 ℃反应30 s退火,72 ℃反应
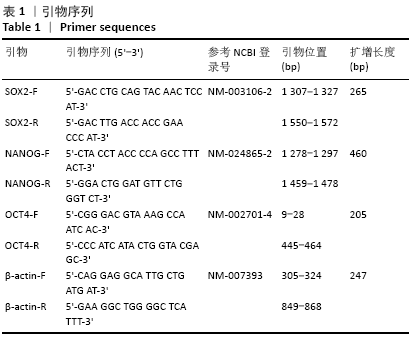
1 min(扩增1 kb片段),使引物在模板上延伸,合成DNA,完成1个循环。重复循环25-35次,使扩增的DNA片段大量累积。引物序列见表1。
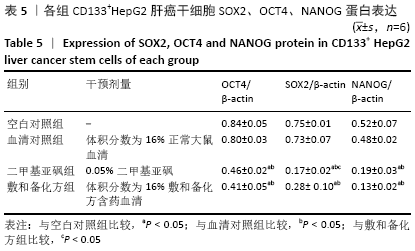
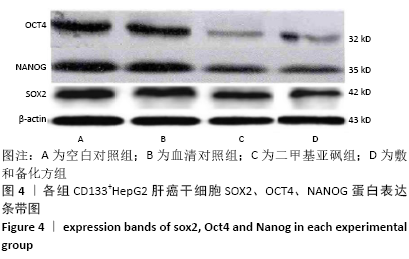
1.4.7 Western blot 检测干性转录因子SOX2、NANOG和OCT4蛋白表达水平 将处于对数生长期CD133+HepG2细胞分为空白对照组、血清对照组、二甲基亚砜组和敷和备化方组。敷和备化方组加入2 mL含体积分数16%敷和备化方含药血清的培养基,血清对照组加入2 mL含体积分数16%正常大鼠血清的培养基,二甲基亚砜组加入含2 mL 0.05%二甲基亚砜的培养基,空白对照组加入无血清培养基,37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2条件下继续培养6 d,第6天进行Western blot检测。收集细胞,用含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液裂解细胞,待细胞充分裂解后,4 ℃ 10 000 r/min离心5 min,移液枪吸取适量上清液至新的EP管,即为细胞全蛋白提取物,测定蛋白标准曲线,剩余上清液放于-80 ℃冰箱冻存。BCA法测定蛋白浓度,酶标仪测定波长为562 nm的吸光度值,根据相应的标准曲线,计算待测样品的浓度及所需稀释的对应量。加入相应量的SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液(Buffer),Buffer∶蛋白体积=1∶4,混匀后于99 ℃水浴中加热8 min,取出后分装备用。制胶后进行蛋白电泳、转膜、染色显影,检测干性转录因子SOX、NANOG和OCT4的蛋白表达。
1.5 主要观察指标 CD133+HepG2细胞百分比;干性转录因子SOX2、NANOG、OCT4 的mRNA及蛋白表达水平。
1.6 统计学分析 实验数据通过SPSS 20.0软件作统计学数据分析,用Excel软件统计作图。实验数据以均数±标准差表示,采用单因素方差分析(one-way analysis of variance,ANOVA)进行多组间比较。检验水准设定为α=0.05,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。