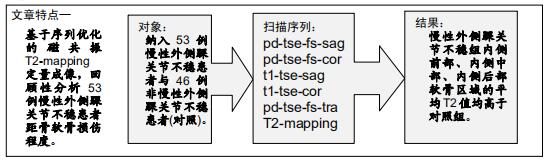
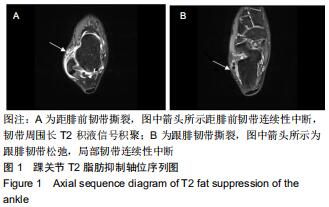
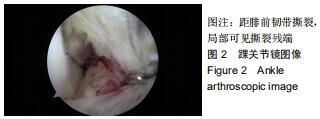
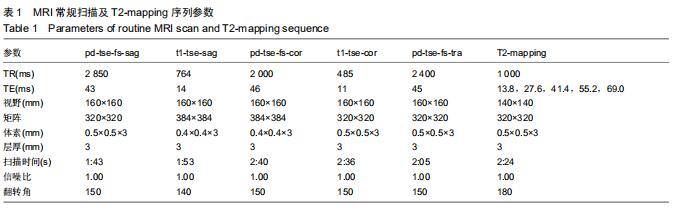
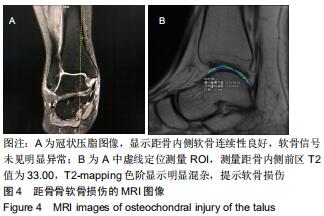
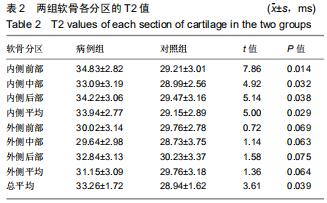
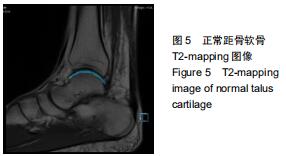
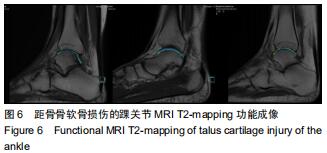
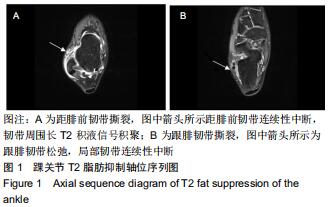
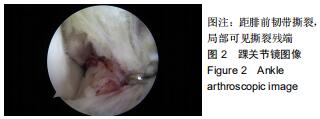
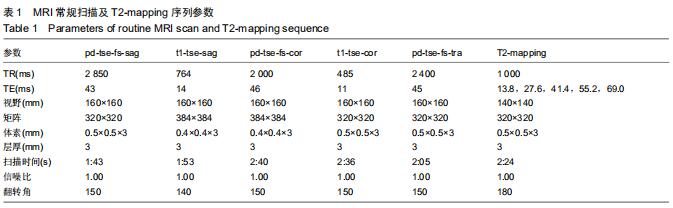
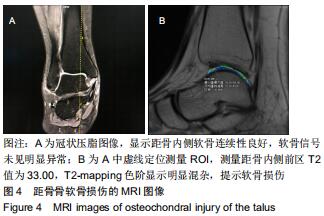
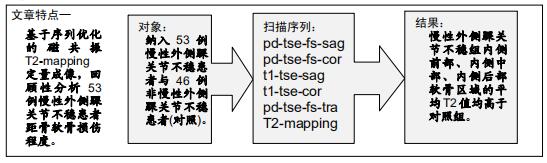
|
[1] GERSTNER GJ. Chronic ankle instability.Foot Ankle Clin. 2012; 17(3): 389-398.
[2] CAPUTO AM, LEE JY, SPRITZER CE, et al. In Vivo Kinematics of the Tibiotalar Joint After Lateral Ankle Instability.Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(11):2241-2248.
[3] 戴海飞,余斌,张凯瑞,等.踝关节周围韧带损伤对距骨稳定性影响的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(2):121-124.
[4] KOVALESKI JE, HEITMAN RJ, GURCHIEK LR, et al. Joint Stability Characteristics of the Ankle Complex After Lateral Ligamentous Injury, Part I: A Laboratory Comparison Using Arthrometric Measurement.J Athl Train.2014;49(2):192-197.
[5] HIROSE K, MURAKAMI G, MINOWA T, et al. Lateral ligament injury of the ankle and associated articular cartilage degeneration in the talocrural joint: anatomic study using elderly cadavers.J Orthop Sci.2004;9(1):37-43.
[6] 卢昌怀,余斌,陈辉强,等.正常步态下距骨三维有限元模型的建立及应力分析[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(10):2273-2276.
[7] RINGLEB SI, UDUPA JK, SIEGLER S, et al. The effect of ankle ligament damage and surgical reconstructions on the mechanics of the ankle and subtalar joints revealed by three-dimensional stress MRI.J Orthop Res. 2005;23(4):743-749.
[8] 刘清华,余斌,庄岩.足踝部数字化研究的现状及浅析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(10):998-998.
[9] KRIPS R, DIJK CNV, HALASI T, et al. Long-Term Outcome of Anatomical Reconstruction Versus Tenodesis for the Treatment of Chronic Anterolateral Instability of the Ankle Joint: A Multicenter Study.Foot Ankle Int.2001;22(5):415-421.
[10] 张禹,刘志成,成永忠,等.旋后外旋型踝关节损伤有限元模型的建立与力学分析[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(3):36-42.
[11] HU H, YANG B, LI Y, et al. Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13 and NF-κB pathways in the cartilage tis- sue of rats with osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Med.2016;38 (6):1922-1932
[12] HUANG X, PAN Q, MAO Z, et al. Sinapic acid inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammation via MAPK downregulation in rat chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2018;41(2):562-568.
[13] WANG D, WENG Y, GUO S, et al. Platelet-rich plasma inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation through activation of Wnt pathway during bone remodeling.Int J Mol Med.2018;41(2):729-738.
[14] BIAN Y, WANG H, SUN S. Taurine alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes from patients with osteoarthritis.Redox Rep. 2018;23(1):118-124.
[15] SANDYA S, ACHAN MA, SUDHAKARAN PR, et al. Multiple matrix metalloproteinases in type II collagen induced arthritis. Indian J Clin Biochem.2009;24(1):42-48.
[16] JANUSZ MJ, BENDELE AM, BROWN KK.Induction of osteoarthritis in the rat by surgical tear of the meniscus:Inhibition of joint damage by a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(10):785-791.
[17] ZWIERZCHOWSKI TJ, STASIKOWSKA-KANICKA O, DANILEWICZ M, et al. Assessment of apoptosis and MMP-1, MMP-3 and TIMP-2 expression in tibial hyaline cartilage afterviable medial meniscus transplantation in the rabbit.Arch Med Sci.2012;8(6):1108-1114.
[18] KAST RE, HALATSCH ME. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in glioblastoma: a trio of old drugs-captopril, disulfiram and nelfinavir-are inhibitors with potential as adjunctive treatments in glioblastoma.Arch Med Res.2012;43(3):243-247.
[19] KAĬLINA AN, OGORODOVA LM, CHASOVSKIKH I, et al. Indices of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1) with juvenile arthritis in children.Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk.2013;(7):36-40.
[20] 马丽艳,宋旭动,张德新,等.MMP-13 和Galectin-3 在骨性关节炎滑膜组织中的临床意义[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013,2(5):280-284.
[21] JAZRAWI LM, ALAIA MJ, CHANG G, et al. Advances in magnetic resonance imaging of articular cartilage.J Am Acad Orthop Sur.2011; 19(7):420-429.
[22] RAYA JG, HORNG A, DIETRICH O, et al. Articular cartilage:in vivo diffusion-tensor imaging.Radiology.2012;262(2):550-559.
[23] NOTOHAMIPRODJO M, KUSCHEL B, HORNG A, et al. 3D-MRI of the ankle with optimized 3D-SPACE. Invest Radiol.2012;47(4):231-239.
[24] 富丽萍,王绍武,宋清伟,等.软骨的MR敏感序列在软骨类病变中的应用研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2007,5(4):12-17.
[25] 杨海涛,王仁法,李锋,等.早期髌骨软化症髌软骨磁共振T2图成像和扩散加权成像的对照研究[J].实用放射学杂志, 2008,24(3):55-57, 61.
[26] PAN JD, PIALAT JB, JOSEPH T, et al. Knee cartilage T2 characteristics and evolution in relation to morphologic abnormalities detected at 3-T MR imaging:a longitudinal study of the normal control cohort from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.Radiology.2011;261(2):507-515.
[27] PRASAD AP, NARDO L, SCHOOLER J, et al. T1ρ and T2 relaxation times predict progression of knee osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):69-76.
[28] STAHL R, LUKE A, LI XJ, et al. T1rho,T2 and focal knee cartilage abnormalities in physically active and sedentary healthy subjects versus early OA patients-a 3.0-Tesla MRI study.Eur Radio.2009;19(1):132-143.
[29] 侯进,梅颖洁,代月黎,等.兔骨性关节炎模型关节软骨的弥散张量研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2014,24(1):1-4.
[30] TAO H, SHANG X, LU R, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance im- aging (MRI)evaluation of cartilage repair after microfracture (MF)treatment for adult unstable osteochondritis disecans (OCD)in the ankle:corelations with clinical outcome.Eur Radiol.2014;24(8):1758-1767.
[31] GOLDITZ T, STEIB S, PFEIFER K, et al. Functional ankle instability as a risk factor for osteoarthritis:using T2-mapping to analyze early cartilage degeneration in the ankle joint of young athletes.Os- teoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(10):1377-1385.
[32] 郭秦炜,胡跃林,焦晨,等.踝关节距骨骨软骨损伤的影像学及关节镜下表现[J].中华关节外科杂志,2010,4(6):723-728.
[33] JOSEPH GB, NEVITT MC, MCCULLOCH CE, et al. Associations between molecular biomarkers and MR-based cartilage composition and knee joint morphology: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2018;26(8):1070-1077.
[34] LI Z, WANG H, LU Y, et al. Diagnostic value of T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences of 3D fat- suppressed spoiled gradient (FS SPGR-3D) 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging for osteoarthritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(1):e13834.
[35] 刘国彬,张国平,任庆云,等.踝关节不同姿势下MRI检查对其周围韧带及肌腱损伤的诊断价值[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(4):598-602.
[36] 吴昆华,王天朝,梁虹,等.3.0T磁共振不同成像技术对膝关节软骨显示对比分析[J].实用放射学杂志,2014,30(6):1010-1013.
[37] 高丽香,袁慧书.T1ρ序列、MR和关节镜在膝关节软骨成像中的应用对比[J].实用放射学杂志,2018,34(2):256-259.
[38] VANTIENDEREN RJ, DUNN JC, KUSNEZOV N, et al. Osteochondral allograft transfer for treatment of osteochondral lesions of the talus: a systematic review.Arthroscopy.2017;33(1):217-222.
[39] GAO F, CHEN N, SUN W, et al. Combined therapy with shock wave and retrograde bone marrow-derived cell transplantation for osteochondral lesions of the talus.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):2106.
[40] RUNGPRAI C, TENNANT JN, GENTRY RD, et al. Management of osteochondral lesions of the talar dome.Open Orthop J.2017;11:743-761.
[41] 李延炜,洪海森,翟文亮.距骨软骨损伤的诊疗及研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(8):3510-3512.
[42] GIZA E, DELMAN C, COETZEE JC, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of talus osteochondral lesions with particulated juvenile allograft cartilage.Foot Ankle Int.2014;35(10):1087-1094.
[43] 刘国彬,张国平,任庆云,雷立存,赵峰,高宏阳,朱超华,李亚光.踝关节不同姿势下MRI检查对其周围韧带及肌腱损伤的诊断价值:单中心、诊断性试验[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(4):598-602.
|