中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (17): 2712-2717.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2675
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧运动可改善糖尿病肾病模型小鼠肾脏的氧化应激损伤
刘晓晨1,王改凤2,张社峰3
- 1河南财政金融学院体育系,河南省郑州市 450000;2河南省中医院脑病科一区,河南省郑州市 450000;3河南省中医药研究院附属医院内分泌科,河南省郑州市 450000
Aerobic exercises alleviate renal oxidative stress injury in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy
Liu Xiaochen1, Wang Gaifeng2, Zhang Shefeng3
- 1Department of Physical Education, Henan Finance University, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Encephalopathy, Henan Province Hospital of TCM, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Endocrinology, the Affiliated Hospital of Henan Academy of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor E2-related factor 2,Nrf2):属于转录因子亮氨酸拉链转录激活因子(CNC)家族成员,为细胞防御多种应激损伤的关键因子。Nrf 2 是诱导Ⅱ相酶基因表达的必需调节因子。
有氧运动:是指人体在氧气充分供应的情况下进行的耐久性运动,其特点是强度低、时间长、不中断、有节奏,能够改善胰岛素抵抗、降低血糖,对糖尿病具有一定的疗效。
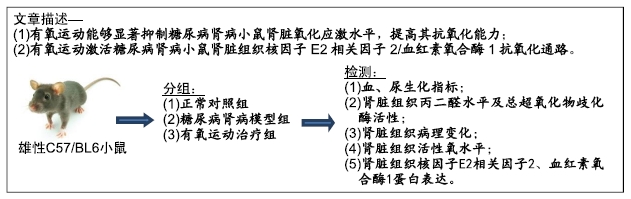
背景:研究证实,长期有规律的有氧运动能够有效降低血糖,改善胰岛素抵抗,是治疗糖尿病肾病的重要措施,但有关其具体机制不明。
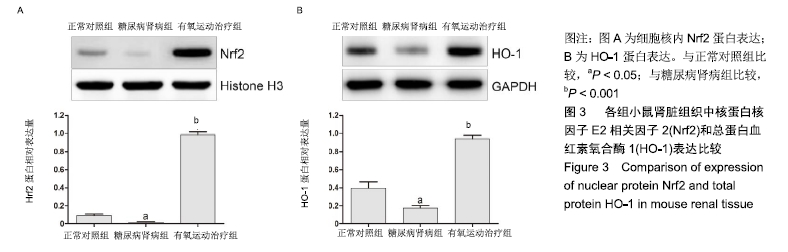
目的:探讨有氧运动对糖尿病肾病小鼠肾脏氧化应激损伤的影响及其与核因子E2相关因子2(Nrf2)/血红素氧合酶1(HO-1)信号通路的关系。
方法:雄性C57/BL6小鼠随机分为正常对照组、糖尿病肾病组及有氧运动治疗组,每组8只。除正常对照组外,其他2组小鼠均采用多次小剂量腹腔注射链脲佐菌素(40 mg/kg,连续注射5 d)建立糖尿病小鼠模型(4周后24 h尿蛋白含量>30 mg提示糖尿病肾病造模成功)。糖尿病小鼠造模成功8周后,有氧运动治疗组小鼠进行为期8周的跑台有氧运动,1 h/d,5 d/周。治疗8周后,测量尾动脉收缩压、24 h尿微量白蛋白排泄率、血糖、血脂及血肌酐、血尿素氮水平;取肾脏组织匀浆,测定丙二醛水平及总超氧化物歧化酶活性;观察肾脏组织肾小球系膜区细胞外基质积聚情况,并检测肾脏组织活性氧水平及核因子E2相关因子2核蛋白和血红素氧合酶1蛋白表达。实验方案经河南省中医药研究院动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为HPHT2015019)。
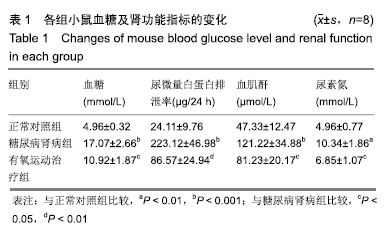
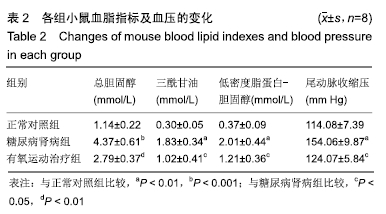
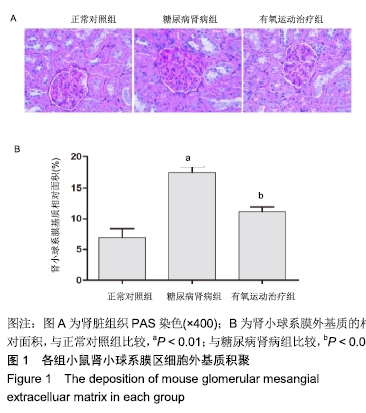
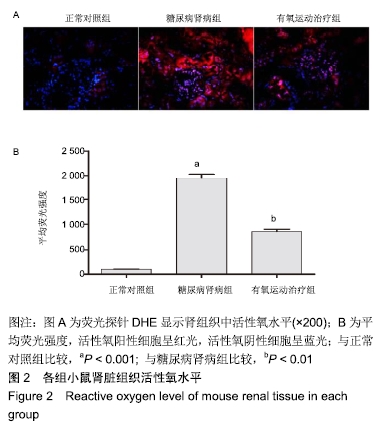
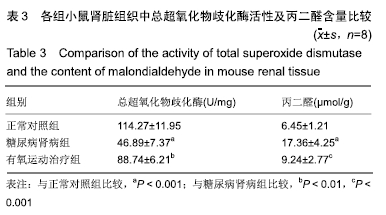
结果与结论:①与正常对照组比较,糖尿病肾病组小鼠24 h尿微量白蛋白排泄率、血糖、血肌酐、尿素氮、总胆固醇、三酰甘油、低密度脂蛋白-胆固醇以及尾动脉收缩压等指标水平显著增加,肾脏肾小球系膜区细胞外基质显著积聚,活性氧水平和丙二醛水平显著增加;与糖尿病肾病组比较,有氧运动治疗组上述各项指标显著降低;②与糖尿病肾病组比较,有氧运动治疗组小鼠总超氧化物歧化酶活性增强,肾小球系膜区细胞外基质积聚显著减少,肾脏组织细胞核蛋白核因子E2相关因子2和总蛋白血红素氧合酶1的表达上调;③结果说明,有氧运动能够降低糖尿病肾病小鼠肾脏氧化应激损伤,可能与Nrf2/HO-1通路激活有关。
ORCID: 0000-0003-1328-3575(刘晓晨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: