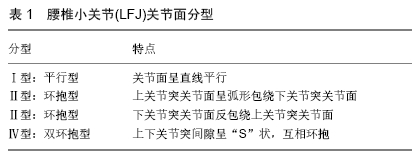
[1] GHORMLEY RK. Low back pain with special reference to the articular facets with presentation as operative procedure. JAMA. 1933;101(23):1773-1777.
[2] MANCHIKANTI L, SINGH V. Review of chronic low back pain of facet joint origin. Pain Physician. 2002;5(1):83-101.
[3] AL-NAJJIM M, SHAH R, RAHUMA M, et al. Lumbar facet joint injection in treating low back pain: Radiofrequency denervation versus SHAM procedure. Systematic review. J Orthop. 2018;15(1):1-8.
[4] 白贤明,邢文华.LBP临床诊断和治疗研究进展[J].内蒙古医学杂志, 2018,50(4):29-32.
[5] BORENSTEIN D. Does osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine cause chronic low back pain? Curr Pain Head Rep. 2004; 8(6):512-517.
[6] TETREAULT L, GOLDSTEIN CL, ARNOLD P, et al. Degenerative cervical myelopathy: a spectrum of related disorders affecting the aging spine. Neurosurgery. 2015;77 Suppl 4:S51-S67.
[7] ALONSO F, KIRKPATRICK CM, JEONG W, et al. Lumbar facet tropism: a comprehensive review. World Neurosurg. 2017;102:91-96.
[8] 胡勇文.退变性腰椎失稳的研究进展[D].北京:北京中医药大学, 2008.
[9] DAI LY. Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop. 2001;25(1):40-42.
[10] ZHANG J, SHU Y, ZHU Q, et al. Lumbar facet joint degeneration contributes to degenerative lumbar scoliosisinduced by asymmetric stress in rabbits. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2019;39(8):993-997.
[11] ZHENG J, YANG Y, CHENG B, et al. Exploring the pathological role of intervertebral disc and facet joint in thedevelopment of degenerative scoliosis by biomechanical methods. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2019;70:83-88.
[12] GLOVER JR. Arthrography of the joints of the lumbar vertebral arches. Orthop Clin North Am. 1977;8(1):37-42.
[13] 孟庆兰.腰椎上关节面方位角变化规律及其临床意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2002,20(4):283-285.
[14] 戴力扬.腰椎关节突关节的临床解剖[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 1991,9(3):179-182.
[15] 李瑞.腰椎关节突关节毗邻血管的应用解剖学及影像学研究现状[J].滨州医学院学报,2013,36(3):201-203,211.
[16] JAUMARD NV, WELCH WC, WINKELSTEIN BA. Spinal facet joint biomechanics and mechanotransduction in normal, injury anddegenerative conditions. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(7): 71010.
[17] BAN E, ZHANG S, ZAREI V, et al. Collagen organization in facet capsular ligaments varies with spinal region and with ligament deformation. J Biomech Eng. 2017,139(7): 710091-710099.
[18] YAMASHITA T, MINAKI Y, OZAKTAY AC, et al. A morphological study of the fibrous capsule of the human lumbar facet joint. Spine. 1996;21(5):538-543.
[19] 黄磊涛,赖琦,李帆,等.人腰椎小关节软骨不同染色方法的差异比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(24):3784-3789.
[20] BOGDUK N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983;8(3):286-293.
[21] SHUANG F, HOU S, ZHU J, et al. Clinical anatomy and measurement of the medial branch of the spinal dorsal ramus. Medicine. 2015;94(52):e2367.
[22] 闫广辉,李志赏,魏巍,等.腰椎间盘和腰椎小关节的退变顺序及其与年龄的相关性分析[J].检验医学与临床,2018,15(6):744-746.
[23] CYRON BM, HUTTON WC. The tensile strength of the capsular ligaments of the apophyseal joints. J Anat. 1981; 132(Pt 1):145-150.
[24] LEWIN T. Osteoarthritis in lumbar synovial joints: a morphologic study. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1964;35(Supp 73):71-73.
[25] ENOKIDA S, TANISHIMA S, TANIDA A, et al. Evaluation of age-related changes in lumbar facet joints using T2 mapping. J Orthop Sci. 2019.
[26] 李宁华,薛庆云,张毅,等.中国六城市中老年人群腰椎骨关节炎患病危险因素地区调查:6128名资料分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(47):9508-9512.
[27] IRWIN RW, WATSON T, MINICK RP, et al. Age, body mass index, and gender differences in sacroiliac joint pathology. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2007;86(1):37-44.
[28] EUBANKS JD, LEE MJ, CASSINELLI E, et al. Prevalence of lumbar facet arthrosis and its relationship to age, sex, and race: an anatomic study of cadaveric specimens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(19):2058-2062.
[29] MORIMOTO M, HIGASHINO K, MANABE H, et al. Age-related changes in axial and sagittal orientation of the facet joints: Comparison with changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):50-56.
[30] FUJIWARA A, TAMAI K, YAMATO M, et al. The relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: an MRI study. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(5):396-401.
[31] WANG YXJ. Menopause as a potential cause for higher prevalence of low back pain in women than in age-matched men. J Orthop Trans. 2016;8:1-4.
[32] MOREL V, MERCAY A, QUINN TM. Prestrain decreases cartilage susceptibility to injury by ramp compression invitro. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(11):964-970.
[33] WORKMAN J, THAMBYAH A, BROOM N. The influence of early degenerative changes on the vulnerability of articularcartilage to impact-induced injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2017;43:40-49.
[34] OROZCO GA, TANSKA P, FLOREA C, et al. A novel mechanobiological model can predict how physiologically relevant dynamic loading causes proteoglycan loss in mechanically injured articular cartilage. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1): 15599.
[35] PAN C, SIMON P, ESPINOZA ORIAS AA, et al. Lumbar facet joint subchondral bone density in low back pain and asymptomaticsubjects. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(4):571-576.
[36] YAMABE D, MURAKAMI H, CHOKAN K, et al. Evaluation of water content in lumbar intervertebral discs and facet joints before and after physiological loading using T2 mapping MRI. Spine. 2017;42(24):E1423-E1428.
[37] 乔聚义.下腰椎小关节退变的磁共振成像及CT表现特征分析[J]. 实用医学影像杂志,2016,17(3):265-266.
[38] CLAESON AA, BAROCAS VH. Computer simulation of lumbar flexion shows shear of the facet capsular ligament. Spine J. 2017;(1):109-119.
[39] YANG KH, KING AI. Mechanism of facet load transmission as a hypothesis for low-back pain. Spine. 1984;9(6):557-565.
[40] 都承斐,李俊伟,刘海英,等.随动载荷对腰椎小关节接触力的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2017,32(4):363-368.
[41] 肖进,原林,赵卫东,等.身体姿势对腰椎小关节受力的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2003,21(1):87-89.
[42] CHOWDHURY SK, BYRNE RM, ZHOU Y, et al. Lumbar facet joint kinematics and load effects during dynamic lifting. Human Factors. 2018,60(8):1130-1145.
[43] BYRNE RM, ZHOU Y, ZHENG L, et al. Segmental variations in facet joint translations during in vivo lumbar extension. J Biomech. 2018;70:88-95.
[44] ZENG Z, ZHU R, WU Y, et al. Effect of graded facetectomy on lumbar biomechanics. J Healthc Eng. 2017;2017(1):1-6.
[45] 吴超,王振宇,林国中,等.颈椎单侧半椎板及不同程度小关节切除术后生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2018,17(4):352-356.
[46] QIAN J, YU SS, LIU JJ, et al. Biomechanics changes of lumbar spine caused by foraminotomy via percutaneoustransforaminal endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2018,98(13):1013-1018.
[47] 李慧友,朱青安,李桂兰,等.双侧小关节分级切除对腰椎稳定性影响的三维运动研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1995,15(10):692-694.
[48] 徐波,金大地,史占军,等.中下颈椎双侧小关节部分切除对颈椎稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1995,5(3): 115-118.
[49] LIU Z, DUAN Y, RONG X, et al. Variation of facet joint orientation and tropism in lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis and disc herniation at L4-L5: A systematic review andmeta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017;161: 41-47.
[50] LIU X, HUANG Z, ZHOU R, et al. The effects of orientation of lumbar facet joints on the facet joint contactforces: an in vitro biomechanical study. Spine. 2018;43(4):E216-E220.
[51] 侯宁.腰椎关节突关节的矢状化和水平化与其退变之间关系的探究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2019.
[52] KARACAN I, AYDIN T, SAHIN Z, et al. Facet angles in lumbar disc herniation: their relation to anthropometricfeatures. Spine. 2004;29(10):1132-1136.
[53] RONG X, WANG B, DING C, et al. The biomechanical impact of facet tropism on the intervertebral disc and facetjoints in the cervical spine. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1926-1931.
[54] KO S, CHAE S, CHOI W, et al. The prevalence of facet tropism and its correlation with low back pain in selected community-based populations. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2): 176-182.
[55] MOHANTY SP, PAI KANHANGAD M, KAMATH S, et al. Morphometric study of the orientation of lumbar zygapophyseal joints in a SouthIndian population. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(3):613399771.
[56] SABNIS AB, CHAMOLI U, DIWAN AD. Is L5-S1 motion segment different from the rest? A radiographic kinematic assessment of 72 patients with chronic low back pain. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(5):1127-1135.
[57] SUN D, LIU P, CHENG J, et al. Correlation between intervertebral disc degeneration, paraspinal muscle atrophy, and lumbar facet joints degeneration in patients with lumbar disc herniation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):167.
[58] SONG Q, LIU X, CHEN D, et al. Evaluation of MRI and CT parameters to analyze the correlation between disc andfacet joint degeneration in the lumbar three-joint complex. Medicine. 2019;98(40):e17336.
[59] SWANEPOEL MW, ADAMS LM, SMEATHERS JE. Human lumbar apophyseal joint damage and intervertebral disc degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995;54(3):182-188.
[60] 付长林,张斌,刘远,等.腰痛患者腰椎小关节退变与椎间盘退变的MRI比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(46):7401-7405.
|