中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (15): 2368-2373.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2632
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
有限元分析验证股骨近端良性病变骨水泥联合钢板内固定的合理性
杨朝昕,牛梦晔,吕家兴,曹海营,孔令伟,赵景新,金 宇
- 承德医学院附属医院创伤骨科,河北省承德市 067000
Finite element analysis to verify the rationality of bone cement combined with plate internal fixation for benign proximal femoral lesions
Yang Zhaoxin, Niu Mengye, Lü Jiaxing, Cao Haiying, Kong Lingwei, Zhao Jingxin, Jin Yu
- Department of Orthopedic Trauma, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
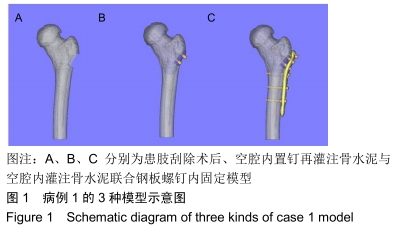
病灶处开窗:从骨皮质处开口对骨内病灶进行病灶刮除,手术的关键是保证无瘤原则,充分显露病灶至正常骨质,开窗范围常需要与病灶长度一致,以此充分刮除病灶降低复发率。
刮除病灶后填充骨水泥联合钢板内固定:为良性骨病变常用手术方式,对于骨病变范围较大时,行病灶刮除术后,局部空腔可采用植骨或骨水泥等异体骨材料填充缺损并联合应用锁定钢板增加局部稳定性。
背景:对于良性骨病变患者,经过外科手术治疗后通常可获得良好的生存周期,通过不断对手术方式进行改进,利用有限元分析技术研究良性骨病变术后股骨近端受力情况,预测并降低术后病理骨折、二次骨折风险,探讨最佳术式与预后,对延长并改善患者生活质量存在重要意义。
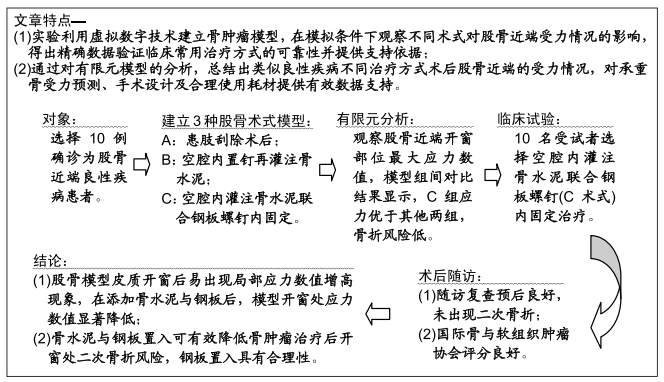
目的:利用三维有限元技术对股骨近端良性病变的不同术式模型进行受力分析,比较不同术式模型差异性并验证钢板置入内固定的合理性与有效性,并针对术后患者随访验证有限元模型的可靠性。
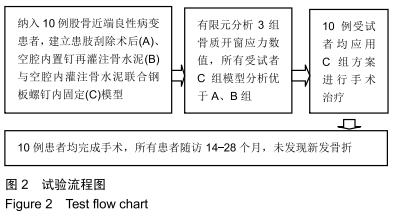
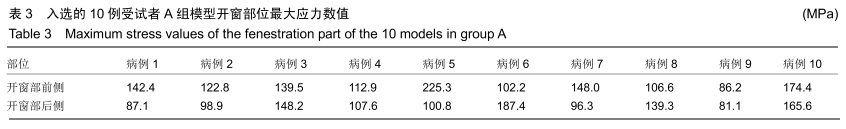
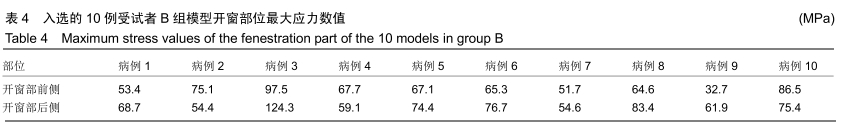
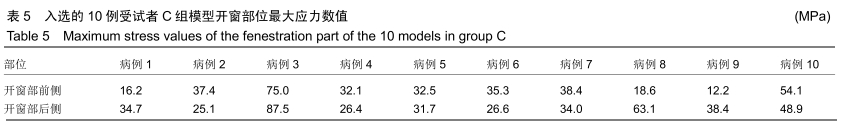
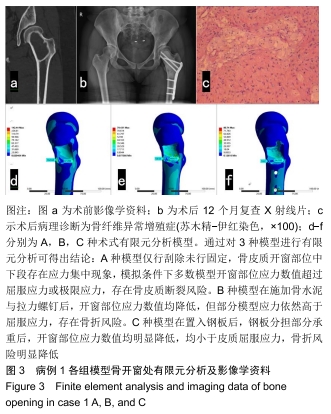
方法:对符合纳入标准的10例股骨近端良性病变患者行术前CT检查,采用MIMICS分别建立患肢刮除术后(A)、空腔内置钉再灌注骨水泥(B)与空腔内灌注骨水泥联合钢板螺钉内固定(C)3种模型,在模拟条件下测量出3种骨皮质模型开窗部位前侧、后侧的最大应力数值并进行对比。所有患者对试验方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。
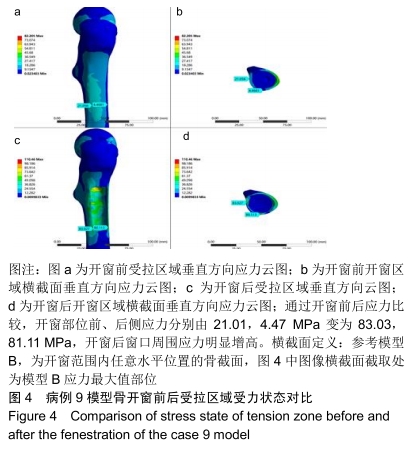
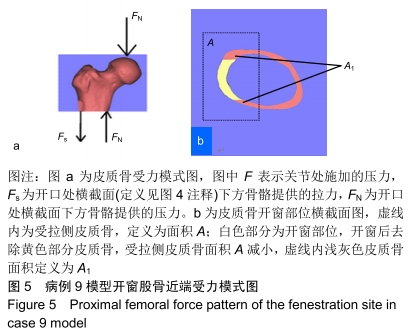
结果与结论:①3组模型中骨皮质开窗部前侧、后侧最大应力数值比较结果为A>B>C,两两比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),说明A组骨折风险高,B组部分模型骨折风险较高,C组应力均可控制在合理范围内,骨折风险低;②因此10名受试者均采用C种术式进行治疗,术后随访复查预后良好,未出现二次骨折;术后1年国际骨与软组织肿瘤协会评分为27-30分;③提示股骨模型皮质开窗后易出现局部应力数值增高现象,在添加骨水泥与钢板后,模型开窗处应力数值显著降低。股骨近端良性病变刮除后,通过置入骨水泥与钢板,可有效降低开窗部位的应力,手术部位发生骨折概率明显降低,说明钢板置入具有合理性。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2705-1604(杨朝昕)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: