[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[2] ZHANG JF, SONG LH, WEI JN, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for the occurrence of symptomatic osteoarthritis in rural regions of Shanxi Province, China. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(8):781-789.
[3] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393(10182):1745-1759.
[4] JOINER DM, LESS KD, VAN WIEREN EM, et al. Accelerated and increased joint damage in young mice with global inactivation of mitogen-inducible gene 6 after ligament and meniscus injury. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R81.
[5] ZHU J, SICLARI VA, LIU F, et al. Amphiregulin-EGFR signaling mediates the migration of bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors toward PTH-stimulated osteoblasts and osteocytes. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50099.
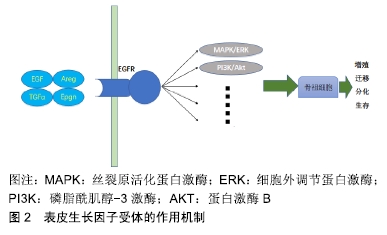
[6] QIN L, BEIER F. EGFR Signaling: Friend or Foe for Cartilage? JBMR Plus. 2019;3(2):e10177.
[7] JIA H, MA X, TONG W, et al. EGFR signaling is critical for maintaining the superficial layer of articular cartilage and preventing osteoarthritis initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(50):14360-14365.
[8] LI H, FENG F, BINGHAM CO 3RD, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitors in cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(2):144-154.
[9] ZHANG X, ZHU J, LIU F, et al. Reduced EGFR signaling enhances cartilage destruction in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Bone Res. 2014;2:14015.
[10] CHEN YT, HOU CH, HOU SM, et al. The effects of amphiregulin induced MMP-13 production in human osteoarthritis synovial fibroblast. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:759028.
[11] HUANG CY, LIN HJ, CHEN HS, et al. Thrombin promotes matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression through the PKCδ c-Src/EGFR/PI3K/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in human chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:326041.
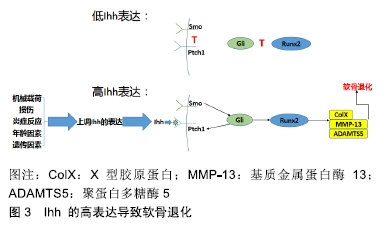
[12] ZHANG C, WEI X, CHEN C, et al. Indian hedgehog in synovial fluid is a novel marker for early cartilage lesions in human knee joint. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5):7250-7265.
[13] LIN AC, SEETO BL, BARTOSZKO JM, et al. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2009;15(12):1421-1425.
[14] WORTHLEY DL, CHURCHILL M, COMPTON JT, et al. Gremlin 1 identifies a skeletal stem cell with bone, cartilage, and reticular stromal potential. Cell. 2015;160(1-2):269-284.
[15] HUANG J, ZHAO L, CHEN D. Growth factor signalling in osteoarthritis. Growth Factors. 2018;36(5-6):187-195.
[16] KIM EJ, CHO SW, SHIN JO, et al. Ihh and Runx2/Runx3 signaling interact to coordinate early chondrogenesis: a mouse model. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55296.
[17] WEI F, ZHOU J, WEI X, et al. Activation of Indian hedgehog promotes chondrocyte hypertrophy and upregulation of MMP-13 in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(7):755-763.
[18] ZHOU J, CHEN Q, LANSKE B, et al. Disrupting the Indian hedgehog signaling pathway in vivo attenuates surgically induced osteoarthritis progression in Col2a1-CreERT2; Ihhfl/fl mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R11.
[19] XU T, XU G, GU Z, et al. Hedgehog signal expression in articular cartilage of rat temporomandibular joint and association with adjuvant-induced osteoarthritis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2017;46(4):284-291.
[20] ZHANG G, GUO B, WU H, et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):307-314.
[21] PIGNATELLO R, SARPIETRO MG, CASTELLI F. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new polymeric conjugate and nanocarrier with osteotropic properties. J Funct Biomater. 2012;3(1):79-99.
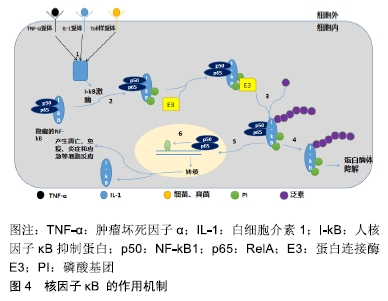
[22] ZHENG C, YIN Q, WU H. Structural studies of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011;21(1):183-195.
[23] RIGOGLOU S, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(11): 2580-2584.
[24] GOLDRING MB, MARCU KB. Cartilage homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3): 224.
[25] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[26] MARCU KB, OTERO M, OLIVOTTO E, et al. NF-kappaB signaling: multiple angles to target OA. Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11(5):599-613.
[27] KRASNOKUTSKY S, ATTUR M, PALMER G, et al. Current concepts in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008;16 Suppl 3:S1-3.
[28] ZHANG LB, MAN ZT, LI W, et al. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol. 2017;87:249-257.
[29] ZHAO Y, LI Z, WANG W, et al. Naringin Protects Against Cartilage Destruction in Osteoarthritis Through Repression of NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation. 2016;39(1):385-392.
[30] BUHRMANN C, MOBASHERI A, BUSCH F, et al. Curcumin modulates nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-mediated inflammation in human tenocytes in vitro: role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(32):28556-28566.
[31] ZHUANG Z, YE G, HUANG B. Kaempferol Alleviates the Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammation in Rat Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes via Suppression of NF-κB. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3925-3931.
[32] XU X, LV H, LI X, et al. Danshen attenuates osteoarthritis-related cartilage degeneration through inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017;95(6):644-651.
[33] QU R, CHEN X, WANG W, et al. Ghrelin protects against osteoarthritis through interplay with Akt and NF-κB signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2018;32(2):1044-1058.
[34] WEINMANN D, MUELLER M, WALZER SM, et al. Brazilin blocks catabolic processes in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes via inhibition of NFKB1/p50. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(9):2431-2438.
[35] DAI T, SHI K, CHEN G, et al. Malvidin attenuates pain and inflammation in rats with osteoarthritis by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(12):1075-1084.
[36] DONG Y, JESSE AM, KOHN A, at el. RBPjk-dependent Notch signaling regulates mesenchymal progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation during skeletal development. Development. 2010;137(9):1461-1471.
[37] KOHN A, DONG Y, MIRANDO AJ, et al. Cartilage-specific RBPjk-dependent and -independent Notch signals regu-late cartilage and bone development. Development. 2010;137(9):1198-1212.
[38] MEAD TJ, YUTZEY KE. Notch pathway regulation of chondrocyte differentiation and proliferation during appendicular and axial skeleton development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(34):14420-14425.
[39] HOSAKA Y, SAITO T, SUGITA S, et al. Notch signaling in chondrocytes modulates endochondral ossification and osteoarthritis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(5):1875-1880.
[40] 曹俊杰,李爱芳,卫亚琳,等.Notch信号参与BMP4诱导的间充质干细胞成骨分化及其机制的初步探讨[J].中国生物工程杂志, 2017,37(4):48-55.
[41] LIU Z, REN Y, MIRANDO AJ, et al. Notch signaling in postnatal joint chondrocytes, but not subchondral osteoblasts, is required for articular cartilage and joint maintenance. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(4):740-751.
[42] LIU Z, CHEN J, MIRANDO AJ, et al. A dual role for NOTCH signaling in joint cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis. Sci Signal. 2015;8(386):ra71.
[43] ZHENG Y, LIU C, NI L, et al. Cell type-specific effects of Notch signaling activation on intervertebral discs: Implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(7):5431-5440.
[44] LUO X, JIANG Y, BI R, et al. Inhibition of notch signaling pathway temporally postpones the cartilage degradation progress of temporomandibular joint arthritis in mice. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(7):1132-1138.
[45] SASSI N, GADGADI N, LAADHAR L, et al. Notch signaling is involved in human articular chondrocytes de-differentiation during osteoarthritis. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014; 34(1):48-57.
[46] WANG J, CHEN H, CAO P, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(3):362-372.
[47] SUGIURA R, SATOH R, ISHIWATA S, et al. Role of RNA-Binding Proteins in MAPK Signal Transduction Pathway. J Signal Transduct. 2011;2011:109746.
[48] LI Z, MENG D, LI G, et al. Celecoxib Combined with Diacerein Effectively Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Rats via Regulating JNK and p38MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation. 2015; 38(4):1563-1572.
[49] SUN HY, HU KZ, YIN ZS. Inhibition of the p38-MAPK signaling pathway suppresses the apoptosis and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Cytokine. 2017;90:135-143.
[50] LIN KC, PARK HW, GUAN KL. Regulation of the Hippo Pathway Transcription Factor TEAD. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(11):862-872.
[51] HEALLEN T, MORIKAWA Y, LEACH J, et al. Hippo signaling impedes adult heart regeneration. Development. 2013; 140(23): 4683-4690.
[52] YU FX, ZHAO B, GUAN KL. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell. 2015;163(4): 811-828.
[53] GONG Y, LI SJ, LIU R, et al. Inhibition of YAP with siRNA prevents cartilage degradation and ameliorates osteoarthritis development. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(1):103-114.
[54] DENG Y, LU J, LI W, et al. Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4564.
|